Nervous System
... and thick filaments slide past each other – I band and H zone decreases in size ...
... and thick filaments slide past each other – I band and H zone decreases in size ...
CHAPTER 35 Human Body Systems: The levels of organization in
... Organs- A group of different types of tissue that work together to perform a single function. Eye is made up of all 4 types of tissue that work together for sight. Organ Systems- A group of organs that perform closely related functions. Like your stomach and intestines are different organs, but work ...
... Organs- A group of different types of tissue that work together to perform a single function. Eye is made up of all 4 types of tissue that work together for sight. Organ Systems- A group of organs that perform closely related functions. Like your stomach and intestines are different organs, but work ...
Slide 1
... are responsible for the reception, transmission, processing of stimuli; the triggering of certain cell activities; the release of neurotransmitters and other informational molecules. ...
... are responsible for the reception, transmission, processing of stimuli; the triggering of certain cell activities; the release of neurotransmitters and other informational molecules. ...
Motor Unit and All or None principle
... Motor unit: a group of fibres activated via the same nerve All muscle fibres of one particular motor unit are always of the same fibre type Muscles needed to perform precise movements generally consist of a large number of motor units and few muscle fibres Less precise movements are carried out by m ...
... Motor unit: a group of fibres activated via the same nerve All muscle fibres of one particular motor unit are always of the same fibre type Muscles needed to perform precise movements generally consist of a large number of motor units and few muscle fibres Less precise movements are carried out by m ...
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... Non-myelinated fibres (Ø < 1.5µm) : < 2.5 m/sec Thinly myelinated (Ø < 1 – 3 µm) : 5 – 15 m/sec Medium (Ø < 5 – 15 µm) : 30 – 80 m/sec Thick (Ø < 12 – 20 µm): 70 – 120 m/sec ...
... Non-myelinated fibres (Ø < 1.5µm) : < 2.5 m/sec Thinly myelinated (Ø < 1 – 3 µm) : 5 – 15 m/sec Medium (Ø < 5 – 15 µm) : 30 – 80 m/sec Thick (Ø < 12 – 20 µm): 70 – 120 m/sec ...
Box 9.1 The Basics of Sound (Part 1)
... • About one third of first-degree relatives In amusic families share the impairment compared to only a few percent for the control families • Genes do not directly control cognitive functions such as music perception • Genes responsible for congenital amusia influence brain development. ...
... • About one third of first-degree relatives In amusic families share the impairment compared to only a few percent for the control families • Genes do not directly control cognitive functions such as music perception • Genes responsible for congenital amusia influence brain development. ...
Slide ()
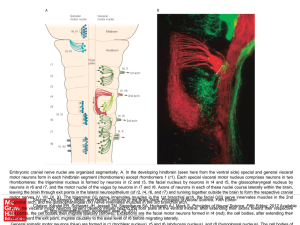
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Somatic senses
... and has connection with it Integrates sensory information like temperature and pressure coming from the primary somatosensory cortex. Forms understanding of the stimulus like size, texture, and relationship of parts Ex.: putting the hand in the pocket and feeling something. The center integrat ...
... and has connection with it Integrates sensory information like temperature and pressure coming from the primary somatosensory cortex. Forms understanding of the stimulus like size, texture, and relationship of parts Ex.: putting the hand in the pocket and feeling something. The center integrat ...
Deep Fibular Nerve Entrapment
... Poorly conditioned people with a history of calcaneal tendinitis. Audible snap during a forceful push off (plantarflexion with the knee extended) followed immediately by sudden calf pain and sudden dorsiflexion of the plantarflexed foot. In a completely ruptured tendon, a gap palpable, 1-5 cm proxim ...
... Poorly conditioned people with a history of calcaneal tendinitis. Audible snap during a forceful push off (plantarflexion with the knee extended) followed immediately by sudden calf pain and sudden dorsiflexion of the plantarflexed foot. In a completely ruptured tendon, a gap palpable, 1-5 cm proxim ...
Parts and Functions of a Nervous System
... Nerve cells or ______________ are highly specialized body cells that convey impulses from one part of the body to the CNS or vice versa. Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consi ...
... Nerve cells or ______________ are highly specialized body cells that convey impulses from one part of the body to the CNS or vice versa. Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consi ...
Clinicals - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... a. Altered sensations from lesions in spinal cord (pain/temp. or proprioceptive) b. Parasthesia c. Increase temperature sensitivity & fall in safety factor for conduction in partially demyelinated axons d. Impulse conduction in normal axons enhanced with rise in temperature, but duration and amplitu ...
... a. Altered sensations from lesions in spinal cord (pain/temp. or proprioceptive) b. Parasthesia c. Increase temperature sensitivity & fall in safety factor for conduction in partially demyelinated axons d. Impulse conduction in normal axons enhanced with rise in temperature, but duration and amplitu ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Called emotional brain Blends higher mental functions and primitive emotions into a whole • Area that makes eating and sexual behavior seem pleasant ...
... Called emotional brain Blends higher mental functions and primitive emotions into a whole • Area that makes eating and sexual behavior seem pleasant ...
Cranial Nerves
... • closed neuronal circuit • circuit is stimulated over and over • when impulse flow ceases, memory does also • unless it enters longterm memory via memory consolidation ...
... • closed neuronal circuit • circuit is stimulated over and over • when impulse flow ceases, memory does also • unless it enters longterm memory via memory consolidation ...
Neuromonitoring for Spine Surgery
... pathways from peripheral nerves to the sensory cortex. Disruption along any part of this pathway may disrupt normal SSEP responses. Anesthetic Implications. SSEPs are progressively suppressed by inhaled anesthetic (vapor or N2O) > 0.5 MAC. All intravenous agents (propofol, barbiturates, midazolam, o ...
... pathways from peripheral nerves to the sensory cortex. Disruption along any part of this pathway may disrupt normal SSEP responses. Anesthetic Implications. SSEPs are progressively suppressed by inhaled anesthetic (vapor or N2O) > 0.5 MAC. All intravenous agents (propofol, barbiturates, midazolam, o ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... light touch and pressure on the skin; and hair receptors, which sense hair movements. 6. Encapsulated nerve endings are dendrites enclosed in glial or connective tissue cells. These include tactile corpuscles for light touch and pressure on the skin; end bulbs for stimulation of the oral mucosa and ...
... light touch and pressure on the skin; and hair receptors, which sense hair movements. 6. Encapsulated nerve endings are dendrites enclosed in glial or connective tissue cells. These include tactile corpuscles for light touch and pressure on the skin; end bulbs for stimulation of the oral mucosa and ...
The Nervous System
... concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse passes through the cell body. [wave of depolarization] After the electrical impulse leaves, the gat ...
... concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse passes through the cell body. [wave of depolarization] After the electrical impulse leaves, the gat ...
18 The Somatosensory System II: Touch, Thermal Sense, and Pain
... • If you step on a sharp object with your left foot, your spinothalamic tract enables you to realize “something sharp is puncturing the sole of my ...
... • If you step on a sharp object with your left foot, your spinothalamic tract enables you to realize “something sharp is puncturing the sole of my ...
high. 1, treated virgin
... ipsilateral uropod blades produced impulses in the fiber and simultaneously excited flexor motoneurons. Thus sensory inputs to the command fiber can be identified, and they have an action identical with that produced by electrical stimulation of the central neuron itself. A command fiber producing e ...
... ipsilateral uropod blades produced impulses in the fiber and simultaneously excited flexor motoneurons. Thus sensory inputs to the command fiber can be identified, and they have an action identical with that produced by electrical stimulation of the central neuron itself. A command fiber producing e ...
Integumentary System Outline
... Makes ridges known as fingerprints Blood vessels, nerve endings, sebaceous and sweat glands, hair follicles ...
... Makes ridges known as fingerprints Blood vessels, nerve endings, sebaceous and sweat glands, hair follicles ...
Skin & Fascia - MBBS Students Club
... surface that interdigitates with the epidermis, strengthening the connection between the two layers of skin. ...
... surface that interdigitates with the epidermis, strengthening the connection between the two layers of skin. ...
Chapter 10 Somatic and Special Senses
... __________ ____________ corpuscles are flattened connective tissue sheaths surrounding two or more nerve fibers and are abundant in hairless areas that are very sensitive to touch, like the lips. ____________ __________________ are large structures of connective tissue and cells that resemble the la ...
... __________ ____________ corpuscles are flattened connective tissue sheaths surrounding two or more nerve fibers and are abundant in hairless areas that are very sensitive to touch, like the lips. ____________ __________________ are large structures of connective tissue and cells that resemble the la ...
Nervous System Notes
... the more a synapse is stimulated, the stronger the connection between the neurons becomes ...
... the more a synapse is stimulated, the stronger the connection between the neurons becomes ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.