Regulation Notes Activity Page 38: Endocrine/Nerve Cell Coloring
... –Moves your limbs & body –Moves food through the digestive tract –Pumps the blood –Constricts and dilates blood vessels to increase or decrease blood flow ...
... –Moves your limbs & body –Moves food through the digestive tract –Pumps the blood –Constricts and dilates blood vessels to increase or decrease blood flow ...
The Nervous System
... Area beneath the terminal branches of the axons Contains acetylcholine receptor complexes Acetylcholine binding opens the receptor complex Cholinesterase degrades acetylcholine into acetate and choline ...
... Area beneath the terminal branches of the axons Contains acetylcholine receptor complexes Acetylcholine binding opens the receptor complex Cholinesterase degrades acetylcholine into acetate and choline ...
Reaction Time and Reflexes – Lab #11 - Science-with
... Closed head injuries, such as bleeding in or around the brain, may be diagnosed by reflex testing. Remember that the oculomotor nerve stimulates the muscles in and around the eyes. If pressure increases in the cranium (such as from an increase in blood volume due to brain bleeding), then the pressur ...
... Closed head injuries, such as bleeding in or around the brain, may be diagnosed by reflex testing. Remember that the oculomotor nerve stimulates the muscles in and around the eyes. If pressure increases in the cranium (such as from an increase in blood volume due to brain bleeding), then the pressur ...
Reactions versus Reflexes Lab - biology-with
... Closed head injuries, such as bleeding in or around the brain, may be diagnosed by reflex testing. Remember that the oculomotor nerve stimulates the muscles in and around the eyes. If pressure increases in the cranium (such as from an increase in blood volu ...
... Closed head injuries, such as bleeding in or around the brain, may be diagnosed by reflex testing. Remember that the oculomotor nerve stimulates the muscles in and around the eyes. If pressure increases in the cranium (such as from an increase in blood volu ...
Neuromuscular Emergencies - S Derghazarian 07 28 10
... • Auto-immune and congenital form • Epidemiology (auto-immune form): – 200-400 cases per million population – Women > men (3:2) – Bimodal incidence • F: 20s, 30s; M: 50s, 60s ...
... • Auto-immune and congenital form • Epidemiology (auto-immune form): – 200-400 cases per million population – Women > men (3:2) – Bimodal incidence • F: 20s, 30s; M: 50s, 60s ...
Comparison of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness between
... RNFL. All polarimetric recordings were obtained with undilated pupils and dim ambient light. For patients with convergent strabismus, temporal base prisms were placed in front of the fixating eye in order to bring the eye under examination into a straight position. The system accepts the image obtai ...
... RNFL. All polarimetric recordings were obtained with undilated pupils and dim ambient light. For patients with convergent strabismus, temporal base prisms were placed in front of the fixating eye in order to bring the eye under examination into a straight position. The system accepts the image obtai ...
Internal structure of spinal cord
... activity. Some of the fibers of the lateral corticospinal tract terminate directly on the motor neurons (anterior horn cells) of the spinal cord, particularly those involved in fine motor control of the fingers and hand. Most others act via the interneurons of the anterior horn, which then influence ...
... activity. Some of the fibers of the lateral corticospinal tract terminate directly on the motor neurons (anterior horn cells) of the spinal cord, particularly those involved in fine motor control of the fingers and hand. Most others act via the interneurons of the anterior horn, which then influence ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... There are two major classes of adrenergic receptors located in effector organs of the sympathetic nervous system: alpha () and beta () Each of these is further divided into sub-classes: 1 and 2, and 1, 2, and 3 Adrenergic receptors are coupled to G proteins that either activate or inhib ...
... There are two major classes of adrenergic receptors located in effector organs of the sympathetic nervous system: alpha () and beta () Each of these is further divided into sub-classes: 1 and 2, and 1, 2, and 3 Adrenergic receptors are coupled to G proteins that either activate or inhib ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... Figure 11.7 Neurotransmitters and receptors in the autonomic nervous system. (a) Neurotransmitters and receptors for the three distinct anatomical pathways of the sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergi ...
... Figure 11.7 Neurotransmitters and receptors in the autonomic nervous system. (a) Neurotransmitters and receptors for the three distinct anatomical pathways of the sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergi ...
Introductory chapter
... Adrian's experiments established three fundamental facts about the neural code. First, he saw that individual sensory neurons produce stereotyped action potentials, or spikes. This is the all-or-none law, which had already been established for muscles and motor neurons: Incoming stimuli either produ ...
... Adrian's experiments established three fundamental facts about the neural code. First, he saw that individual sensory neurons produce stereotyped action potentials, or spikes. This is the all-or-none law, which had already been established for muscles and motor neurons: Incoming stimuli either produ ...
(lateral spinothalamic tract).
... trapezoid body). The MGN projects to the superior transverse temporal gyri of Heschl, areas 41, 42, the ...
... trapezoid body). The MGN projects to the superior transverse temporal gyri of Heschl, areas 41, 42, the ...
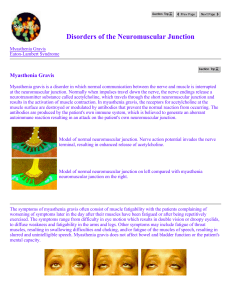
Disorders of the Neuromuscular Junction
... is obtaining blood for detection of acetylcholine receptor antibodies which are present in about 85 to 90 percent of patients with myasthenia gravis. The final diagnostic step is an EMG and nerve conduction study. The nerve conductions and EMG studies are usually normal in myasthenia gravis, but the ...
... is obtaining blood for detection of acetylcholine receptor antibodies which are present in about 85 to 90 percent of patients with myasthenia gravis. The final diagnostic step is an EMG and nerve conduction study. The nerve conductions and EMG studies are usually normal in myasthenia gravis, but the ...
Quick Links - TOP Recommended Websites
... Other techniques and devices have been used and reported to provide some level of either soft tissue or hard tissue anaesthesia. Electronic dental anaesthesia is a technique wherein electrodes are fixed to locations on the patient's face, and the patient is given controls that can send stimuli from ...
... Other techniques and devices have been used and reported to provide some level of either soft tissue or hard tissue anaesthesia. Electronic dental anaesthesia is a technique wherein electrodes are fixed to locations on the patient's face, and the patient is given controls that can send stimuli from ...
1. Dominant Optic Atrophy (DOA): Clinical, genetic and
... Methods: We reviewed all 300 patients assessed for epilepsy surgery with intracranial electrodes and single pulse electrical stimulation (SPES) at King’s College Hospital between 1999 and 2013 to identify the stimulation sites that elicit EEG responses similar to the patient’s Kcomplexes. Results: I ...
... Methods: We reviewed all 300 patients assessed for epilepsy surgery with intracranial electrodes and single pulse electrical stimulation (SPES) at King’s College Hospital between 1999 and 2013 to identify the stimulation sites that elicit EEG responses similar to the patient’s Kcomplexes. Results: I ...
Nerve activates contraction
... •Five elements of a reflex: •Sensory receptor–reacts to a stimulus •Sensory neuron–carries message to the integration center •Integration center (CNS)–processes information and directs motor output •Motor neuron–carries message to an effector •Effector organ–is the muscle or gland to be stimulated ...
... •Five elements of a reflex: •Sensory receptor–reacts to a stimulus •Sensory neuron–carries message to the integration center •Integration center (CNS)–processes information and directs motor output •Motor neuron–carries message to an effector •Effector organ–is the muscle or gland to be stimulated ...
Nervous System - Fuller Anatomy
... withdrawal of the CSF occurs in a procedure called a spinal tap. Spinal taps are done to diagnose CNS infection, severe back pain, disc problems, and some types of strokes. ...
... withdrawal of the CSF occurs in a procedure called a spinal tap. Spinal taps are done to diagnose CNS infection, severe back pain, disc problems, and some types of strokes. ...
Neurobiology of learning
... When you sleep your brain goes through 6 to 9 very short cycles of REM sleep (called Rapid Eye Movement sleep because your eyes move back and forth very quickly). Each cycle lasts about 5 minutes, and during that time your brain does the following: 1) Signal the body to make Human growth hormone whi ...
... When you sleep your brain goes through 6 to 9 very short cycles of REM sleep (called Rapid Eye Movement sleep because your eyes move back and forth very quickly). Each cycle lasts about 5 minutes, and during that time your brain does the following: 1) Signal the body to make Human growth hormone whi ...
Central Nervous System I. Brain - Function A. Hindbrain 1. Medulla
... pattern perception, recognition of faces, facial expression, and emotional content of language and for generating mental images to compare these images to each other. Lateralization is less pronounced in females than in males for language, visual and spatial skills. This is possibly related to the f ...
... pattern perception, recognition of faces, facial expression, and emotional content of language and for generating mental images to compare these images to each other. Lateralization is less pronounced in females than in males for language, visual and spatial skills. This is possibly related to the f ...
File
... Some axons are surrounded by a mixture of protein and phospholipids called myelin that collectively form a myelin sheath Many layers of myelin are deposited around the axon by special cells called Schwann cells The myelin sheath insulates the axon and greatly increases the speed of the nerve i ...
... Some axons are surrounded by a mixture of protein and phospholipids called myelin that collectively form a myelin sheath Many layers of myelin are deposited around the axon by special cells called Schwann cells The myelin sheath insulates the axon and greatly increases the speed of the nerve i ...
Nervous System WS (handed out after section exam)
... f. What part of the neuron is usually wrapped in myelin sheath? The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases becau ...
... f. What part of the neuron is usually wrapped in myelin sheath? The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases becau ...
Test.
... • First attempt in 1956. • Excitement and hype. Stevie Wonder. • Currently – cautious long term optimism. • “To impart a coarse level of vision that would expand a blind person’s autonomy is an ambitious but plausible goal”. John Wyatt (MIT). ...
... • First attempt in 1956. • Excitement and hype. Stevie Wonder. • Currently – cautious long term optimism. • “To impart a coarse level of vision that would expand a blind person’s autonomy is an ambitious but plausible goal”. John Wyatt (MIT). ...
here
... An action potential occurs when a neuron sends an impulse down an axon, away from the cell body. It is an explosion of electrical activity that is created by a depolarizing current. (This means that a stimulus has caused the resting potential to move toward 0 mV.) When the depolarization reache ...
... An action potential occurs when a neuron sends an impulse down an axon, away from the cell body. It is an explosion of electrical activity that is created by a depolarizing current. (This means that a stimulus has caused the resting potential to move toward 0 mV.) When the depolarization reache ...
9.2 Electrochemical Impulses
... prioritization of information received by your brain. Ie: when you are listening to a biology lecture, your sensory info should be directed to Ms. De Souza. Information from other sensory nerves (ie, temp in the room, the pressure receptors confirming you are ...
... prioritization of information received by your brain. Ie: when you are listening to a biology lecture, your sensory info should be directed to Ms. De Souza. Information from other sensory nerves (ie, temp in the room, the pressure receptors confirming you are ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.