NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND RECEPTORS
... • Playing the piano, driving a car, or hitting a tennis ball depends, at one level, on exact muscle coordination. • But if we consider how the muscles can be activated so precisely, we see that more fundamental processes are involved. • For the muscles to produce the complex movements that make up a ...
... • Playing the piano, driving a car, or hitting a tennis ball depends, at one level, on exact muscle coordination. • But if we consider how the muscles can be activated so precisely, we see that more fundamental processes are involved. • For the muscles to produce the complex movements that make up a ...
Homework 5
... by your company. (you only viewed each illustration for a short period of time, less than a second). Later you scroll through a competitor’s magazine that have used some of your pictures that you need to identify. Discuss the probability of you remembering pictures published in your company’s magazi ...
... by your company. (you only viewed each illustration for a short period of time, less than a second). Later you scroll through a competitor’s magazine that have used some of your pictures that you need to identify. Discuss the probability of you remembering pictures published in your company’s magazi ...
Exercises and Tests
... 1. Only glial cells make up the brain. TF 2. Glial cells transmit and receive electro signal to and from the brain. TF 3. The brain contains billions of neurons. TF 4. The number of glial cells is the same as the number of neurons. TF 5. All the neurons have the same size and length. TF 6. The neuro ...
... 1. Only glial cells make up the brain. TF 2. Glial cells transmit and receive electro signal to and from the brain. TF 3. The brain contains billions of neurons. TF 4. The number of glial cells is the same as the number of neurons. TF 5. All the neurons have the same size and length. TF 6. The neuro ...
Chapter 1 - Beulah School District 27
... • Rich sensory experiences create new dendrites, builds new networks for learning • Rich experiences, hugs, hearing music, learning a skill, exploring a toy • Strengthen and refine brain’s wiring ...
... • Rich sensory experiences create new dendrites, builds new networks for learning • Rich experiences, hugs, hearing music, learning a skill, exploring a toy • Strengthen and refine brain’s wiring ...
Draft Proposal to the Keck Foundation KECK CENTER FOR
... multiphoton microscopy, and lifetime resolved microscopy, are combined with genetic or exogenous optical markers to provide new ways to study processes such as cellular trafficking, vesicle membrane fusion, locally regulated dendritic ionic flows and protein synthesis, and rhythmic activities of ind ...
... multiphoton microscopy, and lifetime resolved microscopy, are combined with genetic or exogenous optical markers to provide new ways to study processes such as cellular trafficking, vesicle membrane fusion, locally regulated dendritic ionic flows and protein synthesis, and rhythmic activities of ind ...
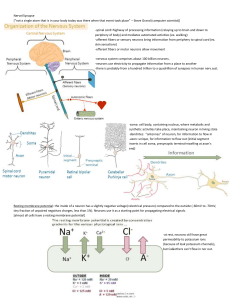
Nervous System - wondersofscience
... B) Peripheral Nervous system • Connects different parts of the body to the central nervous system • Nerves are structures that help transmit information between the central nervous system and various regions of the body • There are two main types of nerves: ...
... B) Peripheral Nervous system • Connects different parts of the body to the central nervous system • Nerves are structures that help transmit information between the central nervous system and various regions of the body • There are two main types of nerves: ...
Self-Directed Neuroplasticity
... !! Less cortical thinning with aging !! Increases activation of left frontal regions, which lifts mood !! Increases power and reach of gamma-range brainwaves !! Decreases stress-related cortisol !! Stronger immune system ...
... !! Less cortical thinning with aging !! Increases activation of left frontal regions, which lifts mood !! Increases power and reach of gamma-range brainwaves !! Decreases stress-related cortisol !! Stronger immune system ...
The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
... by means of connections A person’s linguistic system is largely represented in his/her cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system does what it does by virtue of its connection ...
... by means of connections A person’s linguistic system is largely represented in his/her cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system does what it does by virtue of its connection ...
Purpose
... Occipital Lobe Dysfunction Visual information is sent from the retina in each eye to the thalamus and then to the occipital lobes of the cerebral cortex. At each step along the way, this information is represented topographically; in other words, neighboring nerve cells response to neighboring areas ...
... Occipital Lobe Dysfunction Visual information is sent from the retina in each eye to the thalamus and then to the occipital lobes of the cerebral cortex. At each step along the way, this information is represented topographically; in other words, neighboring nerve cells response to neighboring areas ...
Nancy A. O`Rourke Nicholas C. Weiler Kristina D
... regions. For example, a study of PSDs from rat forebrain and cerebellum revealed marked molecular heterogeneities between the two regions 10. On the other hand, a recent comparison of synaptic vesicle pools between glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses reached the conclusion that the two pools have v ...
... regions. For example, a study of PSDs from rat forebrain and cerebellum revealed marked molecular heterogeneities between the two regions 10. On the other hand, a recent comparison of synaptic vesicle pools between glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses reached the conclusion that the two pools have v ...
NervousSystem2
... must have its origin in the cerebral cortex. Its origin is by excitation of interneurons in an area of the cerebral cortex designated the motor cortex. All stimuli ultimately contribute to effector action. Those that are consciously appreciated utilize pathways that traverse the cerebral cortex and ...
... must have its origin in the cerebral cortex. Its origin is by excitation of interneurons in an area of the cerebral cortex designated the motor cortex. All stimuli ultimately contribute to effector action. Those that are consciously appreciated utilize pathways that traverse the cerebral cortex and ...
Eagleman Ch 1. Introduction
... Understanding how humans make decisions can provide insight into how to encourage us to make better decisions. Brain interface devices, such as cochlear implants and implanted electrodes to enable paralyzed patients to move devices outside their own body, can restore lost functions to individuals. ...
... Understanding how humans make decisions can provide insight into how to encourage us to make better decisions. Brain interface devices, such as cochlear implants and implanted electrodes to enable paralyzed patients to move devices outside their own body, can restore lost functions to individuals. ...
Ch 3 Biological Bases of Behavior
... A highly magnified view of the synapse shown above. Neurotransmitters are stored in tiny sacs called synaptic vesicles. When a nerve impulse arrives at an axon terminal, the vesicles move to the surface and release neurotransmitters. These transmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap to affect the ...
... A highly magnified view of the synapse shown above. Neurotransmitters are stored in tiny sacs called synaptic vesicles. When a nerve impulse arrives at an axon terminal, the vesicles move to the surface and release neurotransmitters. These transmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap to affect the ...
Lecture 2 Powerpoint file
... • But there are some smaller steps that we need to take: – HOW: how do neurons work (physiology) and how do they interact to form circuits? – WHERE: for a given cognitive task, where are the neurons that do that job ...
... • But there are some smaller steps that we need to take: – HOW: how do neurons work (physiology) and how do they interact to form circuits? – WHERE: for a given cognitive task, where are the neurons that do that job ...
The Nervous System
... Neurons = nerve cells – Cells specialized to transmit messages – Major regions of neurons • Cell body – nucleus and metabolic center of the cell • Processes – fibers that extend from the cell body (dendrites and axon) ...
... Neurons = nerve cells – Cells specialized to transmit messages – Major regions of neurons • Cell body – nucleus and metabolic center of the cell • Processes – fibers that extend from the cell body (dendrites and axon) ...
chapter32_part2
... • The cerebral cortex, the outer layer of gray matter, has areas that receive and integrate sensory information. It also controls conscious thought and actions. • The cerebral cortex interacts with the limbic system, a set of brain structures that collectively affect emotions and contribute to memor ...
... • The cerebral cortex, the outer layer of gray matter, has areas that receive and integrate sensory information. It also controls conscious thought and actions. • The cerebral cortex interacts with the limbic system, a set of brain structures that collectively affect emotions and contribute to memor ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
The Nervous System
... hemispheres together and quickens communication b/t the two sides. Gyri (sing. gyrus) are the folds or mountains on the cerebral cortex Sulci (sing. sulcus) are the dips or cracks on the cortex. These peaks and dips are used expand the surface area of the ...
... hemispheres together and quickens communication b/t the two sides. Gyri (sing. gyrus) are the folds or mountains on the cerebral cortex Sulci (sing. sulcus) are the dips or cracks on the cortex. These peaks and dips are used expand the surface area of the ...
The Importance of the Nervous System
... • http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__ chemical_synapse__quiz_1_.html ...
... • http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__ chemical_synapse__quiz_1_.html ...
Biological_Neuroscience
... 1. Damage to the Broca’s area in the left cerebral hemisphere on the brain would likely result in which of the following? (A) A repetition of the speech of others (B) A loss of ability to speak (C) A loss of the ability to comprehend speech (D) A loss of in the ability to comprehend speech (E) An in ...
... 1. Damage to the Broca’s area in the left cerebral hemisphere on the brain would likely result in which of the following? (A) A repetition of the speech of others (B) A loss of ability to speak (C) A loss of the ability to comprehend speech (D) A loss of in the ability to comprehend speech (E) An in ...
How the Gifted Brain Learns
... The brain is made up of cells which are the basic unit of life. The most important are nerve cells or neurons. These are electrically active chemicals that do our thinking. Our brains have billions of neurons. Neurons look like trees with lots of branches. The branches spread out and their job is to ...
... The brain is made up of cells which are the basic unit of life. The most important are nerve cells or neurons. These are electrically active chemicals that do our thinking. Our brains have billions of neurons. Neurons look like trees with lots of branches. The branches spread out and their job is to ...
Unit 3 - Biological Bases - Bearcat Social Studies Corner
... 1. Damage to the Broca’s area in the left cerebral hemisphere on the brain would likely result in which of the following? (A) A repetition of the speech of others (B) A loss of ability to speak (C) A loss of the ability to comprehend speech (D) A loss of in the ability to comprehend speech (E) An in ...
... 1. Damage to the Broca’s area in the left cerebral hemisphere on the brain would likely result in which of the following? (A) A repetition of the speech of others (B) A loss of ability to speak (C) A loss of the ability to comprehend speech (D) A loss of in the ability to comprehend speech (E) An in ...
Chapter 1: Concepts and Methods in Biology - Rose
... e. Role of long-term depression (LTD) and long-term potentiation (LTP) 8. Consciousness represents an emergent property of whole-brain patterns of activity ...
... e. Role of long-term depression (LTD) and long-term potentiation (LTP) 8. Consciousness represents an emergent property of whole-brain patterns of activity ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Thick axons are myelinated Thin axons are unmyelinated, conduct impulses more slowly Myelin Sheaths in the PNS Myalin sheaths formed by Schwann cells (neurolemmacytes) Develop during fetal period and in the first year of postnatal life Schwann cells wrap in concentric layers around the axon, cover t ...
... Thick axons are myelinated Thin axons are unmyelinated, conduct impulses more slowly Myelin Sheaths in the PNS Myalin sheaths formed by Schwann cells (neurolemmacytes) Develop during fetal period and in the first year of postnatal life Schwann cells wrap in concentric layers around the axon, cover t ...
Program booklet - Munich Center for NeuroSciences
... members like p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) have been shown to undergo a regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) process. RIP is an elegant way for cells to transduce signals or simply to quickly remove proteins from the cell surface. It is a tightly regulated mechanism fundamental for key bio ...
... members like p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) have been shown to undergo a regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) process. RIP is an elegant way for cells to transduce signals or simply to quickly remove proteins from the cell surface. It is a tightly regulated mechanism fundamental for key bio ...