Nervous and Endocrine System
... into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrical signals ...
... into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrical signals ...
Chapter 24 Late Adulthood Cognitive Development
... • Older adults who were better at working memory and multitasking used their prefrontal cortex, those who were worse did not. • Multitasking slows down people of every age, but older adults more so. • Older adults usually need to concentrate on one ...
... • Older adults who were better at working memory and multitasking used their prefrontal cortex, those who were worse did not. • Multitasking slows down people of every age, but older adults more so. • Older adults usually need to concentrate on one ...
Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... • Older adults who were better at working memory and multitasking used their prefrontal cortex, those who were worse did not. • Multitasking slows down people of every age, but older adults more so. • Older adults usually need to concentrate on one ...
... • Older adults who were better at working memory and multitasking used their prefrontal cortex, those who were worse did not. • Multitasking slows down people of every age, but older adults more so. • Older adults usually need to concentrate on one ...
Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... • Older adults who were better at working memory and multitasking used their prefrontal cortex, those who were worse did not. • Multitasking slows down people of every age, but older adults more so. • Older adults usually need to concentrate on one ...
... • Older adults who were better at working memory and multitasking used their prefrontal cortex, those who were worse did not. • Multitasking slows down people of every age, but older adults more so. • Older adults usually need to concentrate on one ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... where they attach to specific receptor sites on dendrites, like a key fitting into a lock. • Some of the synapses are excitatory, where an action potential is generated and the message gets sent., and some are inhibitory, preventing neural impulses. • The constant flow of these neuro-chemical impuls ...
... where they attach to specific receptor sites on dendrites, like a key fitting into a lock. • Some of the synapses are excitatory, where an action potential is generated and the message gets sent., and some are inhibitory, preventing neural impulses. • The constant flow of these neuro-chemical impuls ...
The Neurophysiological Basis of Learning and Memory in Advanced
... appears to be organized as a simple feed-forward fanout fan-in type of network. This type of network architecture is frequently found among biological and artificial networks that learn to classify inputs when endowed with the synaptic plasticity that creates learning ability.35 The first fan-out sy ...
... appears to be organized as a simple feed-forward fanout fan-in type of network. This type of network architecture is frequently found among biological and artificial networks that learn to classify inputs when endowed with the synaptic plasticity that creates learning ability.35 The first fan-out sy ...
Nonneurolnal cells engineered to express neuroligins
... scaffolding and signaling molecules, possibly via the PDZ-binding motif at the C-terminus. This scaffold may then signal the assembly of the exocytotic machinery and recruit additional neurexins and thereby neuroligins to form an expanding contact zone. Postsynaptic neuroligin-1 oligomers may contri ...
... scaffolding and signaling molecules, possibly via the PDZ-binding motif at the C-terminus. This scaffold may then signal the assembly of the exocytotic machinery and recruit additional neurexins and thereby neuroligins to form an expanding contact zone. Postsynaptic neuroligin-1 oligomers may contri ...
Neuron Anatomy
... • Associated with the morphological asymmetry is that chemical synapses are, for the most part, unidirectional. • There is a delay of a msec or more between the arrival of information at the presynaptic terminal and its transfer to the postsynaptic cell. This delay may reflect the several steps requ ...
... • Associated with the morphological asymmetry is that chemical synapses are, for the most part, unidirectional. • There is a delay of a msec or more between the arrival of information at the presynaptic terminal and its transfer to the postsynaptic cell. This delay may reflect the several steps requ ...
The Central Nervous System (outline, introduction)
... midbrain and cerebellum. All sensory pathways pass through the Thalamus and are relayed to various areas throughout the brain. The thalamus accomplishes this by filtering incoming information and deciding what to pass on or not to pass on to ...
... midbrain and cerebellum. All sensory pathways pass through the Thalamus and are relayed to various areas throughout the brain. The thalamus accomplishes this by filtering incoming information and deciding what to pass on or not to pass on to ...
Plasticity and nativism: Towards a resolution of
... It would certainly be convenient for nativists if fertilized eggs contained a blueprint for building the brain. Just as an architectural blueprint might specify exactly where every room and corridor in some new office building might be placed, one might imagine the fertilized egg bearing a neural bl ...
... It would certainly be convenient for nativists if fertilized eggs contained a blueprint for building the brain. Just as an architectural blueprint might specify exactly where every room and corridor in some new office building might be placed, one might imagine the fertilized egg bearing a neural bl ...
Plasticity and nativism: Towards a resolution of
... It would certainly be convenient for nativists if fertilized eggs contained a blueprint for building the brain. Just as an architectural blueprint might specify exactly where every room and corridor in some new office building might be placed, one might imagine the fertilized egg bearing a neural bl ...
... It would certainly be convenient for nativists if fertilized eggs contained a blueprint for building the brain. Just as an architectural blueprint might specify exactly where every room and corridor in some new office building might be placed, one might imagine the fertilized egg bearing a neural bl ...
Editorial overview: Development and regeneration: Nervous system
... control the formation of the brain. Three of these reviews focus on the main families of classical axon guidance molecules, including Slit, ephrin and semaphorin signaling. Blockus and Chédotal discuss the many developmental processes that are controlled by Slit proteins through their Robo receptor ...
... control the formation of the brain. Three of these reviews focus on the main families of classical axon guidance molecules, including Slit, ephrin and semaphorin signaling. Blockus and Chédotal discuss the many developmental processes that are controlled by Slit proteins through their Robo receptor ...
glossary of terms
... Ethnography has to focus on the observation of human bodies in interaction ...
... Ethnography has to focus on the observation of human bodies in interaction ...
The Nervous System
... 12 pairs of cranial nerves-from your brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves—from your spinal cord Made up of sensory and motor neurons Can have several impulses going at the same time ...
... 12 pairs of cranial nerves-from your brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves—from your spinal cord Made up of sensory and motor neurons Can have several impulses going at the same time ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given for the term “neuron” from one of my core disciplines, psychology. The first of these is a parenthetical definition, which illustrates the meaning of a term by following it with a c ...
... definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given for the term “neuron” from one of my core disciplines, psychology. The first of these is a parenthetical definition, which illustrates the meaning of a term by following it with a c ...
Technical Definitions
... definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given for the term “neuron” from one of my core disciplines, psychology. The first of these is a parenthetical definition, which illustrates the meaning of a term by following it with a c ...
... definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given for the term “neuron” from one of my core disciplines, psychology. The first of these is a parenthetical definition, which illustrates the meaning of a term by following it with a c ...
Document
... The medulla contains centers that control several automatic, homeostatic functions, including breathing, heart and blood vessel activity, swallowing, vomiting, and digestion. The pons also participates in some of these activities; for example, it regulates the breathing centers in the medulla. ...
... The medulla contains centers that control several automatic, homeostatic functions, including breathing, heart and blood vessel activity, swallowing, vomiting, and digestion. The pons also participates in some of these activities; for example, it regulates the breathing centers in the medulla. ...
How Neurons Talk to Each Other
... Summary: A new paper offers an overview as to how neurons ‘communicate’ with one another. Source: Max Planck Institute. Neurons are connected to each other through synapses, sites where signals are transmitted in the form of chemical messengers. Reinhard Jahn, Director at the Max Planck Institute fo ...
... Summary: A new paper offers an overview as to how neurons ‘communicate’ with one another. Source: Max Planck Institute. Neurons are connected to each other through synapses, sites where signals are transmitted in the form of chemical messengers. Reinhard Jahn, Director at the Max Planck Institute fo ...
Chapter 17:
... connects endocrine to the nervous system, receives sensory info, instincts, temperature control (ANS) pituitary gland – influenced by the hypthalamus, part of the endocrine system (master gland) pineal gland – part of the endocrine system – melatonin production ...
... connects endocrine to the nervous system, receives sensory info, instincts, temperature control (ANS) pituitary gland – influenced by the hypthalamus, part of the endocrine system (master gland) pineal gland – part of the endocrine system – melatonin production ...
VII. The Nervous System
... neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) The sudden in rush of Ca+2 causes synapti ...
... neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) The sudden in rush of Ca+2 causes synapti ...
m5zn_363798b57fd4c88
... perhaps the most important of all the system of the body. Not only does it correlate the activities of the other system but also in the brain is situated the site of conciousness, thought, memory , speech and the will to carry out purposeful actions. These factors all contribute to the formation of ...
... perhaps the most important of all the system of the body. Not only does it correlate the activities of the other system but also in the brain is situated the site of conciousness, thought, memory , speech and the will to carry out purposeful actions. These factors all contribute to the formation of ...
9-2_DescPathwaysBS_BusF
... First of all, important somatic and autonomic centers are located in there, and the processing centers of the cranial nerves are also. Moreover, it’s a functionally significant system because the reticular formation controlling vital respitatory and circulatory mechanism and arousal, is also part of ...
... First of all, important somatic and autonomic centers are located in there, and the processing centers of the cranial nerves are also. Moreover, it’s a functionally significant system because the reticular formation controlling vital respitatory and circulatory mechanism and arousal, is also part of ...
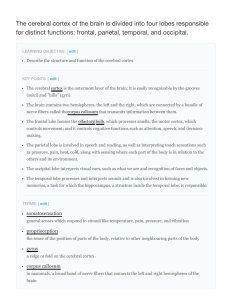
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... The brain contains two hemispheres, the left and the right, which are connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called thecorpus callosum that transmits information between them. The frontal lobe houses the olfactory bulb, which processes smells; the motor cortex, which controls movement; and it control ...
... The brain contains two hemispheres, the left and the right, which are connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called thecorpus callosum that transmits information between them. The frontal lobe houses the olfactory bulb, which processes smells; the motor cortex, which controls movement; and it control ...
Developmental_Part2 - Pemberton Counseling has changed
... Dynamic perception—1 of the 2 principles explaining infant perception; namely, that from birth perception is primed to focus on movement and change 2nd principle explaining infant perception is that babies are fascinated by people Infants most interested in emotional affordances of their caregivers ...
... Dynamic perception—1 of the 2 principles explaining infant perception; namely, that from birth perception is primed to focus on movement and change 2nd principle explaining infant perception is that babies are fascinated by people Infants most interested in emotional affordances of their caregivers ...
OL Chapter 2 overview
... feel most mentally confused and uncoordinated (groggiest) about halfway through the night. But we may feel more lively and vigorous (get new energy) close to the time we would normally wake up. . . . “owls” . . . “larks” . . . Like birds that are nocturnal (owls are an example), many younger adults ...
... feel most mentally confused and uncoordinated (groggiest) about halfway through the night. But we may feel more lively and vigorous (get new energy) close to the time we would normally wake up. . . . “owls” . . . “larks” . . . Like birds that are nocturnal (owls are an example), many younger adults ...