Document
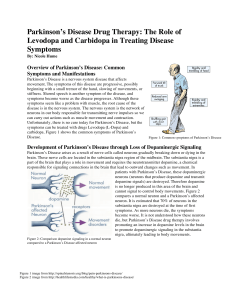
... Parkinson’s Disease arises as a result of nerve cells called neurons gradually breaking down or dying in the brain. These nerve cells are located in the substantia nigra region of the midbrain. The substantia nigra is a part of the brain that plays a role in movement and requires the neurotransmitte ...
... Parkinson’s Disease arises as a result of nerve cells called neurons gradually breaking down or dying in the brain. These nerve cells are located in the substantia nigra region of the midbrain. The substantia nigra is a part of the brain that plays a role in movement and requires the neurotransmitte ...
A2.2.1.TheNeuron
... open your eyes to see the skid marks on the road. Reaching for your cell phone, you dial 911. Your heart races as you run out in the street to see if you can be of any help. So much is happening at one time, you feel like your brain is on overload. Just how does your nervous system deal with so much ...
... open your eyes to see the skid marks on the road. Reaching for your cell phone, you dial 911. Your heart races as you run out in the street to see if you can be of any help. So much is happening at one time, you feel like your brain is on overload. Just how does your nervous system deal with so much ...
Chapter 3
... Globus pallidus (green): deep Nucleus accumbens: (not shown – junction of CN and Putamen) ...
... Globus pallidus (green): deep Nucleus accumbens: (not shown – junction of CN and Putamen) ...
Nervous System Organization and Components
... Outside the myelin, surrounding the axon is a sheath of cells, the neurilemma or Schwann sheath. The neurilemma and myelin are not continuous but are interrupted at intervals along the length of the axon. The point of interruption is the neurofibril node (node of Ranvier). Axons of the PNS Surroundi ...
... Outside the myelin, surrounding the axon is a sheath of cells, the neurilemma or Schwann sheath. The neurilemma and myelin are not continuous but are interrupted at intervals along the length of the axon. The point of interruption is the neurofibril node (node of Ranvier). Axons of the PNS Surroundi ...
Is Political Cognition Like Riding a Bicycle?
... But here is where the parallels end. In the case of riding a bicycle, most of us realize that we can’t easily or accurately explain “exactly how” we manage to roll down the road without falling. Indeed, anyone who has tried to teach another person how to ride knows how inadequate such explanations c ...
... But here is where the parallels end. In the case of riding a bicycle, most of us realize that we can’t easily or accurately explain “exactly how” we manage to roll down the road without falling. Indeed, anyone who has tried to teach another person how to ride knows how inadequate such explanations c ...
Voiding Dysfunction
... CHANGES IN BRAIN ACTIVITY FOLLOWING SACRAL NEUROMODULATION FOR URINARY RETENTION ...
... CHANGES IN BRAIN ACTIVITY FOLLOWING SACRAL NEUROMODULATION FOR URINARY RETENTION ...
Neural Networks algorithms. ppt
... • 1. Initialize network with random weights • 2. For all training cases (called examples): – a. Present training inputs to network and calculate output – b. For all layers (starting with output layer, back to input layer): • i. Compare network output with correct output (error function) • ii. Adapt ...
... • 1. Initialize network with random weights • 2. For all training cases (called examples): – a. Present training inputs to network and calculate output – b. For all layers (starting with output layer, back to input layer): • i. Compare network output with correct output (error function) • ii. Adapt ...
The Nervous system
... The sodium-potassium pump uses ATP to transport sodium ions out and potassium ions in The inside of a resting neuron has a negative charge relative to the outside An action potential is a reversal and restoration of the charge difference across the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the ori ...
... The sodium-potassium pump uses ATP to transport sodium ions out and potassium ions in The inside of a resting neuron has a negative charge relative to the outside An action potential is a reversal and restoration of the charge difference across the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the ori ...
document1004
... action. The comparison with the parameters of intermediate subresulls reveals the correspondence of the stages of realization of the program to the planned ones; the comparison with the parameters of the final result reveals the correspondence between the achieved organism-environment relation and t ...
... action. The comparison with the parameters of intermediate subresulls reveals the correspondence of the stages of realization of the program to the planned ones; the comparison with the parameters of the final result reveals the correspondence between the achieved organism-environment relation and t ...
Physiology 2 - Sheet #6 - Dr.Loai Al-Zgoul - Done by: Yara
... motion. However, his personality and behavior changed severely as a result of his injury. Note: The subcortical is responsible for one’s emotion but what controls the emotion is mainly the prefrontal cortex. An example to get a better understanding of this is when you feel angry-- it’s the subcortic ...
... motion. However, his personality and behavior changed severely as a result of his injury. Note: The subcortical is responsible for one’s emotion but what controls the emotion is mainly the prefrontal cortex. An example to get a better understanding of this is when you feel angry-- it’s the subcortic ...
Final Paper Outline: Effects of Meditation on the Brain
... baseline, the Yogi was able to lower his overall brain activity to a resting state marked by slow delta waves. While in the meditative state, the Yogi showed a significant increase in slow delta wave activity which is similar to individuals who are under analgesia (Peper et al., 2006). Overall, Pepe ...
... baseline, the Yogi was able to lower his overall brain activity to a resting state marked by slow delta waves. While in the meditative state, the Yogi showed a significant increase in slow delta wave activity which is similar to individuals who are under analgesia (Peper et al., 2006). Overall, Pepe ...
Supplemental Information for Free D
... smoothed by convolution with an isotropic Gaussian kernel of 8 mm full-width at half maximum. We examined the main effect of genotype by creating voxel-based, whole-brain, statistical parametric maps using Gaussian random fields theory and the general linear model. More specifically, we used a full ...
... smoothed by convolution with an isotropic Gaussian kernel of 8 mm full-width at half maximum. We examined the main effect of genotype by creating voxel-based, whole-brain, statistical parametric maps using Gaussian random fields theory and the general linear model. More specifically, we used a full ...
Total internal reflection holography for optical interconnections
... pinhole will quadruple the object wave intensity and will divide by four the illumination area in the holographic plane (far-field propagation assumed). This results in an increase of 16 times the object wave irradiance and ofthe ratio between the object and reference beams. ...
... pinhole will quadruple the object wave intensity and will divide by four the illumination area in the holographic plane (far-field propagation assumed). This results in an increase of 16 times the object wave irradiance and ofthe ratio between the object and reference beams. ...
B42010712
... powerful brain-inspired computational models. Which have been employed in various areas such as computing, medicine, engineering, economics, and many others.An artificial neural network is based on the optimization theory. An Artificial Neural Network is a computational model inspired in the functio ...
... powerful brain-inspired computational models. Which have been employed in various areas such as computing, medicine, engineering, economics, and many others.An artificial neural network is based on the optimization theory. An Artificial Neural Network is a computational model inspired in the functio ...
CNS - Algonquin College
... medulla, more commonly referred to as white matter. This is an area of myelinated axons that interconnect neurons both within the nervous system and with other body parts. The surface of the cerebral cortex is marked by ridges and grooves (gyri) and is divided into lobes by spaces called sulci. Ther ...
... medulla, more commonly referred to as white matter. This is an area of myelinated axons that interconnect neurons both within the nervous system and with other body parts. The surface of the cerebral cortex is marked by ridges and grooves (gyri) and is divided into lobes by spaces called sulci. Ther ...
ELD July, 2012 Eyewitness Testimony Adapted from: E. Aronson
... the criminal had blond hair and a mustache?). Eyewitnesses weren't too bad at remembering some details; 100 percent of bystanders correctly remembered whether or not the criminal had facial hair (although crime victims correctly remembered this only 60 percent of the time). Only 48 percent of the by ...
... the criminal had blond hair and a mustache?). Eyewitnesses weren't too bad at remembering some details; 100 percent of bystanders correctly remembered whether or not the criminal had facial hair (although crime victims correctly remembered this only 60 percent of the time). Only 48 percent of the by ...
Development of the central and peripheral nervous system Central
... o basal regions of hemispheres are bulging into the lateral ventricles as the basal ganglia o ependyme and the vascularised mesenchyme forms the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles o hippocampus is also bulging into the lateral ventricles o hemispheres are growing over the diencephalon, mesence ...
... o basal regions of hemispheres are bulging into the lateral ventricles as the basal ganglia o ependyme and the vascularised mesenchyme forms the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles o hippocampus is also bulging into the lateral ventricles o hemispheres are growing over the diencephalon, mesence ...
Nervous System - Lakeridge Health
... medulla, more commonly referred to as white matter. This is an area of myelinated axons that interconnect neurons both within the nervous system and with other body parts. The surface of the cerebral cortex is marked by ridges and grooves (gyri) and is divided into lobes by spaces called sulci. Ther ...
... medulla, more commonly referred to as white matter. This is an area of myelinated axons that interconnect neurons both within the nervous system and with other body parts. The surface of the cerebral cortex is marked by ridges and grooves (gyri) and is divided into lobes by spaces called sulci. Ther ...
The Bifurcating Neuron Network 1q
... where each integrator represents a neuron. These two examples suggest that the possibility of a chaotic network out of non-chaotic elements is plentiful. However, we decided to follow the other option, a network of chaotic neurons, for the following reason. Chaotic activity will be more useful in th ...
... where each integrator represents a neuron. These two examples suggest that the possibility of a chaotic network out of non-chaotic elements is plentiful. However, we decided to follow the other option, a network of chaotic neurons, for the following reason. Chaotic activity will be more useful in th ...
Cerebral Cortex and Corpus Callosum
... The top of the cortex begins with your toes and each body part has a location along the cortex until it reaches the face and tongue. The sensory cortex on the right side of the brain receives sensations from the left side of your body whereas the mirror image on the left side of your brain receives ...
... The top of the cortex begins with your toes and each body part has a location along the cortex until it reaches the face and tongue. The sensory cortex on the right side of the brain receives sensations from the left side of your body whereas the mirror image on the left side of your brain receives ...
A mathematical model on REM-NREM cycle
... The signal is picked up by the neuron via the dendrites, branched structure extending less than one millimeter. Then the soma, also said the body of the neuron, deals with the processing of the signal. We can imagine the soma as an object approximately spherical having a diameter less than 70µm that ...
... The signal is picked up by the neuron via the dendrites, branched structure extending less than one millimeter. Then the soma, also said the body of the neuron, deals with the processing of the signal. We can imagine the soma as an object approximately spherical having a diameter less than 70µm that ...
spinal cord - Dr Magrann
... The spinal nerves come out of the spine, and the cranial nerves come out of the brain directly. There are 12 pairs. They are numbered with Roman numerals. I. OLFACTORY nerves transmit the sense of smell. Outside of the CNS they are called olfactory nerves, and inside of the CNS they are called the o ...
... The spinal nerves come out of the spine, and the cranial nerves come out of the brain directly. There are 12 pairs. They are numbered with Roman numerals. I. OLFACTORY nerves transmit the sense of smell. Outside of the CNS they are called olfactory nerves, and inside of the CNS they are called the o ...
Neural Plasticity in Auditory Cortex
... ‘neural plasticity’ refers to systematic long-term (minutes to months) changes in the responses of neurons to the same physical stimulus (e.g., a tone), due to experience. Neural plasticity in the auditory cortex is interesting not only in itself but also as a case study in the intersection of two s ...
... ‘neural plasticity’ refers to systematic long-term (minutes to months) changes in the responses of neurons to the same physical stimulus (e.g., a tone), due to experience. Neural plasticity in the auditory cortex is interesting not only in itself but also as a case study in the intersection of two s ...
Report 2
... to reconcile with each other (see Pulvermüller, 1999). Is there a way to resolve this unfortunate diversity of opinions? A way out might be pointed by approaches to category-specific semantic processes (Daniele, Giustolisi, Silveri, Colosimo, & Gainotti, 1994; Humphreys & Forde, 2001; Warrington & M ...
... to reconcile with each other (see Pulvermüller, 1999). Is there a way to resolve this unfortunate diversity of opinions? A way out might be pointed by approaches to category-specific semantic processes (Daniele, Giustolisi, Silveri, Colosimo, & Gainotti, 1994; Humphreys & Forde, 2001; Warrington & M ...























