Physiology of Behavior
... are caused by mechanical deformation of the skin. Vibration occurs when we move our fingers across a rough surface. Thus, we use vibration sensitivity to judge an object’s roughness. Sensations of warmth and coolness are produced by objects that raise or lower skin temperature. Sensations of pain ca ...
... are caused by mechanical deformation of the skin. Vibration occurs when we move our fingers across a rough surface. Thus, we use vibration sensitivity to judge an object’s roughness. Sensations of warmth and coolness are produced by objects that raise or lower skin temperature. Sensations of pain ca ...
13.2 part 2
... A special recorder measures the strength of the muscle contraction. The following table shows data from a sample experiment. Strength of stimuli ...
... A special recorder measures the strength of the muscle contraction. The following table shows data from a sample experiment. Strength of stimuli ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CH 48 AND 49
... D. How the nerve impulse moves from one cell to another • The space between two nerve cells is called a synapse • Two nerves communicate with each other by synaptic signaling • How: – When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters into the syna ...
... D. How the nerve impulse moves from one cell to another • The space between two nerve cells is called a synapse • Two nerves communicate with each other by synaptic signaling • How: – When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters into the syna ...
31.1 The Neuron Functions of the Nervous System and external
... Many drugs cause an increase in the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. The brain reacts to high dopamine levels by reducing the number of receptors. With fewer dopamine receptors available, larger amounts of drugs are required to produce a high. This can result in an addiction. 31.3 The Perip ...
... Many drugs cause an increase in the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. The brain reacts to high dopamine levels by reducing the number of receptors. With fewer dopamine receptors available, larger amounts of drugs are required to produce a high. This can result in an addiction. 31.3 The Perip ...
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
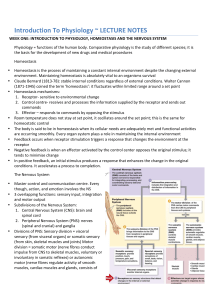
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
Principles of Electrical Currents
... The body becomes the conductor Monophasic application requires one negative electrode and one positive electrode The strongest stimulation is where the current exists the body Electrodes placed close together will give a superficial stimulation and be of high density ...
... The body becomes the conductor Monophasic application requires one negative electrode and one positive electrode The strongest stimulation is where the current exists the body Electrodes placed close together will give a superficial stimulation and be of high density ...
The Brainstem (or brain stem) 4/5/2010
... • Sensory from face, cornea, mouth, nasal passages, teeth, tongue, meninges & their vessels, sinuses, eardrum, TMJ • Motor to muscles of mastication (bite, chew) • *Recent evidence that V axons from blood vessels may cause migraine pain ...
... • Sensory from face, cornea, mouth, nasal passages, teeth, tongue, meninges & their vessels, sinuses, eardrum, TMJ • Motor to muscles of mastication (bite, chew) • *Recent evidence that V axons from blood vessels may cause migraine pain ...
Nerve
... b) A major PNS feature is connective tissue, classified in the following way. (i) ENDONEURIUM: Vascular connective tissue around an individual nerve fiber (ii) PERINEURIUM: Connective tissue that arranges groups of axon fibers into fascicles (iii) EPINEURIUM: Connective tissue that binds nerve fasci ...
... b) A major PNS feature is connective tissue, classified in the following way. (i) ENDONEURIUM: Vascular connective tissue around an individual nerve fiber (ii) PERINEURIUM: Connective tissue that arranges groups of axon fibers into fascicles (iii) EPINEURIUM: Connective tissue that binds nerve fasci ...
Nerves And Neuropathy
... Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) • Common in the general population over age 50 and common in TTR amyloidosis • Also seen with diabetes and low thyroid function • May have this many years before diagnosis is made. • The median nerve runs down from the neck into the ...
... Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) • Common in the general population over age 50 and common in TTR amyloidosis • Also seen with diabetes and low thyroid function • May have this many years before diagnosis is made. • The median nerve runs down from the neck into the ...
Anatomy back forum 2010
... runs from posterior to anterior at about the level of the nipple. What is the diagnosis? Explain the distribution of the rash. a. It follows a Dermatome problem b/c the virus infects dorsal root ganglia and follows their axons to the skin. b. It is herpes zoster 17. Three patients present for follow ...
... runs from posterior to anterior at about the level of the nipple. What is the diagnosis? Explain the distribution of the rash. a. It follows a Dermatome problem b/c the virus infects dorsal root ganglia and follows their axons to the skin. b. It is herpes zoster 17. Three patients present for follow ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... Significance: • The brain and other motor centers e.g. basal ganglia, cerebellum use this information in the control of posture and movements N.B. • Maintaining the body equilibrium or balance needs discharge from 3 kinds of receptors; 1. Proprioceptors of foot 2. Visual receptors 3. Vestibular re ...
... Significance: • The brain and other motor centers e.g. basal ganglia, cerebellum use this information in the control of posture and movements N.B. • Maintaining the body equilibrium or balance needs discharge from 3 kinds of receptors; 1. Proprioceptors of foot 2. Visual receptors 3. Vestibular re ...
Neural Development - Peoria Public Schools
... • Nerve cells migrate to their final position with amoeba like movement a. Once in their final position, mature neurons do not normally move. ...
... • Nerve cells migrate to their final position with amoeba like movement a. Once in their final position, mature neurons do not normally move. ...
Nervous System
... Strong stimuli can generate action potentials more often than weaker stimuli The CNS determines stimulus intensity by the frequency of impulses ...
... Strong stimuli can generate action potentials more often than weaker stimuli The CNS determines stimulus intensity by the frequency of impulses ...
BN16 Neural plasticity
... Folia & lobules analogous gyri & lobes Vermis - along midline output ventromedial pathway Hemispheres output lateral pathway Deep cerebellar nuclei fastigial, interposed, & dentate Major output structures ~ ...
... Folia & lobules analogous gyri & lobes Vermis - along midline output ventromedial pathway Hemispheres output lateral pathway Deep cerebellar nuclei fastigial, interposed, & dentate Major output structures ~ ...
Second exam study questions
... 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? Ho ...
... 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? Ho ...
Limbic System - WELCOME to the future website of
... Connections of the amygdala Major efferent fibers are stria terminalis Functional considerations Emotional and behavioral changes are associated with amygdala (MRI shows different activity level when different emotions are elicited by pictures); memories change are associated with hippocampal format ...
... Connections of the amygdala Major efferent fibers are stria terminalis Functional considerations Emotional and behavioral changes are associated with amygdala (MRI shows different activity level when different emotions are elicited by pictures); memories change are associated with hippocampal format ...
Nervous System Project
... branch out from the brain and go to many places in the head such as the ears, eyes and face. Messages can also travel through the spinal nerves which branch out from the spinal cord. There are two major parts to the peripheral nervous system. The somatic (say so-mat-ik) system: ...
... branch out from the brain and go to many places in the head such as the ears, eyes and face. Messages can also travel through the spinal nerves which branch out from the spinal cord. There are two major parts to the peripheral nervous system. The somatic (say so-mat-ik) system: ...
Sensation
... We look with our eyes, but we see with the brain. Visual images are imported through the optic nerve to ...
... We look with our eyes, but we see with the brain. Visual images are imported through the optic nerve to ...
Chapter 9 Power Point
... of force a muscle or muscle group can exert against an opposing force. Absolute muscular strength -maximum force you are able to exert regardless of size, age, or weight Relative muscular strength - maximum force you are able to exert in relation to your body weight. Muscular Endurance – the abili ...
... of force a muscle or muscle group can exert against an opposing force. Absolute muscular strength -maximum force you are able to exert regardless of size, age, or weight Relative muscular strength - maximum force you are able to exert in relation to your body weight. Muscular Endurance – the abili ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System and Brain Complete
... the same nerves - afferent (sensory) neurons carry action potentials from receptors in periphery of the body to CNS - efferent (motor) neurons carry action potentials from CNS to effectors in the periphery ...
... the same nerves - afferent (sensory) neurons carry action potentials from receptors in periphery of the body to CNS - efferent (motor) neurons carry action potentials from CNS to effectors in the periphery ...
Powerpoint slides are here
... death of dopaminergic substantia nigra neurons hard to initiate and maintain movements ...
... death of dopaminergic substantia nigra neurons hard to initiate and maintain movements ...
Neuron and Nervous System Review Guide
... Biological Psychology: concerned with the links between biology and behavior (also called neuropsychology) Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system Action Potential: a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause ...
... Biological Psychology: concerned with the links between biology and behavior (also called neuropsychology) Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system Action Potential: a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause ...
Neuro_quiz3
... 87. What is the difference between touch sensation & pressure sensation? 88. Rapidly repetitive sensory signals result in ________ sense. 89. Free nerve endings can detect primitive AKA ________ touch. Their speed of conduction is ________ metres/second. They are small/large and of what type(s)? ___ ...
... 87. What is the difference between touch sensation & pressure sensation? 88. Rapidly repetitive sensory signals result in ________ sense. 89. Free nerve endings can detect primitive AKA ________ touch. Their speed of conduction is ________ metres/second. They are small/large and of what type(s)? ___ ...
Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Lectures 4,5,6,7 Which of the
... 39. The ventral area of the medulla has pyramids with _______ fibers that descend from developing cerebral cortex and will eventually form a tract. ...
... 39. The ventral area of the medulla has pyramids with _______ fibers that descend from developing cerebral cortex and will eventually form a tract. ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.