FUNCTIONAL NEUROANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD LEARNING
... Cannal continues up wards to 4th ventricle Inferiorly conus medullaris into terminal ventricle and terminate below with in the root of filum terminale. Lined by ciliated columnar epithelium the ependyma. Closed inferiorly. Anterior white column: Lies between the midline and the point of emergence of ...
... Cannal continues up wards to 4th ventricle Inferiorly conus medullaris into terminal ventricle and terminate below with in the root of filum terminale. Lined by ciliated columnar epithelium the ependyma. Closed inferiorly. Anterior white column: Lies between the midline and the point of emergence of ...
FUNCTIONAL NEUROANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD LEARNING
... Cannal continues up wards to 4th ventricle Inferiorly conus medullaris into terminal ventricle and terminate below with in the root of filum terminale. Lined by ciliated columnar epithelium the ependyma. Closed inferiorly. Anterior white column: Lies between the midline and the point of emergence of ...
... Cannal continues up wards to 4th ventricle Inferiorly conus medullaris into terminal ventricle and terminate below with in the root of filum terminale. Lined by ciliated columnar epithelium the ependyma. Closed inferiorly. Anterior white column: Lies between the midline and the point of emergence of ...
Brachial Plexus Injury - International Federation of Societies for
... The outcomes of nerve transfers for BPI patients depend on four factors which may influence the clinical results. The first factor is patient selection. Studies have shown that younger patients recover from nerve transfer faster and ultimately have better outcomes than older patients. Typically pati ...
... The outcomes of nerve transfers for BPI patients depend on four factors which may influence the clinical results. The first factor is patient selection. Studies have shown that younger patients recover from nerve transfer faster and ultimately have better outcomes than older patients. Typically pati ...
The central nervous system, or CNS for short, is composed of the
... removed and placed into the damaged site. In the new environment, the neurons grew and connected to pre-existing broken ones resulting in severed nerves being reconnected (Davies, et al., 1999). The problem with this is that transplanted nerves grow and attach to any other nerve. In other words, th ...
... removed and placed into the damaged site. In the new environment, the neurons grew and connected to pre-existing broken ones resulting in severed nerves being reconnected (Davies, et al., 1999). The problem with this is that transplanted nerves grow and attach to any other nerve. In other words, th ...
The Nervous System
... around the larger nerve fibers in the PNS. Vital to neuronal regeneration ...
... around the larger nerve fibers in the PNS. Vital to neuronal regeneration ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... As long as the RMP in a nerve cell is undisturbed, it remains polarized. However, in order for a nerve impulse to be started or propagated in a nerve cell, this resting potential must be disturbed. ...
... As long as the RMP in a nerve cell is undisturbed, it remains polarized. However, in order for a nerve impulse to be started or propagated in a nerve cell, this resting potential must be disturbed. ...
Do distinct populations of dorsal root ganglion neurons account for
... TRPV1 receptors or ASIC (30)? Such a finding could suggest mechanisms to be studied further to putatively explain neurogenic CGRP release being so effective in ameliorating hypertensive kidney damage (3, 31). One major problem in this respect lies in the fact that afferent sensory nerve fibers, main ...
... TRPV1 receptors or ASIC (30)? Such a finding could suggest mechanisms to be studied further to putatively explain neurogenic CGRP release being so effective in ameliorating hypertensive kidney damage (3, 31). One major problem in this respect lies in the fact that afferent sensory nerve fibers, main ...
11_16_15- Day 1 - Kenwood Academy High School
... receptors to monitor the stimuli in and out of our body. Integration: we process and interpret stimuli and determine the appropriate response necessary. Motor output: we activate muscle contraction. ...
... receptors to monitor the stimuli in and out of our body. Integration: we process and interpret stimuli and determine the appropriate response necessary. Motor output: we activate muscle contraction. ...
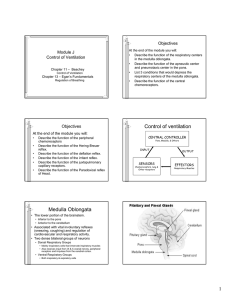
Control of ventilation Medulla Oblongata
... • Two dense bilateral groups of neurons • Dorsal Respiratory Groups • Mainly inspiratory cells that innervate inspiratory muscles • Also receives input from IX & X cranial nerves, peripheral receptors and impulses from the cerebral cortex. ...
... • Two dense bilateral groups of neurons • Dorsal Respiratory Groups • Mainly inspiratory cells that innervate inspiratory muscles • Also receives input from IX & X cranial nerves, peripheral receptors and impulses from the cerebral cortex. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - macomb
... • Two dense bilateral groups of neurons • Dorsal Respiratory Groups • Mainly inspiratory cells that innervate inspiratory muscles • Also receives input from IX & X cranial nerves, peripheral receptors and impulses from the cerebral cortex. ...
... • Two dense bilateral groups of neurons • Dorsal Respiratory Groups • Mainly inspiratory cells that innervate inspiratory muscles • Also receives input from IX & X cranial nerves, peripheral receptors and impulses from the cerebral cortex. ...
Document
... Pain is felt in or just deep to the skin that overlies the stimulated organ or in a surface area far from the stimulated organ. ...
... Pain is felt in or just deep to the skin that overlies the stimulated organ or in a surface area far from the stimulated organ. ...
Increased responses in trigeminocervical nociceptive neurons to cervical input after
... Headache Group, Institute of Neurology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, London, UK ...
... Headache Group, Institute of Neurology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, London, UK ...
1.In the direct pathway
... hoop, passing a football, throwing a baseball, most aspects of vocalization, controlled movements of the eyes . 2. Cognitive Control of motor activity, using both sensory input to the brain plus information already stored in memory. A good example of this would be a person seeing a lion approach and ...
... hoop, passing a football, throwing a baseball, most aspects of vocalization, controlled movements of the eyes . 2. Cognitive Control of motor activity, using both sensory input to the brain plus information already stored in memory. A good example of this would be a person seeing a lion approach and ...
6 - Coach Eikrem's Website
... muscles – when touching a hot surface, nerve impulses travel from a sensory nerve to an interneuron in the spinal cord to a motor neuron, bypassing the brain Reflex video.html Autonomic reflexes – send involuntary stimuli to the cardiac muscles of the heart and the smooth muscles of the organs – d ...
... muscles – when touching a hot surface, nerve impulses travel from a sensory nerve to an interneuron in the spinal cord to a motor neuron, bypassing the brain Reflex video.html Autonomic reflexes – send involuntary stimuli to the cardiac muscles of the heart and the smooth muscles of the organs – d ...
PDF
... the elderly, giant cell arteritis should be considered as well. Migraine may cause transient painful oculomotor nerve palsy. Medial temporal lobe herniation is another cause of oculomotor nerve palsy, usually associated with coma and motor deficits. Inflammation, thrombosis, or trauma anywhere along ...
... the elderly, giant cell arteritis should be considered as well. Migraine may cause transient painful oculomotor nerve palsy. Medial temporal lobe herniation is another cause of oculomotor nerve palsy, usually associated with coma and motor deficits. Inflammation, thrombosis, or trauma anywhere along ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... In neurons, an AP is called a NERVE IMPULSE and only axons can generate one. ...
... In neurons, an AP is called a NERVE IMPULSE and only axons can generate one. ...
Document
... • Heavily myelinated axons of the somatic motor neurons extend from the CNS to the effector • Axons of the ANS are a two-neuron chain • The preganglionic (first) neuron with a lightly myelinated axon • The gangionic (second) neuron that extends to an effector organ ...
... • Heavily myelinated axons of the somatic motor neurons extend from the CNS to the effector • Axons of the ANS are a two-neuron chain • The preganglionic (first) neuron with a lightly myelinated axon • The gangionic (second) neuron that extends to an effector organ ...
Conversations in Glaucoma - Pennsylvania Optometric Association
... • The “art” of effective GLC management is to individualize treatment, being sensitive to patient’s psycho-social makeup and QOL issues. • The “science” of effective GLC management is based on the best current evidence and technology in combination with “old school” ...
... • The “art” of effective GLC management is to individualize treatment, being sensitive to patient’s psycho-social makeup and QOL issues. • The “science” of effective GLC management is based on the best current evidence and technology in combination with “old school” ...
Pathology Test 3 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Conditions caused
... • 50-60: Malaisa, nausea, vertigo, restlessness, lightheadedness, impaired judgment, incoordination • 35-50: marked confusion, cardiac dysrhythmias, labored respiration • 25-35: Decreased renal blood flow, decreased urine output, loss of consciousness, poor oxygenation, poor CO, lactic acidosis, let ...
... • 50-60: Malaisa, nausea, vertigo, restlessness, lightheadedness, impaired judgment, incoordination • 35-50: marked confusion, cardiac dysrhythmias, labored respiration • 25-35: Decreased renal blood flow, decreased urine output, loss of consciousness, poor oxygenation, poor CO, lactic acidosis, let ...
Motor system - Brain Facts
... parietal cortex (area 5, 7). One kind of neuron is active before goal-directed, reaching movements, such as when a monkey stretches its hand toward a banana. Such neurons do not become active, however, in relation to movement in the same direction but without a specific aim, or in relation to a pass ...
... parietal cortex (area 5, 7). One kind of neuron is active before goal-directed, reaching movements, such as when a monkey stretches its hand toward a banana. Such neurons do not become active, however, in relation to movement in the same direction but without a specific aim, or in relation to a pass ...
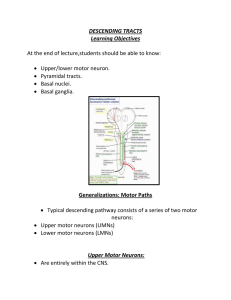
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Not complete paralysis Note: complete paralysis results if both pyramidal and extrapyramidalsystems are involved (as is often the case). ...
... Not complete paralysis Note: complete paralysis results if both pyramidal and extrapyramidalsystems are involved (as is often the case). ...
Nervous System The master controlling and communicating system
... Each neuron has a single axon which arises from the cell body at the axon hillock then narrow to form a process w/ consistent diameter the rest of its length ...
... Each neuron has a single axon which arises from the cell body at the axon hillock then narrow to form a process w/ consistent diameter the rest of its length ...
May 2015
... A) illustrates the process of identifying key anatomical landmarks by gently palpating ribs through the pleura and counting them. In B) the pleura is being pulled slightly away from structures beneath it so that it can be opened by coagulation, as in C), without damage to underlying structures. D) s ...
... A) illustrates the process of identifying key anatomical landmarks by gently palpating ribs through the pleura and counting them. In B) the pleura is being pulled slightly away from structures beneath it so that it can be opened by coagulation, as in C), without damage to underlying structures. D) s ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.