Simple model of spiking neurons
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
Biology - Chpt 14- The Nervous System
... electrical impulses that are quick but the effects are short lived and it involves the CNS (either just spinal cord or both spinal cord and brain) messages are carried by neurons ...
... electrical impulses that are quick but the effects are short lived and it involves the CNS (either just spinal cord or both spinal cord and brain) messages are carried by neurons ...
Touch lab
... Modulating the sense of touch • Does visual-tactile enhancement effect extend to: – Viewing other people’s bodies • Dependent variable: 2PDT estimate • (View object/view body) * +/- other factor – (self/other) • Look for interaction in 2x2 ANOVA • Counterbalancing very important: training effects • ...
... Modulating the sense of touch • Does visual-tactile enhancement effect extend to: – Viewing other people’s bodies • Dependent variable: 2PDT estimate • (View object/view body) * +/- other factor – (self/other) • Look for interaction in 2x2 ANOVA • Counterbalancing very important: training effects • ...
Announcements Memory I
... cannot remember a person for any longer than 10 minutes. He lives in a world where, for him, Truman is still president. News of his mother’s death evokes the same painful grief for a short period of time, and then it is gone. He never really knows exactly how old he is, but reckons that he is about ...
... cannot remember a person for any longer than 10 minutes. He lives in a world where, for him, Truman is still president. News of his mother’s death evokes the same painful grief for a short period of time, and then it is gone. He never really knows exactly how old he is, but reckons that he is about ...
The Nervous System
... turning down pain recognition, encouraging you to eat when you get up, turning off memory and learning (a part of why you don’t ...
... turning down pain recognition, encouraging you to eat when you get up, turning off memory and learning (a part of why you don’t ...
EN Sokolov`s Neural Model of Stimuli as Neuro
... and react to certain physical impacts of stimuli as signals. Receptors are in turn associated with selective detectors – neurons selectively responding to certain stimuli – and this connection can be either direct or, as shown, mediated by the predetectors. Selective detectors operate by the followi ...
... and react to certain physical impacts of stimuli as signals. Receptors are in turn associated with selective detectors – neurons selectively responding to certain stimuli – and this connection can be either direct or, as shown, mediated by the predetectors. Selective detectors operate by the followi ...
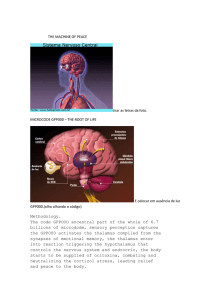
THE MACHINE OF PEACE tirar as letras da foto. MICROCODE
... The thalamus is a center of brain organization, as a crossroads of different neuronal pathways that may influence each other before being redistributed. His connections are more abundant, by far, with the cortex. The main function of the thalamus is to serve as station reorganization of stimuli fro ...
... The thalamus is a center of brain organization, as a crossroads of different neuronal pathways that may influence each other before being redistributed. His connections are more abundant, by far, with the cortex. The main function of the thalamus is to serve as station reorganization of stimuli fro ...
neurobiology of reconstructed memory
... (e.g., Seress, 1992), and its full contribution to memory is not available until this maturation has been completed (Nadel & Willner, 1989). Nadel and Zola-Morgan (1984) argued that the neurobiological immaturity of this critical system might account for at least a portion of "infantile amnesia." Ma ...
... (e.g., Seress, 1992), and its full contribution to memory is not available until this maturation has been completed (Nadel & Willner, 1989). Nadel and Zola-Morgan (1984) argued that the neurobiological immaturity of this critical system might account for at least a portion of "infantile amnesia." Ma ...
Cognitive Psychology Workbook
... Other Evidence for the Multi-Store Model: Cases of Amnesia............................................................. 12 Evidence against the Multi-Store Model .............................................................................................. 13 Levels of Processing (LOP) Model of Memo ...
... Other Evidence for the Multi-Store Model: Cases of Amnesia............................................................. 12 Evidence against the Multi-Store Model .............................................................................................. 13 Levels of Processing (LOP) Model of Memo ...
Terms being described
... 27. It’s a neurological disease that progressively destroys myelin sheaths of neurons in multiple areas of the central nervous system. 29. An action potential is this kind of event as it occurs only in the tiny stimulated region of the axon membrane and not in the rest of the axon. 31. It’s the cond ...
... 27. It’s a neurological disease that progressively destroys myelin sheaths of neurons in multiple areas of the central nervous system. 29. An action potential is this kind of event as it occurs only in the tiny stimulated region of the axon membrane and not in the rest of the axon. 31. It’s the cond ...
Done by : Noor Bjant.hala Dr: loai zghol
... If we activate (sensory touch ) neuron for example in the pathway our brain will understand touch sensation . even if we didn’t touch anything . Also When we feel pain in any visceral oragan , this sensation will travel to the spinal cord and pass through one of its areas . For example : if the im ...
... If we activate (sensory touch ) neuron for example in the pathway our brain will understand touch sensation . even if we didn’t touch anything . Also When we feel pain in any visceral oragan , this sensation will travel to the spinal cord and pass through one of its areas . For example : if the im ...
Specification - King Edward VI School
... Other Evidence for the Multi-Store Model: Cases of Amnesia............................................................. 12 Evidence against the Multi-Store Model .............................................................................................. 13 Levels of Processing (LOP) Model of Memo ...
... Other Evidence for the Multi-Store Model: Cases of Amnesia............................................................. 12 Evidence against the Multi-Store Model .............................................................................................. 13 Levels of Processing (LOP) Model of Memo ...
1285174151_463961
... Brainstem (cont’d.) • Midbrain – Ventral cerebral peduncles: convey impulses from cortex to pons and spinal cord – Dorsal tectum: reflex center – Controls movement of head and eyeball (visual stimuli) – Controls movement of head and trunk (auditory stimuli) ...
... Brainstem (cont’d.) • Midbrain – Ventral cerebral peduncles: convey impulses from cortex to pons and spinal cord – Dorsal tectum: reflex center – Controls movement of head and eyeball (visual stimuli) – Controls movement of head and trunk (auditory stimuli) ...
m5zn_aeb235b83927ffb
... In the mammalian brain, glia outnumber neurons by as many as 50 to 1. The glial cell is called a Schwann cell, which is found in the PNS. (Analogous cells are found in the CNS.) In many vertebrates, axons that convey signals rapidly are enclosed along most of their length by a thick insulating ...
... In the mammalian brain, glia outnumber neurons by as many as 50 to 1. The glial cell is called a Schwann cell, which is found in the PNS. (Analogous cells are found in the CNS.) In many vertebrates, axons that convey signals rapidly are enclosed along most of their length by a thick insulating ...
Chapter 39
... A. A synapse may occur between neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell 1. The neuron that ends at the synapse is the presynaptic neuron; the neuron that begins at a synapse is the postsynaptic neuron 2. Signals across synapses can be electrical or chemical a) Electrical synapses involve very close con ...
... A. A synapse may occur between neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell 1. The neuron that ends at the synapse is the presynaptic neuron; the neuron that begins at a synapse is the postsynaptic neuron 2. Signals across synapses can be electrical or chemical a) Electrical synapses involve very close con ...
The Living Network Lab focuses its group is
... Potter et al (2005). In Bakkum et al (2004), under the control of the neural network a Koala 6wheeled rover was commanded to approach another randomly driven robot. Nonetheless, the dynamics of a network of neurons that receives sensory inputs, stores memories and controls movement and behaviour is ...
... Potter et al (2005). In Bakkum et al (2004), under the control of the neural network a Koala 6wheeled rover was commanded to approach another randomly driven robot. Nonetheless, the dynamics of a network of neurons that receives sensory inputs, stores memories and controls movement and behaviour is ...
The Ventral Stream and Visual Agnosia
... The “ventral stream” refers to the flow of visual information from striate cortex toward the temporal poles Lesions of the ventral stream induce disorders of complex visual processing Receptive fields of neurons in the temporal lobe may be specific for certain semantic ...
... The “ventral stream” refers to the flow of visual information from striate cortex toward the temporal poles Lesions of the ventral stream induce disorders of complex visual processing Receptive fields of neurons in the temporal lobe may be specific for certain semantic ...
Ch 4 Power Point
... • Optic Chiasm: the point where the axons cross to different hemispheres • Light rods and cones neural signals bipolar cells ganglion cells optic nerve optic chiasm opposite half brain • Main pathway: lateral geniculate nucleus (thalamus) primary visual cortex (occipital lobe) (90% o ...
... • Optic Chiasm: the point where the axons cross to different hemispheres • Light rods and cones neural signals bipolar cells ganglion cells optic nerve optic chiasm opposite half brain • Main pathway: lateral geniculate nucleus (thalamus) primary visual cortex (occipital lobe) (90% o ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... d. Somas range from 5–135 μm in diameter, while axons range from 1–20 μm and from a few millimeters to more than a meter in length. e. At the distal end an axon usually has a terminal arborization of fine branches. i. Each branch ends in a synaptic knob (terminal button) that forms a junction (synap ...
... d. Somas range from 5–135 μm in diameter, while axons range from 1–20 μm and from a few millimeters to more than a meter in length. e. At the distal end an axon usually has a terminal arborization of fine branches. i. Each branch ends in a synaptic knob (terminal button) that forms a junction (synap ...
Deep Neural Networks for Anatomical Brain Segmentation
... brain (cortical and sub-cortical areas) into a large number N of anatomical regions, where N is defined by the segmentation protocol (typically around 100). Knowledge of the segmentation protocol is implicitly given through a set of manually labelled 3D brain MRIs. An atlas consists of an MR image a ...
... brain (cortical and sub-cortical areas) into a large number N of anatomical regions, where N is defined by the segmentation protocol (typically around 100). Knowledge of the segmentation protocol is implicitly given through a set of manually labelled 3D brain MRIs. An atlas consists of an MR image a ...
Memento`s Revenge: The Extended Mind
... Taking the argument one step further, we then considered a second example, one designed to address the portability issue and to extend the treatment to the more central case of an agent’s beliefs about the world. This was the case of Otto and Inga. Inga hears of an intriguing exhibition at MOMA (the ...
... Taking the argument one step further, we then considered a second example, one designed to address the portability issue and to extend the treatment to the more central case of an agent’s beliefs about the world. This was the case of Otto and Inga. Inga hears of an intriguing exhibition at MOMA (the ...
OCULAR HEMORRHAGE IN CHILDREN
... migrate tangentially from the germinal zone in the lateral portion of the rhombic lips, to form the external granular layer (EGL) over the surface of the cerebellum. From here, cells migrate inward past the Purkinje cells to form the granular layer. EGL attains maximum cell number in the first few p ...
... migrate tangentially from the germinal zone in the lateral portion of the rhombic lips, to form the external granular layer (EGL) over the surface of the cerebellum. From here, cells migrate inward past the Purkinje cells to form the granular layer. EGL attains maximum cell number in the first few p ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Nervous (5days)
... 2. Where is smooth muscle found? Smooth muscle is found in the lining of the body’s passageways and hollow internal organs, such as in the digestive tract, the urinary bladder, the lining of the blood vessels, and passageways into the lungs. ...
... 2. Where is smooth muscle found? Smooth muscle is found in the lining of the body’s passageways and hollow internal organs, such as in the digestive tract, the urinary bladder, the lining of the blood vessels, and passageways into the lungs. ...