Synapses - UBC Zoology
... to trigger an action potential therefore inhibitory •An ipsp on the dendrite will have less effect due to current loss than an ipsp in the soma ...
... to trigger an action potential therefore inhibitory •An ipsp on the dendrite will have less effect due to current loss than an ipsp in the soma ...
Unit 3 Biological Bases of Behavior 11_12
... neurotransmitters are released to attach to specific receptor sites on membranes of dendrites of your postsynaptic neurons. This is called the “lock and key concept” ...
... neurotransmitters are released to attach to specific receptor sites on membranes of dendrites of your postsynaptic neurons. This is called the “lock and key concept” ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... • B. Compare the central and peripheral N.S. • C. Compare the 3 types of neurons. • D. Compare the two categories of motor neurons. • E. Identify the 7 parts of the neuron and summarize how impulses begin and continue. • F. Summarize the relationship between the ...
... • B. Compare the central and peripheral N.S. • C. Compare the 3 types of neurons. • D. Compare the two categories of motor neurons. • E. Identify the 7 parts of the neuron and summarize how impulses begin and continue. • F. Summarize the relationship between the ...
phys Learning Objectives Chapter 58 [10-31
... Hippocampus is easily hyperexcitable. The result is focal epileptic seizure during which, the person experiences various psychomotor effects (olfactory, auditory, tactile, and other hallucinations) even though the person has not lost consciousness and knows these hallucinations to be unreal. - The r ...
... Hippocampus is easily hyperexcitable. The result is focal epileptic seizure during which, the person experiences various psychomotor effects (olfactory, auditory, tactile, and other hallucinations) even though the person has not lost consciousness and knows these hallucinations to be unreal. - The r ...
The cerebellum chip: an analog VLSI implementation of a
... circuit) connected to a constant current source that produces regular spontaneous activity. The current source is gated by the digital cf_wind signal, such that the spontaneous activity is shut off for the duration of the cs_out trace. The chip allowed one of three learning rules to be connected. Ex ...
... circuit) connected to a constant current source that produces regular spontaneous activity. The current source is gated by the digital cf_wind signal, such that the spontaneous activity is shut off for the duration of the cs_out trace. The chip allowed one of three learning rules to be connected. Ex ...
Biology 12 Name: Nervous System Practice Exam Types of Neurons
... 23. Draw and identify the major components of a Synapse including pre-synaptic membrane, vesicle with EXCITATORY neurotransmitter, synapse, re-uptake transporters, receptor sites and post synaptic membrane. (THIS IS A GOOD CHOICE FOR SHORTANSWER) ...
... 23. Draw and identify the major components of a Synapse including pre-synaptic membrane, vesicle with EXCITATORY neurotransmitter, synapse, re-uptake transporters, receptor sites and post synaptic membrane. (THIS IS A GOOD CHOICE FOR SHORTANSWER) ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... These synapses are called ______________________ (on dendrites) and _________________________ (on soma). They carry input signals to the other neuron. Axons from one neuron can synapse with the axon terminal of another neuron. These synapses are called ________________________, and they regulate the ...
... These synapses are called ______________________ (on dendrites) and _________________________ (on soma). They carry input signals to the other neuron. Axons from one neuron can synapse with the axon terminal of another neuron. These synapses are called ________________________, and they regulate the ...
Notes Chapter 50 Nervous and Sensory Systems
... iii) The action of the parasympathetic division induces the body to. conserve energy. iv) Under normal conditions, both systems usually are activated to some degree. v) The balance of actions of the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system help the body ...
... iii) The action of the parasympathetic division induces the body to. conserve energy. iv) Under normal conditions, both systems usually are activated to some degree. v) The balance of actions of the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system help the body ...
Nervous System Notes
... well-being; insufficient levels associated with Parkinson’s disease • Serotonin – inhibitory; insufficient levels associated with insomnia • Endorphins & enkephalins – generally inhibitory & influence mood; released under stress to reduce pain (blocks substance P) • Substance P – excitatory; helps i ...
... well-being; insufficient levels associated with Parkinson’s disease • Serotonin – inhibitory; insufficient levels associated with insomnia • Endorphins & enkephalins – generally inhibitory & influence mood; released under stress to reduce pain (blocks substance P) • Substance P – excitatory; helps i ...
Ch 31: Urinary System
... - created by the movement of positively charged sodium & potassium ions across the cell membrane of the axon - as charged particles move, they create electrical impulses - considered “all-or-none phenomenon”…either happen completely or not at all ...
... - created by the movement of positively charged sodium & potassium ions across the cell membrane of the axon - as charged particles move, they create electrical impulses - considered “all-or-none phenomenon”…either happen completely or not at all ...
rview
... A) It will either produce an action potential or not, depending entirely upon whether it is an excitatory or inhibitory neuron. B) It will integrate the incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals, with its rate of action potentials depending on the relative amount of each type of signal. C) It will ...
... A) It will either produce an action potential or not, depending entirely upon whether it is an excitatory or inhibitory neuron. B) It will integrate the incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals, with its rate of action potentials depending on the relative amount of each type of signal. C) It will ...
chapter_1
... The neuron activity is an all-or-nothing process, ie., the activation of the neuron is binary. A certain fixed number of synapses (>1) must be excited within a period of latent addition for a neuron to be excited. The only significant delay within the nervous system is synaptic delay. The activity o ...
... The neuron activity is an all-or-nothing process, ie., the activation of the neuron is binary. A certain fixed number of synapses (>1) must be excited within a period of latent addition for a neuron to be excited. The only significant delay within the nervous system is synaptic delay. The activity o ...
FYI information about sensory perception
... brain, and one place this happens is in cortical neurons called feature-detecting neurons. These neurons each receive several different types of information from neurons in the primary somatosensory cortex (which received their information from receptors). This integration of sensations allows us to ...
... brain, and one place this happens is in cortical neurons called feature-detecting neurons. These neurons each receive several different types of information from neurons in the primary somatosensory cortex (which received their information from receptors). This integration of sensations allows us to ...
Lecture Notes - Austin Community College
... interpreting speech & language,smell d. Occipital Lobe Processes incoming visual information stores visual memories e. Insula This lobe is located under the temporal lobe It is involved in memory Interpretation of taste 7. Functional areas of the Cerebral cortex Primary Somatosensory corte ...
... interpreting speech & language,smell d. Occipital Lobe Processes incoming visual information stores visual memories e. Insula This lobe is located under the temporal lobe It is involved in memory Interpretation of taste 7. Functional areas of the Cerebral cortex Primary Somatosensory corte ...
Physiology
... Sensitization of a synapse is the potentiation of the postsynaptic response to a certain stimulus by coupling the stimulus to another intense (usually painful) stimulus (fig.2-1). The terminal which conducts the intense or painful stimulus is called a facilitator terminal which relays on the presyna ...
... Sensitization of a synapse is the potentiation of the postsynaptic response to a certain stimulus by coupling the stimulus to another intense (usually painful) stimulus (fig.2-1). The terminal which conducts the intense or painful stimulus is called a facilitator terminal which relays on the presyna ...
Biology 231
... sensory function – senses stimuli (changes in internal or external environment) integration function – processes sensory inputs and decides on appropriate responses motor function – sends signals to effectors, which respond to the stimuli Neurons – functional cells of nervous system, receive and sen ...
... sensory function – senses stimuli (changes in internal or external environment) integration function – processes sensory inputs and decides on appropriate responses motor function – sends signals to effectors, which respond to the stimuli Neurons – functional cells of nervous system, receive and sen ...
Nervous System - Dr. Eric Schwartz
... remodeling in response to stimulation or injury than in the adult brain, a characteristic known as plasticity. • The basic shapes and locations of major neuronal circuits in the mature central nervous system do not change once formed. • The creation and removal of synaptic contacts begun during feta ...
... remodeling in response to stimulation or injury than in the adult brain, a characteristic known as plasticity. • The basic shapes and locations of major neuronal circuits in the mature central nervous system do not change once formed. • The creation and removal of synaptic contacts begun during feta ...
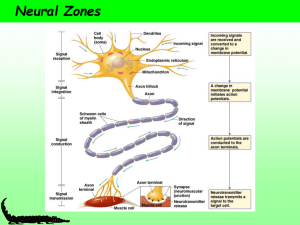
The cells of the nervous system
... provide energy for impulses and ribosomes which synthesise proteins (e.g. enzymes) for the synthesis of neurotransmitters. • Dendrites – these fibres receive nerve impulses and carry them towards the cell body • Axon – this fibre carries nerve impulses away from the cell body. • A neuron in a newly- ...
... provide energy for impulses and ribosomes which synthesise proteins (e.g. enzymes) for the synthesis of neurotransmitters. • Dendrites – these fibres receive nerve impulses and carry them towards the cell body • Axon – this fibre carries nerve impulses away from the cell body. • A neuron in a newly- ...
Cortex
... 1.restricting exposure to stimuli with only certain orientations of visual contrast a shift of all cells toward selectivity for the trained orientation. ...
... 1.restricting exposure to stimuli with only certain orientations of visual contrast a shift of all cells toward selectivity for the trained orientation. ...
nervous system notes
... Nervous system disorders (learn one) Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects the control of voluntary movement. Cause: A deficiency of dopamine, due to loss or damage of tissue in the brain that makes dopamine. Dopamine is used to regulate the nerves controlling mus ...
... Nervous system disorders (learn one) Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects the control of voluntary movement. Cause: A deficiency of dopamine, due to loss or damage of tissue in the brain that makes dopamine. Dopamine is used to regulate the nerves controlling mus ...
Neural circuit rewiring: insights from DD synapse remodeling
... Figure 1. (A) Schematic of DD synapse remodeling. In L1 worms (Left) DD neurons form synapses (green circles) along the ventral neurites and receive cholinergic synaptic inputs (blue) in their dorsal neurites through the ACh receptor (blue diamonds). After DD remodeling in L2 and older animals (righ ...
... Figure 1. (A) Schematic of DD synapse remodeling. In L1 worms (Left) DD neurons form synapses (green circles) along the ventral neurites and receive cholinergic synaptic inputs (blue) in their dorsal neurites through the ACh receptor (blue diamonds). After DD remodeling in L2 and older animals (righ ...
THE NeurobiologyOF “We”
... THE BRAIN, to wonder two decades ago, “What kind of internal experience is generated by the neuronal activity captured on a brain scan? Even more important, how can we use scientific discoveries linking inner experience with brain function to effect constructive changes in everyday life?”1 A student ...
... THE BRAIN, to wonder two decades ago, “What kind of internal experience is generated by the neuronal activity captured on a brain scan? Even more important, how can we use scientific discoveries linking inner experience with brain function to effect constructive changes in everyday life?”1 A student ...
Biological Basis of Emotions - California Training Institute
... The Main Areas Involved with Emotions It is important to stress that all these structures interconnect intensively and none of them is the sole responsible for any specific emotional state. However, some contribute more than others to this or that kind of emotion. We shall review now ...
... The Main Areas Involved with Emotions It is important to stress that all these structures interconnect intensively and none of them is the sole responsible for any specific emotional state. However, some contribute more than others to this or that kind of emotion. We shall review now ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVE 5: Explain how an injured nerve fiber may
... neuron process which connects the dendrites to the axon? Answer: In unipolar sensory neurons, the portion of the neuron process which connects dendrites to axon conveys properties of both. Therefore, that portion from dendrites to cell body, is sometimes referred to as the peripheral process, wherea ...
... neuron process which connects the dendrites to the axon? Answer: In unipolar sensory neurons, the portion of the neuron process which connects dendrites to axon conveys properties of both. Therefore, that portion from dendrites to cell body, is sometimes referred to as the peripheral process, wherea ...
Intelligence and Patterns - Paradigm Shift International
... matter" that makes up 80% of the human brain, is responsible for our ability to remember, think, reflect, empathize, communicate, adapt to new situations and plan for the future. The cortex first appeared in mammals, and it has a fundamentally simple repetitive structure that is the same across all ...
... matter" that makes up 80% of the human brain, is responsible for our ability to remember, think, reflect, empathize, communicate, adapt to new situations and plan for the future. The cortex first appeared in mammals, and it has a fundamentally simple repetitive structure that is the same across all ...