Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
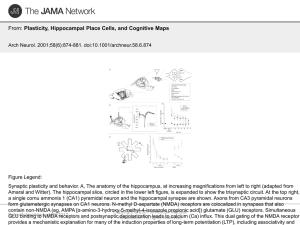
... Synaptic plasticity and behavior. A, The anatomy of the hippocampus, at increasing magnifications from left to right (adapted from Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1 ...
... Synaptic plasticity and behavior. A, The anatomy of the hippocampus, at increasing magnifications from left to right (adapted from Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1 ...
Neurotransmitters
... Glutamate is used at the great majority of fast excitatory synapses in the brain and spinal cord. It is also used at most synapses that are "modifiable", i.e. capable of increasing or decreasing in strength. Modifiable synapses are thought to be the main memory-storage elements in the brain. GABA is ...
... Glutamate is used at the great majority of fast excitatory synapses in the brain and spinal cord. It is also used at most synapses that are "modifiable", i.e. capable of increasing or decreasing in strength. Modifiable synapses are thought to be the main memory-storage elements in the brain. GABA is ...
What” and ”where” – dynamic parallel processing of sound
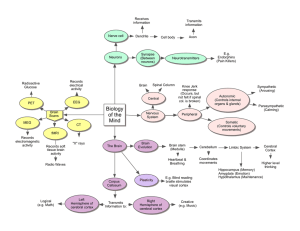
... What is plasticity? • Functional organization of the brain reflects adaptation to environment • As long as the environment (and the neural systems) stay approximately the same, functional organization remains the same • Changes in the environment and in the neural systems (such as after a lesion) t ...
... What is plasticity? • Functional organization of the brain reflects adaptation to environment • As long as the environment (and the neural systems) stay approximately the same, functional organization remains the same • Changes in the environment and in the neural systems (such as after a lesion) t ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... The chemical component of neural communication is accomplished through neurotransmitters released at the synapse ...
... The chemical component of neural communication is accomplished through neurotransmitters released at the synapse ...
Here we can focus directly on the input neurons, the Schaffer
... pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pull synaptic target rather than a p synaptic target. The Schaffer collaterals come in, they re ...
... pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pull synaptic target rather than a p synaptic target. The Schaffer collaterals come in, they re ...
LTP
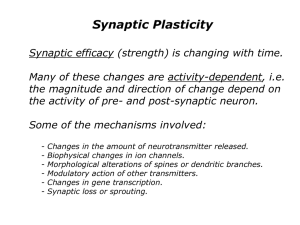
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
synaptic transmission worksheet
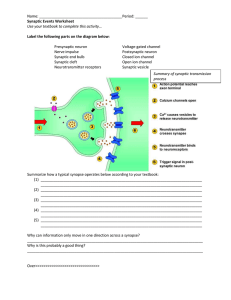
... Name: ________________________________________ Period: ______ Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
... Name: ________________________________________ Period: ______ Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
Ca 2+
... describe the observation that synaptic strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a f ...
... describe the observation that synaptic strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a f ...
Brainsignals, Synaptic Transmission and Short
... describe the observation that synaptic strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a f ...
... describe the observation that synaptic strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a f ...
Transcription and translation of new gene products is critical for
... Transcription and translation of new gene products is critical for establishing and maintaining long lasting memory. To initiate activity‐dependent transcription, neuronal inputs that arrive at the synapse must be relayed to the nucleus to trigger changes in gene expression. Many of these synaptic c ...
... Transcription and translation of new gene products is critical for establishing and maintaining long lasting memory. To initiate activity‐dependent transcription, neuronal inputs that arrive at the synapse must be relayed to the nucleus to trigger changes in gene expression. Many of these synaptic c ...
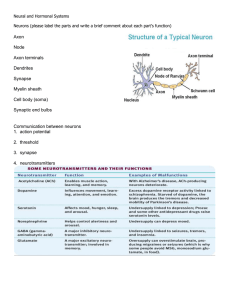
Neural and Hormonal Systems Neurons (please label the parts and
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
Barry Jacobs presentation
... • There are times during development when conditions must be right or it may be difficult or impossible to correct them later. • A young child who is abused or neglected may have great difficulty in successfully navigating adult social life. • If not corrected early on in life an infant with catarac ...
... • There are times during development when conditions must be right or it may be difficult or impossible to correct them later. • A young child who is abused or neglected may have great difficulty in successfully navigating adult social life. • If not corrected early on in life an infant with catarac ...
File
... •Credited with the idea that learning involves the establishment and strengthening of neural connections at the synapse •Learning results in the creation of ‘cell assemblies’ (interconnected groups of neurons that form networks or pathways) • When neurotransmitter is repeatedly sent across the synap ...
... •Credited with the idea that learning involves the establishment and strengthening of neural connections at the synapse •Learning results in the creation of ‘cell assemblies’ (interconnected groups of neurons that form networks or pathways) • When neurotransmitter is repeatedly sent across the synap ...
Focusing on connections and signaling mechanisms to
... as well as qualitatively which changes are due to rewiring and which due to changes in the efficacy of existing synapses. In the study of learning, it seems possible that different experiences that give rise to different patterns of activity may analagously engage distinct mechanisms to regulate the ...
... as well as qualitatively which changes are due to rewiring and which due to changes in the efficacy of existing synapses. In the study of learning, it seems possible that different experiences that give rise to different patterns of activity may analagously engage distinct mechanisms to regulate the ...
Prémio Artigo Destaque SPN_2011 Cellular and Molecular
... Neurons are capable of integrating information spatially and temporally. They can process electrical signals at specific locations called synapses, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. The information can then be built or not into an output signal, the action potential, carried by the axon. The dy ...
... Neurons are capable of integrating information spatially and temporally. They can process electrical signals at specific locations called synapses, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. The information can then be built or not into an output signal, the action potential, carried by the axon. The dy ...
Behavioural and electrophysiological studies of learning, memory and long-term potentiation.
... Our laboratory has adopted a novel approach to address this long‐standing problem in cognitive neurobiology. We are studying olfactory conditioning in rats by training them to associate the pairing of an odour and direct electrical stimulation of the perforant path to the dentate gyr ...
... Our laboratory has adopted a novel approach to address this long‐standing problem in cognitive neurobiology. We are studying olfactory conditioning in rats by training them to associate the pairing of an odour and direct electrical stimulation of the perforant path to the dentate gyr ...
Harnessing Plasticity to Reset Dysfunctional Neurons
... the brain’s repertoire and improved function. Plastic changes, however, can also harbor potential danger. The new pattern of neural activation may in itself lead to reorganization and new behaviors that are maladaptive and that not only lack an obvious protective or reparative benefit but, in fact, ...
... the brain’s repertoire and improved function. Plastic changes, however, can also harbor potential danger. The new pattern of neural activation may in itself lead to reorganization and new behaviors that are maladaptive and that not only lack an obvious protective or reparative benefit but, in fact, ...
Adult Cortical Plasticity
... Long-term potentiation (LTP) and Long-term depression (LTD) -- Persistent increase or decrease in synaptic response due to repetitive activity, found in hippocampus and cortex -- Brief high-frequency stimulation – LTP Prolonged low-frequency stimulation – LTD Mechanism: 1. Induction of either LTP or ...
... Long-term potentiation (LTP) and Long-term depression (LTD) -- Persistent increase or decrease in synaptic response due to repetitive activity, found in hippocampus and cortex -- Brief high-frequency stimulation – LTP Prolonged low-frequency stimulation – LTD Mechanism: 1. Induction of either LTP or ...
drugs and neuronal plasticity summary
... of learning processes drug-associated cues can trigger craving and compulsive drugseeking behaviour voluntary control is lost. Abused drugs can also modulate long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) in neuronal circuits associated with the addiction process, suggesting a way f ...
... of learning processes drug-associated cues can trigger craving and compulsive drugseeking behaviour voluntary control is lost. Abused drugs can also modulate long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) in neuronal circuits associated with the addiction process, suggesting a way f ...
Actin , Synaptic plasticity in Parallel fibre-Purkinje Neuron
... The neuronal plasticity induced by long term depression (LTD) in parallel fibre Purkinje cell synapse has been known to be one of the important mechanisms of motor learning. The molecular mechanisms behind this plasticity are being elucidated at various levels. Cytoskeleton is speculated to have a m ...
... The neuronal plasticity induced by long term depression (LTD) in parallel fibre Purkinje cell synapse has been known to be one of the important mechanisms of motor learning. The molecular mechanisms behind this plasticity are being elucidated at various levels. Cytoskeleton is speculated to have a m ...
Developmental plasticity: Pruning
... temporally correlates with postmortem findings of increased synaptic pruning during adolescence and early adulthood. The primary cause for loss of GM density is unknown. It may be driven at least partially by the process of synaptic pruning, together with trophic glial and vascular changes and or ce ...
... temporally correlates with postmortem findings of increased synaptic pruning during adolescence and early adulthood. The primary cause for loss of GM density is unknown. It may be driven at least partially by the process of synaptic pruning, together with trophic glial and vascular changes and or ce ...