Evaluation of ventral root reimplantation as a treatment of
... and the muscular effectors might be a limiting factor for anatomical and functional restoration, a factor that is less significant in small animals such as rats, 2/ in the experimental models, roots are generally avulsed just before reimplantation. Thus, this procedure does not take into account the ...
... and the muscular effectors might be a limiting factor for anatomical and functional restoration, a factor that is less significant in small animals such as rats, 2/ in the experimental models, roots are generally avulsed just before reimplantation. Thus, this procedure does not take into account the ...
Activity of Krebs cycle enzymes in mdx mice - Genoma
... DMD is characterized by progressive muscle wasting and weakness. At the cellular level, the loss of dystrophin initiates a complex series of pathophysiological changes that drive skeletal muscle cell to weakness, atrophy, and death. Most prominent is abnormal Ca2+ influx and handling that is thought ...
... DMD is characterized by progressive muscle wasting and weakness. At the cellular level, the loss of dystrophin initiates a complex series of pathophysiological changes that drive skeletal muscle cell to weakness, atrophy, and death. Most prominent is abnormal Ca2+ influx and handling that is thought ...
Ch14 notes Martini 9e
... 1. Each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from, and sends motor commands to, the opposite side of the body 2. The two hemispheres have different functions, although their structures are alike 3. Correspondence between a specific function and a specific region of cerebral cortex is © 2 ...
... 1. Each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from, and sends motor commands to, the opposite side of the body 2. The two hemispheres have different functions, although their structures are alike 3. Correspondence between a specific function and a specific region of cerebral cortex is © 2 ...
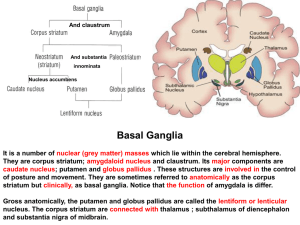
21. Basal ganglion
... purposeful behaviour and movements and to inhibit unwanted or inappropriate (not suitable ) movements. When a movement is initiated from the cerebral ...
... purposeful behaviour and movements and to inhibit unwanted or inappropriate (not suitable ) movements. When a movement is initiated from the cerebral ...
EMG Blind Spots Disorders of the NMJ
... 45 year old man with progressive ptosis, dysphagia FH: mother with “seronegative myasthenia gravis” Examination: bilateral ptosis and extraocular muscle weakness without clear fatigability; mild proximal limb weakness Antibody testing: AChR and MuSK Antibodies (-) EMG and NCS: decrement on repetitiv ...
... 45 year old man with progressive ptosis, dysphagia FH: mother with “seronegative myasthenia gravis” Examination: bilateral ptosis and extraocular muscle weakness without clear fatigability; mild proximal limb weakness Antibody testing: AChR and MuSK Antibodies (-) EMG and NCS: decrement on repetitiv ...
spinal cord and reflexes - Sinoe Medical Association
... A reflex is a direct connection between stimulus and response, which does not require conscious thought. There are voluntary and involuntary reflexes. It is the voluntary reflexes we are considering here. As discussed earlier, a reflex involves at least 2 or 3 neurons. The reflex shown in this fi ...
... A reflex is a direct connection between stimulus and response, which does not require conscious thought. There are voluntary and involuntary reflexes. It is the voluntary reflexes we are considering here. As discussed earlier, a reflex involves at least 2 or 3 neurons. The reflex shown in this fi ...
14-1 SENSATION FIGURE 14.1 1. The general senses provide
... C. The cranial nerves and their pathways carry unconscious proprioception to the cerebellum from the head. 2. Organization of neurons in the spinocerebellar tracts. A. In the spinocerebellar tracts the primary neurons enter the spinal cord and synapse with ...
... C. The cranial nerves and their pathways carry unconscious proprioception to the cerebellum from the head. 2. Organization of neurons in the spinocerebellar tracts. A. In the spinocerebellar tracts the primary neurons enter the spinal cord and synapse with ...
Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis
... coughing and sneezing are bodily functions which are caused by sensitivity and small pain to the throat and nose. Since she was unable to feel pain, her body did not respond to these stimuli either. Unfortunately, ÒMs. CÓ died prematurely at the age of 29, from infections in her knees, hips and spin ...
... coughing and sneezing are bodily functions which are caused by sensitivity and small pain to the throat and nose. Since she was unable to feel pain, her body did not respond to these stimuli either. Unfortunately, ÒMs. CÓ died prematurely at the age of 29, from infections in her knees, hips and spin ...
14-1 SENSATION 1. The general senses provide information about
... C. The cranial nerves and their pathways carry unconscious proprioception to the cerebellum from the head. 2. Organization of neurons in the spinocerebellar tracts. A. In the spinocerebellar tracts the primary neurons enter the spinal cord and synapse with ...
... C. The cranial nerves and their pathways carry unconscious proprioception to the cerebellum from the head. 2. Organization of neurons in the spinocerebellar tracts. A. In the spinocerebellar tracts the primary neurons enter the spinal cord and synapse with ...
Bio211 Lecture 19
... state of wakefulness (reticular activating system) Subconscious coordination of skeletal muscle activity, maintains posture ...
... state of wakefulness (reticular activating system) Subconscious coordination of skeletal muscle activity, maintains posture ...
Hyperstiffness
... • Fractionation is the ability to activate individual muscles independently of other muscles. • Interruption of lateral corticospinal signals prevents fractionation, profoundly affecting the ability to use the hand. ...
... • Fractionation is the ability to activate individual muscles independently of other muscles. • Interruption of lateral corticospinal signals prevents fractionation, profoundly affecting the ability to use the hand. ...
Brain Part
... Name the interconnected cavities within the cerebrum and brain stem and identify the fluid that fills these spaces and name the cells that line these spaces. ...
... Name the interconnected cavities within the cerebrum and brain stem and identify the fluid that fills these spaces and name the cells that line these spaces. ...
The Late Effects of Polio - Polio Outreach of Washington
... wheelchair users with pelvic obliquity associated with scoliosis. Three patients had piriformis syndrome. The other joints in addition to the ones of the spine showed signs of wear-and-tear arthritis. As in the case of the back, abnormal biomechanics and overuse (or sometimes abuse) causes wear and ...
... wheelchair users with pelvic obliquity associated with scoliosis. Three patients had piriformis syndrome. The other joints in addition to the ones of the spine showed signs of wear-and-tear arthritis. As in the case of the back, abnormal biomechanics and overuse (or sometimes abuse) causes wear and ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 19.1 Evidence of synapse elimination
... in the shrinkage of the columns representing the deprived eye (dark stripes) and an expansion of the columns of the nondeprived eye (light stripes). (C) Aschematic representation of ocular dominance column development represents the way in which a gradual segregation ocular dominance column could le ...
... in the shrinkage of the columns representing the deprived eye (dark stripes) and an expansion of the columns of the nondeprived eye (light stripes). (C) Aschematic representation of ocular dominance column development represents the way in which a gradual segregation ocular dominance column could le ...
Unit 13 Autonomic Nervous System
... – Parasympathetic – Almost all organs and glands receive nerves from both branches ...
... – Parasympathetic – Almost all organs and glands receive nerves from both branches ...
central mechanisms underlying short-term and long
... whether there is a common set of "command neurons" within this region of the hypothalamus that trigger both the somatomotor and autonomic changes. It is well known that acute emotional or threatening stimuli can also elicit a marked cardiovascular response. For example, the classic "defence" or "ale ...
... whether there is a common set of "command neurons" within this region of the hypothalamus that trigger both the somatomotor and autonomic changes. It is well known that acute emotional or threatening stimuli can also elicit a marked cardiovascular response. For example, the classic "defence" or "ale ...
For Immediate Release SCIENTIFIC BREAKTHROUGH
... proven to prevent and treat muscle cramps. Neuro Muscular Performance: A New Category in Sports Nutrition In their pursuit to find a solution for muscle cramps, MacKinnon and Bean accidentally unlocked the power of Neuro Muscular Performance – the way that an athlete’s nerves and muscles work togeth ...
... proven to prevent and treat muscle cramps. Neuro Muscular Performance: A New Category in Sports Nutrition In their pursuit to find a solution for muscle cramps, MacKinnon and Bean accidentally unlocked the power of Neuro Muscular Performance – the way that an athlete’s nerves and muscles work togeth ...
CranialN11
... (ascending) pathways, [cranial nerves nuclei are analogous to ventral horn nuclei]. E.g., especially evident in the lowest n. XI – spinal accessory. Review 3 Functional Categories (we will go over 2 today). -located medially relative to sensory nuclei, in columns. -review the cranial nerves associat ...
... (ascending) pathways, [cranial nerves nuclei are analogous to ventral horn nuclei]. E.g., especially evident in the lowest n. XI – spinal accessory. Review 3 Functional Categories (we will go over 2 today). -located medially relative to sensory nuclei, in columns. -review the cranial nerves associat ...
1 - Hatboro
... Calcium 14. What are two places where calcium (Ca2+) is normally found prior to a muscle contracting (to start things off)? outside the synaptic knob, in the sarcoplamsmic reticulum ...
... Calcium 14. What are two places where calcium (Ca2+) is normally found prior to a muscle contracting (to start things off)? outside the synaptic knob, in the sarcoplamsmic reticulum ...
Peripheral part of the vestibular system
... • is a tumor of the tissue that covers nerves, called the nerve sheath. • develop from a type of cell called a Schwann cell, which gives them their name. • Schwannomas are often not cancerous (benign). The most common type of benign schwannoma is the acoustic neuroma. This can cause deafness. • When ...
... • is a tumor of the tissue that covers nerves, called the nerve sheath. • develop from a type of cell called a Schwann cell, which gives them their name. • Schwannomas are often not cancerous (benign). The most common type of benign schwannoma is the acoustic neuroma. This can cause deafness. • When ...
a spiking stretch receptor with central cell bodies in the uropod
... response characteristics (Fig. 6). These afferent units can be recorded after all nerves other than those innervating the elastic strand have been cut, but a more intact preparation was usually used, since no difference could be detected. There is no 'off' response on relaxation of the receptor. (2) ...
... response characteristics (Fig. 6). These afferent units can be recorded after all nerves other than those innervating the elastic strand have been cut, but a more intact preparation was usually used, since no difference could be detected. There is no 'off' response on relaxation of the receptor. (2) ...
Isolated Ocular Motor Nerve Palsies
... fibers. Diffuse infiltrative processes such as lymphoma or carcinomatosis may involve multiple CNs, including the lower CNs such as VII, IX, X, or XII, within the subarachnoid space on the leptomeningeal surface of the brain. Otorrhea with sixth nerve palsy suggests petrous apicitis, whereas the prese ...
... fibers. Diffuse infiltrative processes such as lymphoma or carcinomatosis may involve multiple CNs, including the lower CNs such as VII, IX, X, or XII, within the subarachnoid space on the leptomeningeal surface of the brain. Otorrhea with sixth nerve palsy suggests petrous apicitis, whereas the prese ...
CME Restoration of Elbow Flexion after Brachial Plexus Injury: The
... nerve grafts. However, the later group had earlier evidence of motor reinnervation, improvement in protective sensation, and a reduction in arm pain. Phrenic Nerve Transfer ...
... nerve grafts. However, the later group had earlier evidence of motor reinnervation, improvement in protective sensation, and a reduction in arm pain. Phrenic Nerve Transfer ...
Evidence of sympathetic ®bers in the male rat pelvic nerve
... organs and distal colon seems to be generally applicable to all mammalian species investigated thus far, including man.6 In the male rat, pelvic neuroanatomy has been previously described and appears simpler when compared to larger species.13±16 In this species the pelvic and hypogastric nerves cons ...
... organs and distal colon seems to be generally applicable to all mammalian species investigated thus far, including man.6 In the male rat, pelvic neuroanatomy has been previously described and appears simpler when compared to larger species.13±16 In this species the pelvic and hypogastric nerves cons ...
Cerebellum Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the
... Refers to disordered contractions of agonist and antagonist muscles and lack of coordination between movements at different joints typically seen in patients with cerebellar lesions. Normal movements require coordination of agonist and antagonist muscles at different joints in order for movement to ...
... Refers to disordered contractions of agonist and antagonist muscles and lack of coordination between movements at different joints typically seen in patients with cerebellar lesions. Normal movements require coordination of agonist and antagonist muscles at different joints in order for movement to ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.