HP Unit 3 - student handout
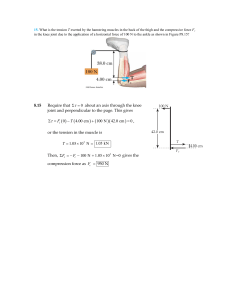
... Assume a frictionless & negligible mass pulley. If the system is released from rest, determine the speed of the 5kg mass after it has fallen for 1.3s. ...
... Assume a frictionless & negligible mass pulley. If the system is released from rest, determine the speed of the 5kg mass after it has fallen for 1.3s. ...
mi05sol
... given by fk = kN. The constants s and k are called the coefficients of friction and are determined experimentally. They depend on the properties of the two surfaces, and we usually assume that they don’t depend on the speed of the sliding. In contrast, air resistance does depend on the velocity o ...
... given by fk = kN. The constants s and k are called the coefficients of friction and are determined experimentally. They depend on the properties of the two surfaces, and we usually assume that they don’t depend on the speed of the sliding. In contrast, air resistance does depend on the velocity o ...
Vitreous Enamel Coated Wirewound Resistors - KNP
... The KNP-VE Series of vitreous enamel coated power resistors from Token offers a cost-competitive alternative over the 2.5W-12W power range. The range is available with resistance values of 1Ω to 39KΩ in power ratings of 2.5W, 3W, 5W, 6W, 8W, 9W and 12W (at 25°C), and with body sizes that match the i ...
... The KNP-VE Series of vitreous enamel coated power resistors from Token offers a cost-competitive alternative over the 2.5W-12W power range. The range is available with resistance values of 1Ω to 39KΩ in power ratings of 2.5W, 3W, 5W, 6W, 8W, 9W and 12W (at 25°C), and with body sizes that match the i ...
FRICTION
... FRICTION - the force that present whenever two surfaces are in contact and always acts opposite to the direction of motion. Depends on: • Type of materials in contact • Surfaces of materials ...
... FRICTION - the force that present whenever two surfaces are in contact and always acts opposite to the direction of motion. Depends on: • Type of materials in contact • Surfaces of materials ...
Document
... what factor does the dissipated power change? a) the same b) doubles (factor of 2) c) quadruples (factor of 4) d) halves (factor of 0.5) Ax2 and lx4 so Rx2. Vx2 (note that I=V/R=constant) P=V2/R so Px2 PHY232 - Current & Resistance ...
... what factor does the dissipated power change? a) the same b) doubles (factor of 2) c) quadruples (factor of 4) d) halves (factor of 0.5) Ax2 and lx4 so Rx2. Vx2 (note that I=V/R=constant) P=V2/R so Px2 PHY232 - Current & Resistance ...
Current & Resistance PHY232 – Spring 2008 Jon Pumplin
... electric current III: what really happens When electrons move through a wire they undergo many collisions and a typical path looks like: ...
... electric current III: what really happens When electrons move through a wire they undergo many collisions and a typical path looks like: ...
Chapter 3 lecture notes
... rest above your head? What is the net force on it after you release it? 3. A bear that weighs 4000 N grasps a vertical tree and slides down at constant velocity. What is the friction force that acts on the bear? 4. Two basketballs are dropped from a high building through the air. One ball is hollow ...
... rest above your head? What is the net force on it after you release it? 3. A bear that weighs 4000 N grasps a vertical tree and slides down at constant velocity. What is the friction force that acts on the bear? 4. Two basketballs are dropped from a high building through the air. One ball is hollow ...
Rolling resistance

Rolling resistance, sometimes called rolling friction or rolling drag, is the force resisting the motion when a body (such as a ball, tire, or wheel) rolls on a surface. It is mainly caused by non-elastic effects; that is, not all the energy needed for deformation (or movement) of the wheel, roadbed, etc. is recovered when the pressure is removed. Two forms of this are hysteresis losses (see below), and permanent (plastic) deformation of the object or the surface (e.g. soil). Another cause of rolling resistance lies in the slippage between the wheel and the surface, which dissipates energy. Note that only the last of these effects involves friction, therefore the name ""rolling friction"" is to an extent a misnomer.In analogy with sliding friction, rolling resistance is often expressed as a coefficient times the normal force. This coefficient of rolling resistance is generally much smaller than the coefficient of sliding friction.Any coasting wheeled vehicle will gradually slow down due to rolling resistance including that of the bearings, but a train car with steel wheels running on steel rails will roll farther than a bus of the same mass with rubber tires running on tarmac. Factors that contribute to rolling resistance are the (amount of) deformation of the wheels, the deformation of the roadbed surface, and movement below the surface. Additional contributing factors include wheel diameter, speed, load on wheel, surface adhesion, sliding, and relative micro-sliding between the surfaces of contact. The losses due to hysteresis also depend strongly on the material properties of the wheel or tire and the surface. For example, a rubber tire will have higher rolling resistance on a paved road than a steel railroad wheel on a steel rail. Also, sand on the ground will give more rolling resistance than concrete.