temporal lobe
... Anterior segment filled with aqueous humor – liquid, replaced continuously Anterior chamber between cornea and iris Posterior chamber between iris and lens Glaucoma when problem with drainage resulting in increased intraocular pressure ...
... Anterior segment filled with aqueous humor – liquid, replaced continuously Anterior chamber between cornea and iris Posterior chamber between iris and lens Glaucoma when problem with drainage resulting in increased intraocular pressure ...
Chapter 3 Quiz
... Imagine the following scenario: Administrators at the local high school have been impressed by recent media reports of cerebral hemispheric specialization, and are considering curricular reform to achieve a better balance between “left-brained” and “right-brained” activities. You have been hired to ...
... Imagine the following scenario: Administrators at the local high school have been impressed by recent media reports of cerebral hemispheric specialization, and are considering curricular reform to achieve a better balance between “left-brained” and “right-brained” activities. You have been hired to ...
Cranial Nerves
... ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. This cranial nerve conveys impulses for touch, pain, and temperature sensations and proprioception. It is also involved in chewing. It is a mixed nerve. Cranial nerve VI is also mixed, and is called the abducens nerve. It is involved in movement of the eye, and ...
... ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. This cranial nerve conveys impulses for touch, pain, and temperature sensations and proprioception. It is also involved in chewing. It is a mixed nerve. Cranial nerve VI is also mixed, and is called the abducens nerve. It is involved in movement of the eye, and ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Fox Valley Lutheran High School
... at the next point of the membrane Unlike dominoes, it can restore itself. The mov’t. is only in one direction because Na gates will not open. The Role of Myelin Made of lipids & proteins, it forms an insulated sheath, wrapping around the the axon. Myelin has small nodes, gaps, between adjacent sheat ...
... at the next point of the membrane Unlike dominoes, it can restore itself. The mov’t. is only in one direction because Na gates will not open. The Role of Myelin Made of lipids & proteins, it forms an insulated sheath, wrapping around the the axon. Myelin has small nodes, gaps, between adjacent sheat ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... A sensory neuron that conducts the afferent impulse to the CNS The integration center (in interneuron of CNS) The motor neuron that conducts the efferent motor impulse from the CNS to an effector The effector which is muscle fibers or glands that respond to the motor impulse ...
... A sensory neuron that conducts the afferent impulse to the CNS The integration center (in interneuron of CNS) The motor neuron that conducts the efferent motor impulse from the CNS to an effector The effector which is muscle fibers or glands that respond to the motor impulse ...
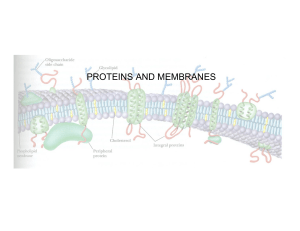
PROTEINS AND MEMBRANES
... applied heat stimuli to 186 healthy women, they found that those with the rare version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
... applied heat stimuli to 186 healthy women, they found that those with the rare version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
Neurophysiology
... - Trauma (caused by a fall or a blow) - Multiple sclerosis (destruction of Myelin sheath)) - Cerebral palsy (defect or injury to the brain that occurs at or shortly after birth) - Metabolic disorder (interferes with body's ability to maintain itself). ...
... - Trauma (caused by a fall or a blow) - Multiple sclerosis (destruction of Myelin sheath)) - Cerebral palsy (defect or injury to the brain that occurs at or shortly after birth) - Metabolic disorder (interferes with body's ability to maintain itself). ...
Nervous System WS (handed out after section exam)
... The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases because the myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing ion loss f ...
... The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases because the myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing ion loss f ...
11-Jun-15 1 - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... The synapse Neurons are separated by narrow gaps called synapses. synapses. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon it must pass to the next neuron. The neuron before the synapse (pre (pre-synaptic neuron) releases chemicals called neurotransmitters in response to the action potential. ...
... The synapse Neurons are separated by narrow gaps called synapses. synapses. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon it must pass to the next neuron. The neuron before the synapse (pre (pre-synaptic neuron) releases chemicals called neurotransmitters in response to the action potential. ...
Parts of the Nervous System
... Stellate cells of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum Spiny stellate cells represent the other major excitatory input to cortical pyramidal cells Small multipolar cells with local dendritic and axonal arborizations use glutamate or aspartate as transmitter. (NB. multipolar, meaning they have more tha ...
... Stellate cells of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum Spiny stellate cells represent the other major excitatory input to cortical pyramidal cells Small multipolar cells with local dendritic and axonal arborizations use glutamate or aspartate as transmitter. (NB. multipolar, meaning they have more tha ...
The Brain: It`s All In Your Mind
... changes in our environment and can be internal or external. ...
... changes in our environment and can be internal or external. ...
Neurophysiology
... Superior Olivary Complex Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculus Medial Geniculate Body Primary Auditory Cortex ...
... Superior Olivary Complex Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculus Medial Geniculate Body Primary Auditory Cortex ...
Biology and Behaviour
... Seems to me that if we are to truly understand behaviour and that if we accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
... Seems to me that if we are to truly understand behaviour and that if we accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
Nervous System powerpoint new
... 2. the frequency at which the neurons fire 3. the threshold level of different neurons (lower threshold neurons are more likely to fire, and are found in more “sensitive” ...
... 2. the frequency at which the neurons fire 3. the threshold level of different neurons (lower threshold neurons are more likely to fire, and are found in more “sensitive” ...
Ch.10
... spreads smoothly along the axon. • In myelinated fibers, action potential jump across the myelin segments to nodes of Ranvier. The hopping from node to node is much faster than non-myelinated conduction. • Additionally, ion channels are clustered at the nodes. • AP’s travel faster in large-diameter ...
... spreads smoothly along the axon. • In myelinated fibers, action potential jump across the myelin segments to nodes of Ranvier. The hopping from node to node is much faster than non-myelinated conduction. • Additionally, ion channels are clustered at the nodes. • AP’s travel faster in large-diameter ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 8) Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9) Describe the characteristics of an action potential. Explain the role of voltage-gated channels in this process. 10) Describe the two main factors that underlie the repolarizing phase of the action potential. 1 ...
... 8) Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9) Describe the characteristics of an action potential. Explain the role of voltage-gated channels in this process. 10) Describe the two main factors that underlie the repolarizing phase of the action potential. 1 ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 8) Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9) Describe the characteristics of an action potential. Explain the role of voltage-gated channels in this process. 10) Describe the two main factors that underlie the repolarizing phase of the action potential. 1 ...
... 8) Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9) Describe the characteristics of an action potential. Explain the role of voltage-gated channels in this process. 10) Describe the two main factors that underlie the repolarizing phase of the action potential. 1 ...
Neurons - E-Learning/An-Najah National University
... Neurons, also called nerve cells, are highly specialized to transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. Although neurons differ structurally, they have many common features (Figure 7.4). All have a cell body, which contains the nucleus and is the metabolic center of the ...
... Neurons, also called nerve cells, are highly specialized to transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. Although neurons differ structurally, they have many common features (Figure 7.4). All have a cell body, which contains the nucleus and is the metabolic center of the ...
nervoussystemwebquest
... Sensory neuron transmits information from a sensory receptor to a motor neuron, which signals an effector cell to carry out the response. The knee jerking reaction goes through the sensory neurons which relays the information to the stretch receptor in the thigh muscle, to interneurons in the spinal ...
... Sensory neuron transmits information from a sensory receptor to a motor neuron, which signals an effector cell to carry out the response. The knee jerking reaction goes through the sensory neurons which relays the information to the stretch receptor in the thigh muscle, to interneurons in the spinal ...
The Nervous System
... • Provides a two-way conduction pathway from the brain to and from the brain • 31 pairs of spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord • Cauda equina is a collection of spinal nerves at the inferior end ...
... • Provides a two-way conduction pathway from the brain to and from the brain • 31 pairs of spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord • Cauda equina is a collection of spinal nerves at the inferior end ...
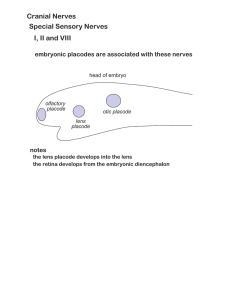
Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII
... Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
... Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
06 Muscular tissue Connective tissue
... • Homeostasis restored by inflammation and regeneration ...
... • Homeostasis restored by inflammation and regeneration ...
emboj7600621-sup
... point where nerve ring axons meet the midline. DAFD, DAWB, and DAWC are the distances from the grinder in terminal bulb to the center of each cell body. ...
... point where nerve ring axons meet the midline. DAFD, DAWB, and DAWC are the distances from the grinder in terminal bulb to the center of each cell body. ...
The Nervous System
... Nerves can regenerate in the PNS but not in the CNS Also the nervous system boasts the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) The ANS regulates involuntary actions such as: ...
... Nerves can regenerate in the PNS but not in the CNS Also the nervous system boasts the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) The ANS regulates involuntary actions such as: ...