File
... 6.5.1 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. 6.5.2 Draw and label the structure of a motor neuron, include; dendrites, cell body with nucleus, axon, myelin sh ...
... 6.5.1 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. 6.5.2 Draw and label the structure of a motor neuron, include; dendrites, cell body with nucleus, axon, myelin sh ...
Ch 13 - lanoue
... thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time. Repeat twice. Record the results. Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites addition or multiplication facts. Compare the results. What happened to ...
... thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time. Repeat twice. Record the results. Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites addition or multiplication facts. Compare the results. What happened to ...
Ch 49 Pract Test Nervous System
... Tolerance means that decreasing amounts of a drug are needed to be effective. d. A lethal dose is a dose that results in death. ...
... Tolerance means that decreasing amounts of a drug are needed to be effective. d. A lethal dose is a dose that results in death. ...
Estimating Dynamic Neural Interactions in Awake Behaving Animals
... Collective spiking activity of neurons is the basis of information processing in the brain. Sparse neuronal activity in a population of neurons limits possible spiking patterns and, thereby, influences the information content conveyed by each pattern. However, because of the combinatorial explosion ...
... Collective spiking activity of neurons is the basis of information processing in the brain. Sparse neuronal activity in a population of neurons limits possible spiking patterns and, thereby, influences the information content conveyed by each pattern. However, because of the combinatorial explosion ...
The Nervous System - Hastings High School
... B. Memory can be short-term (primary) memory or long-term memory Memory consolidation is the conversion of the short-term memory into long-term memory Hippocampus – a region of the cerebral cortex located in the temporal lobe and is associated with learning and memory for processing spatial, vis ...
... B. Memory can be short-term (primary) memory or long-term memory Memory consolidation is the conversion of the short-term memory into long-term memory Hippocampus – a region of the cerebral cortex located in the temporal lobe and is associated with learning and memory for processing spatial, vis ...
PSYCH 2 StudyGuide
... 12- What is the difference between sensory and association cortex: Sensory processes body touch and movement sensations while association cortex is not involved in ...
... 12- What is the difference between sensory and association cortex: Sensory processes body touch and movement sensations while association cortex is not involved in ...
BGandcerebellum - UCSD Cognitive Science
... What are the two principal input structures of the basal ganglia? Caudate & Putamen (hint; these two structures form Striatum) Neurons in Putamen receive input from the somatosensory and motor cortex and have activity correlated with both active & passive mvmt. but not with specific sensory moda ...
... What are the two principal input structures of the basal ganglia? Caudate & Putamen (hint; these two structures form Striatum) Neurons in Putamen receive input from the somatosensory and motor cortex and have activity correlated with both active & passive mvmt. but not with specific sensory moda ...
Early Care and Education: Our Social Experiment
... that the development and migration of the neurons in the developing brain consist of a series of biological events that proceed in a relatively well-ordered but overlapping sequence. This sequence consists in the birth and migration of cells, the growth of the axon, and the formation of dendrites wh ...
... that the development and migration of the neurons in the developing brain consist of a series of biological events that proceed in a relatively well-ordered but overlapping sequence. This sequence consists in the birth and migration of cells, the growth of the axon, and the formation of dendrites wh ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... The cerebrum is divided into two halves, called the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere is subdivided into five functional areas called lobes. Outer surface of an adult brain exhibits folds called gyri (gyrus) and shallow depressions between those folds called sulci (sulcus). The br ...
... The cerebrum is divided into two halves, called the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere is subdivided into five functional areas called lobes. Outer surface of an adult brain exhibits folds called gyri (gyrus) and shallow depressions between those folds called sulci (sulcus). The br ...
Slide ()
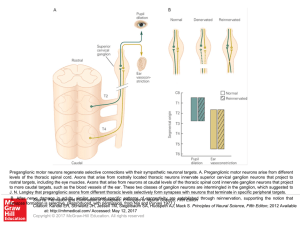
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
The Computational Brain
... Moving from a comparatively unresearched topic to one that is the basis of computing, the temporal lobe has many roles. Within this section of the brain, tasks of auditory reception, sorting new information, short-term memory, visual memory, and verbal memory are located. With so much information be ...
... Moving from a comparatively unresearched topic to one that is the basis of computing, the temporal lobe has many roles. Within this section of the brain, tasks of auditory reception, sorting new information, short-term memory, visual memory, and verbal memory are located. With so much information be ...
7-Nerves - bloodhounds Incorporated
... regulating neurotransmitter release from sympathetic nerves and from adrenergic neurons in the central nervous system ...
... regulating neurotransmitter release from sympathetic nerves and from adrenergic neurons in the central nervous system ...
Full text - Ip Lab - Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
... another Rho GTPase Cdc42. Both intersectin and its binding partner N-WASP, as well as Cdc42, are crucial for spine formation [22]. Finally, EphB forward signaling can lead to increased RhoA activity via focal adhesion kinase (FAK) [23]. It is possible that multiple GEF and Rho GTPases are activated ...
... another Rho GTPase Cdc42. Both intersectin and its binding partner N-WASP, as well as Cdc42, are crucial for spine formation [22]. Finally, EphB forward signaling can lead to increased RhoA activity via focal adhesion kinase (FAK) [23]. It is possible that multiple GEF and Rho GTPases are activated ...
File - firestone falcons
... • Neurons send signals to other cells as electrochemical waves travelling along thin fibers called axons, which cause chemicals called neurotransmitters to be released at junctions called synapses. • A cell that receives a synaptic signal may be excited, inhibited, or otherwise modulated. ...
... • Neurons send signals to other cells as electrochemical waves travelling along thin fibers called axons, which cause chemicals called neurotransmitters to be released at junctions called synapses. • A cell that receives a synaptic signal may be excited, inhibited, or otherwise modulated. ...
The Nervous system - Locust Trace Veterinary Assistant Program
... ■ Brain Stem– Controls respirations, circulation, heart rate, blood pressure – Damage to this region of the brain instantly can cause death ...
... ■ Brain Stem– Controls respirations, circulation, heart rate, blood pressure – Damage to this region of the brain instantly can cause death ...
in the central nervous system
... a) Gland – will increase or decrease activity b) Muscle – will contract ...
... a) Gland – will increase or decrease activity b) Muscle – will contract ...
The Five Senses In the Brain
... • Examine the circuit below. The two red neurons are excitatory and the two blue neurons are inhibitory. • What effect would removing the two blue inhibitory neurons have on this circuit’s activity? ...
... • Examine the circuit below. The two red neurons are excitatory and the two blue neurons are inhibitory. • What effect would removing the two blue inhibitory neurons have on this circuit’s activity? ...
Document
... The Limbic System The limbic system connects us to our emotions and motivations. Most of these emotions and motivations are related to survival. ...
... The Limbic System The limbic system connects us to our emotions and motivations. Most of these emotions and motivations are related to survival. ...
Ch10 Reading Guide
... T. The two divisions of the motor division are __________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ U. The somatic nervous system is involved in __________________________________ V. The autonomic nervous system is involved in __________________ ...
... T. The two divisions of the motor division are __________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ U. The somatic nervous system is involved in __________________________________ V. The autonomic nervous system is involved in __________________ ...
Document
... Identify the parts of the body involved. What senses are being used? Can we train ourselves to react more quickly? Does practice make perfect? Can we alter reflex actions? – think of a situations where it is possible to alter the automatic response (not dropping a hot object, deliberately breathing ...
... Identify the parts of the body involved. What senses are being used? Can we train ourselves to react more quickly? Does practice make perfect? Can we alter reflex actions? – think of a situations where it is possible to alter the automatic response (not dropping a hot object, deliberately breathing ...
Chapter 3
... Ex. teacher calls your name - RAS stimulates higher brain centers that allow you to become alert. OR while sleeping your reticular formation restricts most environmental stimuli from entering your brain. ...
... Ex. teacher calls your name - RAS stimulates higher brain centers that allow you to become alert. OR while sleeping your reticular formation restricts most environmental stimuli from entering your brain. ...
learning objectives chapter 2
... 20. Explain the roles of Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area in language production and comprehension. (see “Association Cortex”) 21. Explain how split-brain studies provide insight into the specialized functions of the brain’s two hemispheres. (see “The Divided Brain: Lateralization”) ...
... 20. Explain the roles of Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area in language production and comprehension. (see “Association Cortex”) 21. Explain how split-brain studies provide insight into the specialized functions of the brain’s two hemispheres. (see “The Divided Brain: Lateralization”) ...
The Nervous System
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
The Nervous System
... e.g. Burning your hand on the stove. Most nerves are both sensory and motor ...
... e.g. Burning your hand on the stove. Most nerves are both sensory and motor ...
Topic Option A Neurobio
... 12. Application: Events such as strokes may 3. Neurons are initially produced by differentiation promote reorganization of brain function. in the neural tube. 13. Skill: Annotation of a diagram of embryonic 4. Immature neurons migrate to a final location. tissues in Xenopus, used as an animal model, ...
... 12. Application: Events such as strokes may 3. Neurons are initially produced by differentiation promote reorganization of brain function. in the neural tube. 13. Skill: Annotation of a diagram of embryonic 4. Immature neurons migrate to a final location. tissues in Xenopus, used as an animal model, ...