Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... o General sensory receptors (touch, light, external heat, pain) o Visceral receptors (monitoring internal organ function) Information moves from PNS to CNS Information is processed by the CNS and the appropriate response is determined Motor response is sent from CNS via PNS to appropriate musc ...
... o General sensory receptors (touch, light, external heat, pain) o Visceral receptors (monitoring internal organ function) Information moves from PNS to CNS Information is processed by the CNS and the appropriate response is determined Motor response is sent from CNS via PNS to appropriate musc ...
Chapter 27
... monosynaptic: the reflex arc has only 1 synapse between the sensory & motor neurons in the spinal cord polysynaptic: reflexes involving two or more synapses ...
... monosynaptic: the reflex arc has only 1 synapse between the sensory & motor neurons in the spinal cord polysynaptic: reflexes involving two or more synapses ...
Nervous System
... Stimulus for a new AP at this time is much higher due to the neuron trying to rebalance itself. ...
... Stimulus for a new AP at this time is much higher due to the neuron trying to rebalance itself. ...
File
... •Coordinates between the brain and the other body structures •Reflexes are processed in spinal cord ...
... •Coordinates between the brain and the other body structures •Reflexes are processed in spinal cord ...
Nerves and Special Senses
... The Eye and Vision • 70 percent of all sensory receptors are in the eyes • Each eye has over a million nerve fibers • Protection for the eye – Most of the eye is enclosed in a bony orbit – A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye ...
... The Eye and Vision • 70 percent of all sensory receptors are in the eyes • Each eye has over a million nerve fibers • Protection for the eye – Most of the eye is enclosed in a bony orbit – A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye ...
Sensory Processes - Department of Psychology | University of Toronto
... • Change in sensitivity that occurs when a sensory system is either stimulated or not stimulated for a length of time. • Absence of stimulation – Sensory system becomes temporarily more sensitive – Responds to weaker stimuli ...
... • Change in sensitivity that occurs when a sensory system is either stimulated or not stimulated for a length of time. • Absence of stimulation – Sensory system becomes temporarily more sensitive – Responds to weaker stimuli ...
lecture 14 File
... fibers; where axons are sheathed by Schwann cells. • Axons of small diameter are unmyelinated nerve fibers. ...
... fibers; where axons are sheathed by Schwann cells. • Axons of small diameter are unmyelinated nerve fibers. ...
Nervous System - El Camino College
... General Motor area lies in front of central sulcus and control voluntary movements of skeletal muscles. The area just behind central sulcus is the general Sensory Area to receive sensory input. Primary vision area lies in visual cortex in occipital lobe. Primary Gustatory Area lies on lateral side o ...
... General Motor area lies in front of central sulcus and control voluntary movements of skeletal muscles. The area just behind central sulcus is the general Sensory Area to receive sensory input. Primary vision area lies in visual cortex in occipital lobe. Primary Gustatory Area lies on lateral side o ...
Analgetics - TMA Department Sites
... Similar gating mechanisms exist in the nerve fibers descending from the thalamus and the cortex. These areas of the brain regulate thoughts and emotions. Thus, with a pain stimulus, one’s thoughts and emotions can actually modify the pain experience. ...
... Similar gating mechanisms exist in the nerve fibers descending from the thalamus and the cortex. These areas of the brain regulate thoughts and emotions. Thus, with a pain stimulus, one’s thoughts and emotions can actually modify the pain experience. ...
Ch 7 The Nervous System Notes
... 1. Sensory (Afferent) Division- nerve fibers that carry impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors located throughout body sensory fibers types: 1. somatic sensory fibers- delivering impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, & joints 2. visceral sensory fibers- transmitting impulses from the viscera ...
... 1. Sensory (Afferent) Division- nerve fibers that carry impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors located throughout body sensory fibers types: 1. somatic sensory fibers- delivering impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, & joints 2. visceral sensory fibers- transmitting impulses from the viscera ...
Chapter 28- Nervous System
... from sending info, action potentials can be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitters) • The action potential triggers vesicles to fuse with plasma membrane • Neurotransmitters bind to receptors and open ion channels to ions that start new action potential or stops one • Neurotransmitter is t ...
... from sending info, action potentials can be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitters) • The action potential triggers vesicles to fuse with plasma membrane • Neurotransmitters bind to receptors and open ion channels to ions that start new action potential or stops one • Neurotransmitter is t ...
Sensory receptors and somatic sensation
... Inadequate Stimuli: e.g. the adequate stimulus of the retinal receptors is light but can also stimulated by mechanical pressure. ...
... Inadequate Stimuli: e.g. the adequate stimulus of the retinal receptors is light but can also stimulated by mechanical pressure. ...
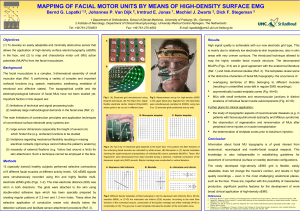
mapping of facial motor units by means of high
... overlapping territories of MUs belonging to different muscles (resulting in unidentified cross-talk in regular EMG recordings). ...
... overlapping territories of MUs belonging to different muscles (resulting in unidentified cross-talk in regular EMG recordings). ...
Chapter Outline
... membrane where they bind with specific receptors. e. The type of neurotransmitter and/or receptor determines if the response is excitation or inhibition. f. Excitatory neurotransmitters use gated ion channels and are fast acting. g. Other neurotransmitters affect the metabolism of the postsynaptic c ...
... membrane where they bind with specific receptors. e. The type of neurotransmitter and/or receptor determines if the response is excitation or inhibition. f. Excitatory neurotransmitters use gated ion channels and are fast acting. g. Other neurotransmitters affect the metabolism of the postsynaptic c ...
Electrophysiological Methods for Mapping Brain Motor and Sensory
... • Sharpened rods of tungsten, platinum/iridium • Insulated with glass, epoxy • Uninsulated tip of 5-12µA • Low impedance: 0.7 – 1.5 MΩ ...
... • Sharpened rods of tungsten, platinum/iridium • Insulated with glass, epoxy • Uninsulated tip of 5-12µA • Low impedance: 0.7 – 1.5 MΩ ...
Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses
... Cutaneous senses receive various signals from the skin that form the sense of touch Pressure Vibration Heating/cooling Stimuli ...
... Cutaneous senses receive various signals from the skin that form the sense of touch Pressure Vibration Heating/cooling Stimuli ...
Somatosensory System
... or a peripheral nerve. Motor unit damage cuts off the muscle fibers in the motor unit from both voluntary and reflex innervation. The affected muscles are extremely weak (plegic), and there is a marked diminution of muscle tone (hypotonia), as well as a loss of reflexes (areflexia) because the monos ...
... or a peripheral nerve. Motor unit damage cuts off the muscle fibers in the motor unit from both voluntary and reflex innervation. The affected muscles are extremely weak (plegic), and there is a marked diminution of muscle tone (hypotonia), as well as a loss of reflexes (areflexia) because the monos ...
Lab 12
... Study spinal cord models and be able to identify (p493,495): 1. gray horns _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ a. anterior, lateral and posterior ...
... Study spinal cord models and be able to identify (p493,495): 1. gray horns _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ a. anterior, lateral and posterior ...
Muscle and NerveKD13
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
File
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Somatosensory system. Cutaneous touch receptors: Free nerve endings. Meissner’s corpuscles. Merkel complexes or discs. Terminal organ of hair. Ruffini endings. Pacini corpuscles. Krause’s end-bulbs. Subcutaneous Golgi-Mazzoni corpuscles. Propioceptive receptors: The nerve endings of joints. The nerv ...
... Somatosensory system. Cutaneous touch receptors: Free nerve endings. Meissner’s corpuscles. Merkel complexes or discs. Terminal organ of hair. Ruffini endings. Pacini corpuscles. Krause’s end-bulbs. Subcutaneous Golgi-Mazzoni corpuscles. Propioceptive receptors: The nerve endings of joints. The nerv ...
UNIT 2: Internal geological agents
... Picks up information and produces answers Controls important functions as growth Its answer is rapid and does not last long Its answer is slow and lasts long It consists of neurons which transmit It consists og endocrine glands which release information through electrical and chemical hormons signal ...
... Picks up information and produces answers Controls important functions as growth Its answer is rapid and does not last long Its answer is slow and lasts long It consists of neurons which transmit It consists og endocrine glands which release information through electrical and chemical hormons signal ...
Neurophysiology
... • Language Processing in the left hemisphere. (Remember the right ear has the strongest connections to the left hemisphere) • Most people show a right-ear advantage in processing linguistic stimuli ...
... • Language Processing in the left hemisphere. (Remember the right ear has the strongest connections to the left hemisphere) • Most people show a right-ear advantage in processing linguistic stimuli ...
Nervous Sys Learning targets
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.