Neural-Ville
... neurotransmitter are sent into the tiny space between nerve cells, called the synaptic gap. ...
... neurotransmitter are sent into the tiny space between nerve cells, called the synaptic gap. ...
Medial Longitudinal Fissure
... Relay olfactory impulses from the olfactory bulbs to the entorhinal cortex ...
... Relay olfactory impulses from the olfactory bulbs to the entorhinal cortex ...
A17 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... Sensory receptors - transducers that convert various forms of energy in environment into action potentials in neurons. sensory receptors may be: a) neurons (distal tip of peripheral axon of sensory neuron) – e.g. in skin receptors. b) specialized cells (that release neurotransmitter and generate a ...
... Sensory receptors - transducers that convert various forms of energy in environment into action potentials in neurons. sensory receptors may be: a) neurons (distal tip of peripheral axon of sensory neuron) – e.g. in skin receptors. b) specialized cells (that release neurotransmitter and generate a ...
Lesson 1 | The Nervous System
... 4. There are three kinds of these cells: (sensory/peripheral), (motor/chemical), and (intra–/inter–). ...
... 4. There are three kinds of these cells: (sensory/peripheral), (motor/chemical), and (intra–/inter–). ...
$doc.title
... In the BioSystems Interface Laboratory we develop novel sensing and stimulating systems to overcome sensory loss. To enhance sound perception with cochlear implants, we have developed advanced thin-‐film intracoch ...
... In the BioSystems Interface Laboratory we develop novel sensing and stimulating systems to overcome sensory loss. To enhance sound perception with cochlear implants, we have developed advanced thin-‐film intracoch ...
Vision
... Adequate stimulus = the stimulus to which the receptor is most sensitive Convert forms of energy into electrical signals (action potentials) ...
... Adequate stimulus = the stimulus to which the receptor is most sensitive Convert forms of energy into electrical signals (action potentials) ...
神经系统传导通路
... •nucleus of oculomotor nerve •nucleus of trochlear nerve •nucleus of abducent nerve •motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve •the superior part of nucleus of ...
... •nucleus of oculomotor nerve •nucleus of trochlear nerve •nucleus of abducent nerve •motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve •the superior part of nucleus of ...
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... • Merocrine glands: release fluid by exocytosis • Eccrine – Most common – Secretion is mostly water with solutes – Cools body down ...
... • Merocrine glands: release fluid by exocytosis • Eccrine – Most common – Secretion is mostly water with solutes – Cools body down ...
Autonomic nervous system
... Can modify activity of preganglionic autonomic neurons. Medulla: – Most directly controls activity of autonomic system. ...
... Can modify activity of preganglionic autonomic neurons. Medulla: – Most directly controls activity of autonomic system. ...
Plants and Pollinators
... information about past sensory input • Stored in stages – Temporary storage in cerebral cortex ...
... information about past sensory input • Stored in stages – Temporary storage in cerebral cortex ...
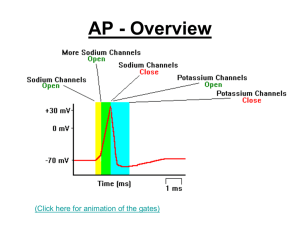
AP – All or nothing
... • The axons of many neurones are encased in a fatty myelin sheath (Schwann cells). • Where the sheath of one Schwann cell meets the next, the axon is unprotected. • The voltage-gated sodium channels of myelinated neurons are confined to these spots (called nodes of Ranvier). ...
... • The axons of many neurones are encased in a fatty myelin sheath (Schwann cells). • Where the sheath of one Schwann cell meets the next, the axon is unprotected. • The voltage-gated sodium channels of myelinated neurons are confined to these spots (called nodes of Ranvier). ...
Power Point
... Fig. 3. SAPNS allows axons to regenerate through the lesion site in brain. The dark-field composite photos are parasagittal sections from animals 30 days after lesion and treatment. (a) Section from brain of 30-day-old hamster with 10 µl of saline injected in the lesion at P2. The cavity shows the ...
... Fig. 3. SAPNS allows axons to regenerate through the lesion site in brain. The dark-field composite photos are parasagittal sections from animals 30 days after lesion and treatment. (a) Section from brain of 30-day-old hamster with 10 µl of saline injected in the lesion at P2. The cavity shows the ...
The nervous system - Mr T Pities the Fool
... • Cells called receptors detect stimuli (changes) in our environment. • Our receptors can be found: • Eyes – sensitive to light • Ears – sensitive to sound • Nose – sensitive to smell • Skin – sensitive to touch, pressure, and temperature • Mouth – sensitive to chemicals in food. ...
... • Cells called receptors detect stimuli (changes) in our environment. • Our receptors can be found: • Eyes – sensitive to light • Ears – sensitive to sound • Nose – sensitive to smell • Skin – sensitive to touch, pressure, and temperature • Mouth – sensitive to chemicals in food. ...
The Somatic Senses - Appoquinimink High School
... feeling to seem to come from the stimulated receptors. This is at the same time the sensation forms. Basically the brain projects the sensation back to its apparent source. This allows to pinpoint the region of stimulation. ...
... feeling to seem to come from the stimulated receptors. This is at the same time the sensation forms. Basically the brain projects the sensation back to its apparent source. This allows to pinpoint the region of stimulation. ...
Brain
... Substantia nigra inhibits activity of basal nuclei by releasing DOPAMINE Basal nuclei become more active with less Dopamine – increased muscle tone – Parkinson’s Disease have difficulty starting voluntary movements B/C opposing muscle groups DO NOT RELAX ( not enough Dopamine is excreted by substant ...
... Substantia nigra inhibits activity of basal nuclei by releasing DOPAMINE Basal nuclei become more active with less Dopamine – increased muscle tone – Parkinson’s Disease have difficulty starting voluntary movements B/C opposing muscle groups DO NOT RELAX ( not enough Dopamine is excreted by substant ...
Nerves
... Sensory (afferent) signals picked up by sensor receptors, carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS, innervate muscles and glands Divided according to region they serve ...
... Sensory (afferent) signals picked up by sensor receptors, carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS, innervate muscles and glands Divided according to region they serve ...
Vertebrate Nervous System
... Important cell for normal functioning of the nervous system Without astrocytes you would have significant damage to your functions Microglia – phagocytosis Resting microglia and fully activated microglia Signals from damaged neurons are cascading into the interstitial fluid that initiates series of ...
... Important cell for normal functioning of the nervous system Without astrocytes you would have significant damage to your functions Microglia – phagocytosis Resting microglia and fully activated microglia Signals from damaged neurons are cascading into the interstitial fluid that initiates series of ...
07. Pons Internal Features 0102010-10-01 05:141.9
... Medial lemniscus: twists as it leaves the medulla, and lies horizontally in the ventral pontine tegmentum. The fibers from the cuneate nucleus are medial to those from the gracile nucleus. It carries proprioceptive & fine touch sensation from opposite side of body to the thalamus. Trigeminal lemnis ...
... Medial lemniscus: twists as it leaves the medulla, and lies horizontally in the ventral pontine tegmentum. The fibers from the cuneate nucleus are medial to those from the gracile nucleus. It carries proprioceptive & fine touch sensation from opposite side of body to the thalamus. Trigeminal lemnis ...
Nervous System ppt
... of candy provided, make a neuron! Use your journal picture (and this one) to help you! ...
... of candy provided, make a neuron! Use your journal picture (and this one) to help you! ...
Exercise 17
... Nissl bodies: elaborate type of rough ER; involved in the metabolic activity of the the cell Dendrites: are receptive regions that bear receptors for neurotransmitters released by other neurons Axons: are nerve impulse generators and transmitters Collaterals: branches of axons from neurons Axon Hill ...
... Nissl bodies: elaborate type of rough ER; involved in the metabolic activity of the the cell Dendrites: are receptive regions that bear receptors for neurotransmitters released by other neurons Axons: are nerve impulse generators and transmitters Collaterals: branches of axons from neurons Axon Hill ...
I. Neurons are the anatomical elements of neural systems
... The Trigeminal Nerve: Signals for Touch and Pain A. Two of the three trigeminal divisions carry signals from the eye and surrounding tissues. a. Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V) differs from other cranial nerves because it collects the cell bodies of its neurons in a large ganglion, the gasserian ...
... The Trigeminal Nerve: Signals for Touch and Pain A. Two of the three trigeminal divisions carry signals from the eye and surrounding tissues. a. Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V) differs from other cranial nerves because it collects the cell bodies of its neurons in a large ganglion, the gasserian ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.