Modulation of Inhibitory Synaptic Potentials in the Piriform Cortex
... In these equations, W represents the average strength of excitatory synapses arising from cortical pyramidal cells and synapsing on other excitatory neurons. If neuronal output is in spikes/ms, then synaptic strength reflects the change in membrane voltage per spike (mV/ spike) because of the membra ...
... In these equations, W represents the average strength of excitatory synapses arising from cortical pyramidal cells and synapsing on other excitatory neurons. If neuronal output is in spikes/ms, then synaptic strength reflects the change in membrane voltage per spike (mV/ spike) because of the membra ...
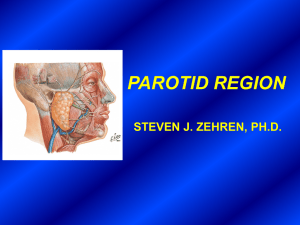
Slide 1
... Gustatory Sweating (Frey's Syndrome) This woman had undergone a parotidectomy for a benign mixed tumor of the parotid gland a year before this photo was taken. The picture was taken just as she was taking some food by mouth. ...
... Gustatory Sweating (Frey's Syndrome) This woman had undergone a parotidectomy for a benign mixed tumor of the parotid gland a year before this photo was taken. The picture was taken just as she was taking some food by mouth. ...
Neurotransmitter Transporters
... back to the outside for another cycle of transport, led to early models of transporters that moved across the membrane or rotated in place. The structural information contained in the primary sequence of the transporter genes and a wealth of experimental data now indicate that transporters form a po ...
... back to the outside for another cycle of transport, led to early models of transporters that moved across the membrane or rotated in place. The structural information contained in the primary sequence of the transporter genes and a wealth of experimental data now indicate that transporters form a po ...
CNS 424 Block Educational Framework (Week 1)
... unconscious proprioception from the limbs and trunk. Describe lateral spinothalamic tract and pathways for pain and temperature from the limbs and trunk. Describe ventral spinothalamic tract and pathways for simple touch from the limbs and trunk. Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with e ...
... unconscious proprioception from the limbs and trunk. Describe lateral spinothalamic tract and pathways for pain and temperature from the limbs and trunk. Describe ventral spinothalamic tract and pathways for simple touch from the limbs and trunk. Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with e ...
Five Sources of a Dorsal Root Potential: Their Interactions and
... roots. A single shock to the purely muscle nerve to the gastrocnemius generates only a weak DRP (Wall 1958), and we, like many others, used a brief repetitive volley to generate a clear DRP (Jankowska 1992). The mechanisms producing these two DRPs are presumed to be interrelated because they mutuall ...
... roots. A single shock to the purely muscle nerve to the gastrocnemius generates only a weak DRP (Wall 1958), and we, like many others, used a brief repetitive volley to generate a clear DRP (Jankowska 1992). The mechanisms producing these two DRPs are presumed to be interrelated because they mutuall ...
PDF
... Experiments on the pretreatment of sensory ganglia in vitro Sensory ganglia were dissected from 8-day-old chick embryos and incubated in rings (0-5 x2-3 cm) containing either 1 ml of control medium (C) (medium 199:chicken serum:buffered saline; 2:1:1, v/v) or 1 ml of medium containing NGF (N) (as C ...
... Experiments on the pretreatment of sensory ganglia in vitro Sensory ganglia were dissected from 8-day-old chick embryos and incubated in rings (0-5 x2-3 cm) containing either 1 ml of control medium (C) (medium 199:chicken serum:buffered saline; 2:1:1, v/v) or 1 ml of medium containing NGF (N) (as C ...
CHAPTER TWO - Test Bank 1
... 27. Juan’s toe was severed and was quickly sewn back on by a surgeon. As a result, he regained some function and feeling in his toe. Which of the following are responsible for Juan’s ability to regain function and feeling in his toe? a) myelin Incorrect. Myelin speeds up the neural impulse. b) glial ...
... 27. Juan’s toe was severed and was quickly sewn back on by a surgeon. As a result, he regained some function and feeling in his toe. Which of the following are responsible for Juan’s ability to regain function and feeling in his toe? a) myelin Incorrect. Myelin speeds up the neural impulse. b) glial ...
ANS: c, p. 46, F, LO=2.1, (1) - test bank and solution manual for your
... 27. Juan’s toe was severed and was quickly sewn back on by a surgeon. As a result, he regained some function and feeling in his toe. Which of the following are responsible for Juan’s ability to regain function and feeling in his toe? a) myelin Incorrect. Myelin speeds up the neural impulse. b) glial ...
... 27. Juan’s toe was severed and was quickly sewn back on by a surgeon. As a result, he regained some function and feeling in his toe. Which of the following are responsible for Juan’s ability to regain function and feeling in his toe? a) myelin Incorrect. Myelin speeds up the neural impulse. b) glial ...
Sample
... Incorrect: Incorrect. Synaptic vesicles are structures within the synaptic knobs. Answer: D Type: MC Page Ref: 53 Objective: 2.3 28) The saclike structures found inside the synaptic knob containing chemicals are called: A) axon terminals. B) synaptic gaps. C) synaptic vesicles. D) receptor sites. Co ...
... Incorrect: Incorrect. Synaptic vesicles are structures within the synaptic knobs. Answer: D Type: MC Page Ref: 53 Objective: 2.3 28) The saclike structures found inside the synaptic knob containing chemicals are called: A) axon terminals. B) synaptic gaps. C) synaptic vesicles. D) receptor sites. Co ...
Distribution of Agrin mRNAs in the Chick Embryo Nervous System
... and Godfrey, 1992). Thus, agrin appears to be involved in neuromuscular synaptogenesis from the time axons contact muscle cells. In addition to agrin’s localization in the synaptic basal lamina, agrin-like proteins are also present in most other basal laminae (Godfrey et al., 1988a,b; Godfrey, 199 1 ...
... and Godfrey, 1992). Thus, agrin appears to be involved in neuromuscular synaptogenesis from the time axons contact muscle cells. In addition to agrin’s localization in the synaptic basal lamina, agrin-like proteins are also present in most other basal laminae (Godfrey et al., 1988a,b; Godfrey, 199 1 ...
Clonal analysis of the mushroom bodies
... learning and memory. Characterization of the development and projection patterns of individual MB neurons will be important for elucidating their functions. Using mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker (Lee, T. and Luo, L. (1999) Neuron 22, 451-461), we have positively marked the axons and d ...
... learning and memory. Characterization of the development and projection patterns of individual MB neurons will be important for elucidating their functions. Using mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker (Lee, T. and Luo, L. (1999) Neuron 22, 451-461), we have positively marked the axons and d ...
Sympathetic innervation of human muscle spindles
... In muscle spindles labeled with antibodies against NPY, NPY receptor and TH, specific staining was found between the fibers where no blood vessels were seen. Based upon previous studies (Ballard, 1978; Barker & Saito, 1981; Bombardi et al. 2006), we conclude that this staining is most Iikely located ...
... In muscle spindles labeled with antibodies against NPY, NPY receptor and TH, specific staining was found between the fibers where no blood vessels were seen. Based upon previous studies (Ballard, 1978; Barker & Saito, 1981; Bombardi et al. 2006), we conclude that this staining is most Iikely located ...
ANS: c, p. 46, F, LO=2.1, (1)
... ANS: a, pp. 46–47, C, LO=2.1, (2) APA=1.1 14. Your teacher asks you to describe the sequence of parts of a neuron that the impulse travels during neural conduction. Which of the following sequences will you offer? a) dendrites, axon, soma, synaptic knob b) terminal buttons, axon, soma, dendrites c) ...
... ANS: a, pp. 46–47, C, LO=2.1, (2) APA=1.1 14. Your teacher asks you to describe the sequence of parts of a neuron that the impulse travels during neural conduction. Which of the following sequences will you offer? a) dendrites, axon, soma, synaptic knob b) terminal buttons, axon, soma, dendrites c) ...
Structure of Receptive Fields in Area 3b of Primary Somatosensory
... The same photographic negative with a single random dot pattern, 28 mm wide and 250 mm long, was used to construct the random dot stimuli for all three monkeys. In the experiments performed on one monkey, the pattern was trimmed to 175 mm long to make room for a segment with oriented bars. Otherwise ...
... The same photographic negative with a single random dot pattern, 28 mm wide and 250 mm long, was used to construct the random dot stimuli for all three monkeys. In the experiments performed on one monkey, the pattern was trimmed to 175 mm long to make room for a segment with oriented bars. Otherwise ...
Optic neuritis
... Fundus: pale disc swelling often involving only a segment of the disc, flame-shaped hemorrhages, optic atrophy after the edema resolves Visual field: altitudinal or central visual field defect Clinical types: Areritic Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy: due to giant cell arteritis: nonArerit ...
... Fundus: pale disc swelling often involving only a segment of the disc, flame-shaped hemorrhages, optic atrophy after the edema resolves Visual field: altitudinal or central visual field defect Clinical types: Areritic Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy: due to giant cell arteritis: nonArerit ...
Nap, a Novel Member of the Pentraxin Family, Promotes Neurite
... pentraxin family. When cocultured with Narp-secreting COS-1 cells, neurons of cortical explants exhibit enhanced growth of neuronal dendritic processes. Neurite outgrowth-promoting activity is also observed using partially purified Narp and can be specifically immunodepleted, demonstrating that Narp ...
... pentraxin family. When cocultured with Narp-secreting COS-1 cells, neurons of cortical explants exhibit enhanced growth of neuronal dendritic processes. Neurite outgrowth-promoting activity is also observed using partially purified Narp and can be specifically immunodepleted, demonstrating that Narp ...
The Formation of Terminal Fields in the Absence of Competitive
... cones follow a common pathway out of the spinal cord, and their axons are closely associated until they reach the horizontal septum, where they then proceed along divergent paths. By labeling individual CaP and RoP motoneurons with long-lasting vital fluorescent dyes, we were able to observe them di ...
... cones follow a common pathway out of the spinal cord, and their axons are closely associated until they reach the horizontal septum, where they then proceed along divergent paths. By labeling individual CaP and RoP motoneurons with long-lasting vital fluorescent dyes, we were able to observe them di ...
Highwire Regulates Guidance of Sister Axons in the
... which share a RING finger domain with ligase activity (Po et al., 2010). In Drosophila and C. elegans, PHR regulates synapse development at the axon terminal by downregulating the MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) Wallenda (Wnd)/DLK (dual leucine zipper kinase) to restrict MAPK signaling (Nakata et ...
... which share a RING finger domain with ligase activity (Po et al., 2010). In Drosophila and C. elegans, PHR regulates synapse development at the axon terminal by downregulating the MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) Wallenda (Wnd)/DLK (dual leucine zipper kinase) to restrict MAPK signaling (Nakata et ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The nervous system depends on a balance between neural excitation and inhibition to function effectively. B) Excitatory effects make an action potential more likely to occur, whereas inhibitory effects make action potentials less likely to occur. C) All neurotransmitters have both excitatory and ...
... A) The nervous system depends on a balance between neural excitation and inhibition to function effectively. B) Excitatory effects make an action potential more likely to occur, whereas inhibitory effects make action potentials less likely to occur. C) All neurotransmitters have both excitatory and ...
2009 McGraw-Hill Higher Education Site Map Any use is subject to
... Question 10 /novella/ALAQuiz ...
... Question 10 /novella/ALAQuiz ...
VIP in Neurological Diseases: More Than A Neuropeptide
... Fig. (2). Neuroimmune interactions in pathological states of the CNS. In the healthy central nervous system (CNS), an immune quiescent-like situation is showed, in which immune participation is related with neuron survival and brain protection. After CNS injury, important differences could be observ ...
... Fig. (2). Neuroimmune interactions in pathological states of the CNS. In the healthy central nervous system (CNS), an immune quiescent-like situation is showed, in which immune participation is related with neuron survival and brain protection. After CNS injury, important differences could be observ ...
Modality-Based Organization of Ascending Somatosensory Axons in
... was conducted in Shriners Hospitals Pediatric Research Center, Temple University. All surgical and postoperative procedures were performed in accordance with Temple’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and National Institutes of Health guidelines. Dorsal root transection of L4 –L5 was perfo ...
... was conducted in Shriners Hospitals Pediatric Research Center, Temple University. All surgical and postoperative procedures were performed in accordance with Temple’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and National Institutes of Health guidelines. Dorsal root transection of L4 –L5 was perfo ...
Mechanisms Underlying the Cardioinhibitory and Pressor
... stimulated by microinjection of sodium glutamate (25 mM Glu, 70 nl). To study if the NA, DMV, and CVLM relayed the cardioinhibitory messages from the FTG, 24 mM kainic acid (KA, 100 nl) was used as an excitotoxic agent to lesion neurons in the NA, DMV or CVLM. We found that the cardioinhibition indu ...
... stimulated by microinjection of sodium glutamate (25 mM Glu, 70 nl). To study if the NA, DMV, and CVLM relayed the cardioinhibitory messages from the FTG, 24 mM kainic acid (KA, 100 nl) was used as an excitotoxic agent to lesion neurons in the NA, DMV or CVLM. We found that the cardioinhibition indu ...
Anatomical Distribution of Serotonin- Containing
... axons will also be described. In the Results section, references to the work of other authors are given systematically after the description of our own observations. In this work, it was found that 5-HT-immunoreactive axons and varicosities arborize in every part of the gray matter in the brain and ...
... axons will also be described. In the Results section, references to the work of other authors are given systematically after the description of our own observations. In this work, it was found that 5-HT-immunoreactive axons and varicosities arborize in every part of the gray matter in the brain and ...
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Mediates Activity
... extent of the dendritic tree and saved for off-line tracing and analysis. Images were taken with the lowest practical laser intensity and the shortest practical illumination time to limit photodynamic damage, and slices were kept outside the incubator for ⬍1 hr per session. This imaging protocol was ...
... extent of the dendritic tree and saved for off-line tracing and analysis. Images were taken with the lowest practical laser intensity and the shortest practical illumination time to limit photodynamic damage, and slices were kept outside the incubator for ⬍1 hr per session. This imaging protocol was ...