Document
... Someone with paralysis of the anterior thigh muscles would have damage at which spinal segments? ...
... Someone with paralysis of the anterior thigh muscles would have damage at which spinal segments? ...
full program with abstracts
... occurring in these mice, we have performed high-coverage advanced quantitative sequential windowed dataindependent acquisition of total high-resolution mass spectra (SWATH-MS) mass spectrometry. Using this technique, we profiled proteomic changes in brain and spinal cord of transgenic rNLS TDP-43 mi ...
... occurring in these mice, we have performed high-coverage advanced quantitative sequential windowed dataindependent acquisition of total high-resolution mass spectra (SWATH-MS) mass spectrometry. Using this technique, we profiled proteomic changes in brain and spinal cord of transgenic rNLS TDP-43 mi ...
The resting membrane potential - Lectures For UG-5
... • As the current flows along the membrane, some of the current leaks through open leak channels (mainly K+) in the neighboring areas. As a result the membrane potential progressively decreases with increasing distance from the ...
... • As the current flows along the membrane, some of the current leaks through open leak channels (mainly K+) in the neighboring areas. As a result the membrane potential progressively decreases with increasing distance from the ...
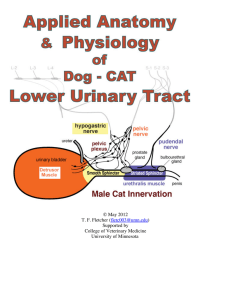
May 2012 TF Fletcher ()
... activated by parasympathetic innervation conveyed by the pelvic nerve. 2. Smooth muscle sphincter (internal urethral sphincter) = smooth muscle of the bladder neck and, in the case of females and male cat, the cranial urethra. It provides tonic resistance, when contracted by sympathetic innervation ...
... activated by parasympathetic innervation conveyed by the pelvic nerve. 2. Smooth muscle sphincter (internal urethral sphincter) = smooth muscle of the bladder neck and, in the case of females and male cat, the cranial urethra. It provides tonic resistance, when contracted by sympathetic innervation ...
Chapter 17- The Special Senses
... A) hyperopia B) myopia C) astigmatism D) astigmatism and myopia E) astigmatism and hyperopia 27) Which of the following is correct? A) Convergence refers to the type of vision resulting when both eyes focus on one set of objects. B) Binocular vision refers to medial movements that directed both eyes ...
... A) hyperopia B) myopia C) astigmatism D) astigmatism and myopia E) astigmatism and hyperopia 27) Which of the following is correct? A) Convergence refers to the type of vision resulting when both eyes focus on one set of objects. B) Binocular vision refers to medial movements that directed both eyes ...
Primate Red Nucleus Discharge Encodes the Dynamics of Limb
... The timing of the onset of both neuronal discharge and movement can be reliably determined from Fig. 1 as can mean firing rates during and between movements. Discharge of this neuron began 70 { 20 (SD) ms before wrist movement onset. The latency between discharge and movement termination was shorter ...
... The timing of the onset of both neuronal discharge and movement can be reliably determined from Fig. 1 as can mean firing rates during and between movements. Discharge of this neuron began 70 { 20 (SD) ms before wrist movement onset. The latency between discharge and movement termination was shorter ...
Watching synapses during sensory information
... Spines cover the entire dendrites of many neurons, and have been widely accepted as major sites for receiving synaptic inputs that contain specific features of information [2]. The integrative properties of inputs by dendrites are determined by multiple factors, including dendritic morphology, activ ...
... Spines cover the entire dendrites of many neurons, and have been widely accepted as major sites for receiving synaptic inputs that contain specific features of information [2]. The integrative properties of inputs by dendrites are determined by multiple factors, including dendritic morphology, activ ...
From Membrane to Cytoskeleton: Minireview
... (Abl kinase) important in regulating axon guidance. These studies provide a provocative link from the cell surface to the actin cytoskeleton through the Ena/VASP family of proteins and Profilin, both of which are known to regulate actin dynamics and are shown in these papers to play important roles ...
... (Abl kinase) important in regulating axon guidance. These studies provide a provocative link from the cell surface to the actin cytoskeleton through the Ena/VASP family of proteins and Profilin, both of which are known to regulate actin dynamics and are shown in these papers to play important roles ...
Copy of the full paper
... and describes individual ionic and synaptic conductances for each neuron in accordance with the dynamics of ionic channels. This type of model is necessary to emulate the dynamics of individual neurons within a network. Conductance-based models reduced to 2 dimensions are also very popular, as they ...
... and describes individual ionic and synaptic conductances for each neuron in accordance with the dynamics of ionic channels. This type of model is necessary to emulate the dynamics of individual neurons within a network. Conductance-based models reduced to 2 dimensions are also very popular, as they ...
Dendrites as separate compartment – local protein synthesis
... spines on pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex, (Spacek and Hartmann 1983, Spacek 1985). These numbers indicate that polyribosomes are ubiquitous component of the dendroplasm and that local protein synthesis may be a common process in multiple classes of brain neurons. Although there are no late ...
... spines on pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex, (Spacek and Hartmann 1983, Spacek 1985). These numbers indicate that polyribosomes are ubiquitous component of the dendroplasm and that local protein synthesis may be a common process in multiple classes of brain neurons. Although there are no late ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... back and gives rise to nerves of the limbs. i. The anterior rami vary from one region to another; in the thoracic region it forms an intercostal nerve, and in all other regions form the nerve plexuses. ii. The anterior ramus also gives off a pair of communicating rami that connect with a string of s ...
... back and gives rise to nerves of the limbs. i. The anterior rami vary from one region to another; in the thoracic region it forms an intercostal nerve, and in all other regions form the nerve plexuses. ii. The anterior ramus also gives off a pair of communicating rami that connect with a string of s ...
Signalling organelle for retrograde axonal transport of
... more likely that the neurotrophins stimulate retrograde transport of the activated Trks, bound to their cognate ligand, to transmit this information14 by delivering an activated receptor to the cell body.15 Neurotrophins have two types of receptor: the high-affinity Trk family of tyrosine kinase rec ...
... more likely that the neurotrophins stimulate retrograde transport of the activated Trks, bound to their cognate ligand, to transmit this information14 by delivering an activated receptor to the cell body.15 Neurotrophins have two types of receptor: the high-affinity Trk family of tyrosine kinase rec ...
Olfaction
... Mice have more than 1400 different types of olfactory receptor proteins, humans have about 350 different types, and fish about 60 different types. ...
... Mice have more than 1400 different types of olfactory receptor proteins, humans have about 350 different types, and fish about 60 different types. ...
Lab #6: Neurophysiology Simulation
... black mambas) prevents voltage-gated K+ channels from opening, preventing repolarization of an axon during an action potential and thus greatly increasing the refractory period for an action potential and slowing conduction velocity. 2) Synaptic transmission of signals – the primary means by which m ...
... black mambas) prevents voltage-gated K+ channels from opening, preventing repolarization of an axon during an action potential and thus greatly increasing the refractory period for an action potential and slowing conduction velocity. 2) Synaptic transmission of signals – the primary means by which m ...
Assisted morphogenesis: glial control of dendrite
... documented [1]. This diversity is in no small part a result of each dendrite’s unique task: to gather information from specific synaptic partners or from the environment, and to transmit this information to the axon. In mammals, dendritic arbors can be highly branched, and individual dendrite branch ...
... documented [1]. This diversity is in no small part a result of each dendrite’s unique task: to gather information from specific synaptic partners or from the environment, and to transmit this information to the axon. In mammals, dendritic arbors can be highly branched, and individual dendrite branch ...
Network Self-Organization Explains the Statistics and
... due to STDP grows approximately linearly with the strength of the synapse (Fig. 5A). The fraction of connections undergoing depression depends much less on connection weight (Fig. 5B). Thus, the net effect is that stronger synaptic connections have a higher chance to be potentiated by STDP establish ...
... due to STDP grows approximately linearly with the strength of the synapse (Fig. 5A). The fraction of connections undergoing depression depends much less on connection weight (Fig. 5B). Thus, the net effect is that stronger synaptic connections have a higher chance to be potentiated by STDP establish ...
Swim Initiation Neurons in Tritonia diomedea1
... was hyperpolarized to prevent its spiking. This procedure failed to prevent the swim motor program, consistent with the view that DRI is not part of the cycle generating mechanism, but instead functions as a preCPG command neuron. During the swim motor program, C2, DSI and DRI received inhibition du ...
... was hyperpolarized to prevent its spiking. This procedure failed to prevent the swim motor program, consistent with the view that DRI is not part of the cycle generating mechanism, but instead functions as a preCPG command neuron. During the swim motor program, C2, DSI and DRI received inhibition du ...
Page SCH 23390 SCH 23390 is a synthetic compound that
... inhibition and this disruption is reversed by classical and atypical antipsychotics. Pretreatment with the D1 antagonist SCH 23390 (0.01, 0.05, 0.1 mg/kg SC) or the D2 antagonist eticlopride (0.01, 0.05, 0.1 mg/kg SC) attenuated the disruptive effects of apomorphine. These results indicate that sele ...
... inhibition and this disruption is reversed by classical and atypical antipsychotics. Pretreatment with the D1 antagonist SCH 23390 (0.01, 0.05, 0.1 mg/kg SC) or the D2 antagonist eticlopride (0.01, 0.05, 0.1 mg/kg SC) attenuated the disruptive effects of apomorphine. These results indicate that sele ...
Patterning and axon guidance of cranial motor neurons
... and r5, the glossopharyngeal nucleus (nucleus IX; BM and VM neurons) lies in r6 (in mice) or r6 and r7 (in chicks), and the vagus nucleus (nucleus X; BM and VM neurons) and cranial accessory nucleus (XI; BM neurons) occupy r7 and r8 (REF.10) (FIG. 2). In the caudal hindbrain, the abducens nucleus (n ...
... and r5, the glossopharyngeal nucleus (nucleus IX; BM and VM neurons) lies in r6 (in mice) or r6 and r7 (in chicks), and the vagus nucleus (nucleus X; BM and VM neurons) and cranial accessory nucleus (XI; BM neurons) occupy r7 and r8 (REF.10) (FIG. 2). In the caudal hindbrain, the abducens nucleus (n ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.