Physical Science Practice Midterm
... you put in. o (W out) can never be greater than (Win) In an ideal machine, Win = Wout o In this system Fe x de = Fr x dr o In most cases, a machine multiplies the force applied to it, Fr is greater than Fe o The machine multiplies your effort but you must move the handle a greater distance. ...
... you put in. o (W out) can never be greater than (Win) In an ideal machine, Win = Wout o In this system Fe x de = Fr x dr o In most cases, a machine multiplies the force applied to it, Fr is greater than Fe o The machine multiplies your effort but you must move the handle a greater distance. ...
Principles of Engineering
... The ___________ effect of a force about a point, equal to the magnitude of the force times the perpendicular distance from the point to the line of action from the force. Moment = __________ x ____________ Torque: A force that produces or tends to produce ____________ or ____________. Lever Moment C ...
... The ___________ effect of a force about a point, equal to the magnitude of the force times the perpendicular distance from the point to the line of action from the force. Moment = __________ x ____________ Torque: A force that produces or tends to produce ____________ or ____________. Lever Moment C ...
force - Cloudfront.net
... Weight and Mass • Weight and mass are not the same. • Weight is a force and mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains. • Weight and mass are related. Weight increases as mass increases. ...
... Weight and Mass • Weight and mass are not the same. • Weight is a force and mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains. • Weight and mass are related. Weight increases as mass increases. ...
Force and acceleration Chapter_3_Lesson_1
... • If two surfaces are in contact, welding or sticking occurs where the bumps touch each other. • These microwelds are the source of friction. ...
... • If two surfaces are in contact, welding or sticking occurs where the bumps touch each other. • These microwelds are the source of friction. ...
Homework 6 Problems: Energy and Work
... angle of 25° below the horizontal. The force is just sufficient to overcome various frictional forces so the cart moves at constant speed. a. Find the work done by the shopper as she moves down a 50.0-m length aisle. b. What is the net work done on the cart? Explain why. c. The shopper goes down the ...
... angle of 25° below the horizontal. The force is just sufficient to overcome various frictional forces so the cart moves at constant speed. a. Find the work done by the shopper as she moves down a 50.0-m length aisle. b. What is the net work done on the cart? Explain why. c. The shopper goes down the ...
Supplementary exercise for Ch.1 to 4
... Which of the following phenomena can be explained with the Newton’s first law of motion? (1) When a car stops suddenly, passengers will be thrown forwards. (2) A coin and a feather will fall with the same acceleration in vacuum. (3) A spaceman on the moon can lift up a body heavier than on the earth ...
... Which of the following phenomena can be explained with the Newton’s first law of motion? (1) When a car stops suddenly, passengers will be thrown forwards. (2) A coin and a feather will fall with the same acceleration in vacuum. (3) A spaceman on the moon can lift up a body heavier than on the earth ...
Forces Review Game
... Andy pushes 65 kg crate with a horizontal force of 250 N across the physics portable at a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s. Trying to be helpful and knowing a bit of physics, Betty uses a rope to pull directly up on the box. The coefficient of static friction is 0.70 and the coefficient of kinetic frict ...
... Andy pushes 65 kg crate with a horizontal force of 250 N across the physics portable at a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s. Trying to be helpful and knowing a bit of physics, Betty uses a rope to pull directly up on the box. The coefficient of static friction is 0.70 and the coefficient of kinetic frict ...
Forces and Motion Review2
... accelerating…but still moving) The object is falling at a constant velocity ...
... accelerating…but still moving) The object is falling at a constant velocity ...
Motion and Forces ppt.
... ACCELERATION – Change in the speed or direction of an object over time. *A decrease in velocity is negative acceleration *An increase in velocity is positive acceleration ...
... ACCELERATION – Change in the speed or direction of an object over time. *A decrease in velocity is negative acceleration *An increase in velocity is positive acceleration ...
Chapter 4 Introducing Forces
... contact but which act over a distance are called non contact forces e.g. electric, magnetic, gravitational ...
... contact but which act over a distance are called non contact forces e.g. electric, magnetic, gravitational ...
Document
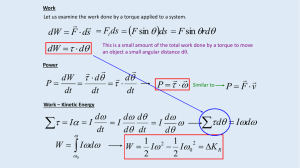
... Rolling motion (No Slipping) The majority of motion we have been discussing is translational motion. We have recently been exploring rotational motion. Now we will look at both together. If a wheel is placed on a flat surface and a force is applied at the center of the wheel what will it do? It wil ...
... Rolling motion (No Slipping) The majority of motion we have been discussing is translational motion. We have recently been exploring rotational motion. Now we will look at both together. If a wheel is placed on a flat surface and a force is applied at the center of the wheel what will it do? It wil ...
Exam 1
... people on the small island, who had been stranded there due to a ship wreck watched the box fall and they know the box contains food as they had been in contact with rescue crews earlier for a brief moment before their cell phone died and expected the plane to search for them and bring food even tho ...
... people on the small island, who had been stranded there due to a ship wreck watched the box fall and they know the box contains food as they had been in contact with rescue crews earlier for a brief moment before their cell phone died and expected the plane to search for them and bring food even tho ...
Rolling resistance

Rolling resistance, sometimes called rolling friction or rolling drag, is the force resisting the motion when a body (such as a ball, tire, or wheel) rolls on a surface. It is mainly caused by non-elastic effects; that is, not all the energy needed for deformation (or movement) of the wheel, roadbed, etc. is recovered when the pressure is removed. Two forms of this are hysteresis losses (see below), and permanent (plastic) deformation of the object or the surface (e.g. soil). Another cause of rolling resistance lies in the slippage between the wheel and the surface, which dissipates energy. Note that only the last of these effects involves friction, therefore the name ""rolling friction"" is to an extent a misnomer.In analogy with sliding friction, rolling resistance is often expressed as a coefficient times the normal force. This coefficient of rolling resistance is generally much smaller than the coefficient of sliding friction.Any coasting wheeled vehicle will gradually slow down due to rolling resistance including that of the bearings, but a train car with steel wheels running on steel rails will roll farther than a bus of the same mass with rubber tires running on tarmac. Factors that contribute to rolling resistance are the (amount of) deformation of the wheels, the deformation of the roadbed surface, and movement below the surface. Additional contributing factors include wheel diameter, speed, load on wheel, surface adhesion, sliding, and relative micro-sliding between the surfaces of contact. The losses due to hysteresis also depend strongly on the material properties of the wheel or tire and the surface. For example, a rubber tire will have higher rolling resistance on a paved road than a steel railroad wheel on a steel rail. Also, sand on the ground will give more rolling resistance than concrete.