Synaptic Competition during the Reformation of a Neuromuscular Map
... and C7 branches were stimulated with suction electrodes. T ypical stimulation parameters were 1–10 V for 0.1 msec at 1–3 Hz. Muscle contraction was prevented by raising the Mg concentration to 12–17 mM or by stretching the muscle. Intracellular recordings were made from muscle fibers of sectors II a ...
... and C7 branches were stimulated with suction electrodes. T ypical stimulation parameters were 1–10 V for 0.1 msec at 1–3 Hz. Muscle contraction was prevented by raising the Mg concentration to 12–17 mM or by stretching the muscle. Intracellular recordings were made from muscle fibers of sectors II a ...
The Nervous System
... Some cranial nerves contain only afferent fibres They are the first cells entering the CNS The efferent NS is subdivided into somatic & autonomic Innervate skeletal muscle Innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands & neurones in GI tract In parallel Cerebral cortex – responsible for conscious r ...
... Some cranial nerves contain only afferent fibres They are the first cells entering the CNS The efferent NS is subdivided into somatic & autonomic Innervate skeletal muscle Innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands & neurones in GI tract In parallel Cerebral cortex – responsible for conscious r ...
What does the eye tell the brain? Development of a system for the large-scale recording of retinal output activity
... plot: it records the analog waveforms on all the electrodes, preserving the spatial and temporal correlations associated with a spike on a “seed” electrode. An important consideration concerning neuron identification by manual clustering is that it is a very time-consuming and subjective procedure. ...
... plot: it records the analog waveforms on all the electrodes, preserving the spatial and temporal correlations associated with a spike on a “seed” electrode. An important consideration concerning neuron identification by manual clustering is that it is a very time-consuming and subjective procedure. ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... 3. Cortical or voluntary control of the autonomic nervous system may be possible. 4. Biofeedback training may enable a person to alter some involuntary functions. ...
... 3. Cortical or voluntary control of the autonomic nervous system may be possible. 4. Biofeedback training may enable a person to alter some involuntary functions. ...
Слайд 1 - sechenov.ru
... Manifestations of the hyperkinetic movement disorders ● Increased amplitude and amount of movements ● Unintended movements ● Abnormal coordination of movement ...
... Manifestations of the hyperkinetic movement disorders ● Increased amplitude and amount of movements ● Unintended movements ● Abnormal coordination of movement ...
Chapter 15: Special Senses
... • Both adapt rapidly at first, but continue to generate impulses at a low frequency • Pain is produced below 50 and over 118 degrees F. Tortora & Grabowski 9/e 2000 JWS ...
... • Both adapt rapidly at first, but continue to generate impulses at a low frequency • Pain is produced below 50 and over 118 degrees F. Tortora & Grabowski 9/e 2000 JWS ...
Nerve activates contraction
... 1.Using the materials at hand build a motor neuron 2.Be sure to include: - dendrite cell body axon myelin sheath schwann cell nodes of Ranvier axon terminal synapse neurotransmitter 3.Include a description of the role each of the above structures plays in nerve cell function. 4.Surround your nerve c ...
... 1.Using the materials at hand build a motor neuron 2.Be sure to include: - dendrite cell body axon myelin sheath schwann cell nodes of Ranvier axon terminal synapse neurotransmitter 3.Include a description of the role each of the above structures plays in nerve cell function. 4.Surround your nerve c ...
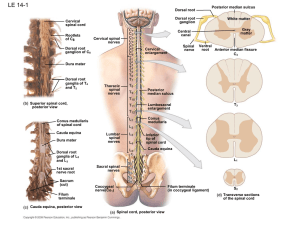
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... Spinal Cord Physiology / Motor Tracts Motor info. travels from the brain down the spinal cord to muscles and glands via the; 1. Pyramidal tracts 2. Extrapyramidal tracts ...
... Spinal Cord Physiology / Motor Tracts Motor info. travels from the brain down the spinal cord to muscles and glands via the; 1. Pyramidal tracts 2. Extrapyramidal tracts ...
Spinal Nerves and Nerve Plexus
... Motor info. travels from the brain down the spinal cord to muscles and glands via the; • Pyramidal tracts • Extrapyramidal tracts ...
... Motor info. travels from the brain down the spinal cord to muscles and glands via the; • Pyramidal tracts • Extrapyramidal tracts ...
Introduction
... 64x64 pixels to be treated as a complete image. 4096 inputs and 1 final input () The hidden layer with 256 or 512 neurons ...
... 64x64 pixels to be treated as a complete image. 4096 inputs and 1 final input () The hidden layer with 256 or 512 neurons ...
nervous system physiology 4
... -methacholine, carbachol, and nicotine- these Ach agonists are not destroyed by cholinesterase or are destroyed so slowly that their action often persists for many minutes to several hours. -they cause localized areas of depolarization of motor end plate every time the muscle fiber recovers from a ...
... -methacholine, carbachol, and nicotine- these Ach agonists are not destroyed by cholinesterase or are destroyed so slowly that their action often persists for many minutes to several hours. -they cause localized areas of depolarization of motor end plate every time the muscle fiber recovers from a ...
Biological Theories of Aging
... PNS Sensory System Changes with Aging • Decreased number of unmyelinated and myelinated nerve fibers • Blood vessels become atherosclerotic ―Loss of blood supply to nerve fibers ―Major factor of the increased prevalence of peripheral neuropathies with age ...
... PNS Sensory System Changes with Aging • Decreased number of unmyelinated and myelinated nerve fibers • Blood vessels become atherosclerotic ―Loss of blood supply to nerve fibers ―Major factor of the increased prevalence of peripheral neuropathies with age ...
MENNONITE COLLEGE OF NURSING AT ILLINOIS STATE
... Palpate all bones, joints, and surrounding muscles. Note any heat, tenderness, swelling, crepitus, or resistance to pressure. No pain or discomfort when pressure is applied to bones and joints. Muscles should feel firm but not hard or soft. RANGE OF MOTION Examine active and passive range of motion ...
... Palpate all bones, joints, and surrounding muscles. Note any heat, tenderness, swelling, crepitus, or resistance to pressure. No pain or discomfort when pressure is applied to bones and joints. Muscles should feel firm but not hard or soft. RANGE OF MOTION Examine active and passive range of motion ...
A Pain in the Ear: The Radiology of Otalgia
... glands, and thyroid gland (2, 4, 5) (Fig 1C). Synalgia and telalgia are rarely used synonyms for referred pain (6). Pathways Mediating Primary Otalgia The skin of the ear is an interface between branchial and postbranchial innervation. Therefore, sensory innervation of the external ear is mediated b ...
... glands, and thyroid gland (2, 4, 5) (Fig 1C). Synalgia and telalgia are rarely used synonyms for referred pain (6). Pathways Mediating Primary Otalgia The skin of the ear is an interface between branchial and postbranchial innervation. Therefore, sensory innervation of the external ear is mediated b ...
Spinal Cord - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... maintain balance • Rubrospinal tracts – originate in ‘red nucleus’ of midbrain; control flexor muscles • Tectospinal tracts - originate in superior colliculi and mediate head and eye movements towards visual targets (flash of light) ...
... maintain balance • Rubrospinal tracts – originate in ‘red nucleus’ of midbrain; control flexor muscles • Tectospinal tracts - originate in superior colliculi and mediate head and eye movements towards visual targets (flash of light) ...
The evolution of different skin colours
... Charles Darwin proposed sexual selection to explain light skin colour based on, among other things, the fact that Asian people living near Equator had the same skin colour as Inuits living near the poles: The Esquimaux live exclusively on animal food; they are clothed in thick fur, and are exposed t ...
... Charles Darwin proposed sexual selection to explain light skin colour based on, among other things, the fact that Asian people living near Equator had the same skin colour as Inuits living near the poles: The Esquimaux live exclusively on animal food; they are clothed in thick fur, and are exposed t ...
Document
... • !!! Impulse leaves the spinal cord by way of the axon of intercalated neuron. It is also called preganglionic fiber. • 3-d, motor (efferent) neuron is located in the sympathetic ganglion. The axon of the ganglion cell is called the ...
... • !!! Impulse leaves the spinal cord by way of the axon of intercalated neuron. It is also called preganglionic fiber. • 3-d, motor (efferent) neuron is located in the sympathetic ganglion. The axon of the ganglion cell is called the ...
Electrophysiology applications 1
... animals. In this approach, the animal is anesthetized, most commonly with a barbiturate, urethane, chloralose, or halothane. The animal is then placed in a stereotaxic instrument which positions the skull in an exact position and orientation with respect to submillimeter scales in three dimensions o ...
... animals. In this approach, the animal is anesthetized, most commonly with a barbiturate, urethane, chloralose, or halothane. The animal is then placed in a stereotaxic instrument which positions the skull in an exact position and orientation with respect to submillimeter scales in three dimensions o ...
The Brainstem
... general sensations (not pain) from the face • Motor plan sent into cerebellum for coordination (this is what makes the big bulge on the ventral pons) • Tracts: – Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) – Ascending sensory axons from body AND face ...
... general sensations (not pain) from the face • Motor plan sent into cerebellum for coordination (this is what makes the big bulge on the ventral pons) • Tracts: – Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) – Ascending sensory axons from body AND face ...
Nervous System PPT notes
... 1. Explain your observations of the Patellar reflex using your knowledge of a Reflex Arc. Did each group member have the reflex? Do you think the patellar reflex is a monosynaptic or polysynaptic reflex arc? Back your answer up. 2. Describe the Reflex Arc involved in the direct Pupillary Light Refle ...
... 1. Explain your observations of the Patellar reflex using your knowledge of a Reflex Arc. Did each group member have the reflex? Do you think the patellar reflex is a monosynaptic or polysynaptic reflex arc? Back your answer up. 2. Describe the Reflex Arc involved in the direct Pupillary Light Refle ...
Summary - SCIENCE HELP @ ne3me.com
... The brain is divided into several regions. The cerebrum controls voluntary actions. The cerebellum controls actions of the muscles. The brain stem controls basic body functions. The thalamus receives impulses from the senses and sends them to the cerebrum. The hypothalamus connects the nervous and e ...
... The brain is divided into several regions. The cerebrum controls voluntary actions. The cerebellum controls actions of the muscles. The brain stem controls basic body functions. The thalamus receives impulses from the senses and sends them to the cerebrum. The hypothalamus connects the nervous and e ...
Electrophysiological recordings from behaving animals—going
... intracellular parameters can be deduced from extracellular spike waveforms. The width and amplitude of the intracellular spike are reflected by distinct properties of the extracellular waveform. Modeling studies try to better understand the source of variability of the extracellular signals. To that ...
... intracellular parameters can be deduced from extracellular spike waveforms. The width and amplitude of the intracellular spike are reflected by distinct properties of the extracellular waveform. Modeling studies try to better understand the source of variability of the extracellular signals. To that ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... The patellar (knee-jerk) reflex is a monosynaptic reflex that physicians use to assess the functioning of the spinal cord. By tapping the patellar ligament with a reflex hammer, the muscle spindles in the quadriceps muscles are stretched. Produces a noticeable kick of the leg. ...
... The patellar (knee-jerk) reflex is a monosynaptic reflex that physicians use to assess the functioning of the spinal cord. By tapping the patellar ligament with a reflex hammer, the muscle spindles in the quadriceps muscles are stretched. Produces a noticeable kick of the leg. ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.