APPLICATION OF FORCES
... • Angular Velocity – the rate of movement in rotation (its speed) • Newton’s 1st Law of Angular Motion: • ‘a rotating body will continue to turn about its axis with constant angular momentum unless an external force acts upon it. ...
... • Angular Velocity – the rate of movement in rotation (its speed) • Newton’s 1st Law of Angular Motion: • ‘a rotating body will continue to turn about its axis with constant angular momentum unless an external force acts upon it. ...
J.
... it exhibits the difficulty of associating the effect of the magnetic field with the sign change of half-integer spin particles under rotations through 2m'. The point is this: Any rotation of a particle with nonzero angular momentum must be effected by applying a torque. Such a torque would be repres ...
... it exhibits the difficulty of associating the effect of the magnetic field with the sign change of half-integer spin particles under rotations through 2m'. The point is this: Any rotation of a particle with nonzero angular momentum must be effected by applying a torque. Such a torque would be repres ...
rotational kinetic energy
... KE (rotatory) = KE (translatory) if k = 1 or I = mR2. This is true for a ring. Hence, answer is (d). ...
... KE (rotatory) = KE (translatory) if k = 1 or I = mR2. This is true for a ring. Hence, answer is (d). ...
Scattering
... The material parameters in the Maxwell equations are macroscopic quantities. Therefore, the electromagnetic fields solved from the equations are some kind of averages of the microscopic field distributions. For example, when we study radio wave propagation in the air we do not solve the fields actin ...
... The material parameters in the Maxwell equations are macroscopic quantities. Therefore, the electromagnetic fields solved from the equations are some kind of averages of the microscopic field distributions. For example, when we study radio wave propagation in the air we do not solve the fields actin ...
Rotational Motion
... closer to the center of rotation because it is an internal force that redistributes her mass with respect to the rotational axis. Only an external force with a lever arm can generate an external torque which can change the angular momentum. The skater’s movements decrease her moment of inertia, whic ...
... closer to the center of rotation because it is an internal force that redistributes her mass with respect to the rotational axis. Only an external force with a lever arm can generate an external torque which can change the angular momentum. The skater’s movements decrease her moment of inertia, whic ...
Polarization
... • Circa1670 Christian Huygens first suggested the vectoral nature of light to explain its behavior propagating through crystals. • In the words of Newton (~1672), it appeared as though light had “sides…” • In 1818 Fresnel and Arago were able to explain Young’s interference experiment with a with a ...
... • Circa1670 Christian Huygens first suggested the vectoral nature of light to explain its behavior propagating through crystals. • In the words of Newton (~1672), it appeared as though light had “sides…” • In 1818 Fresnel and Arago were able to explain Young’s interference experiment with a with a ...
Chapter 8: Energy Quantization
... 1. While the electron is most likely to be found at certain radii, which in the language of quantum mechanics is the expectation value, they
must be treated as waves and therefore do not
have fixed radial distances. In fact, the electrons
do not travel in circular orbits, but can be found
anywh ...
... 1. While the electron is most likely to be found at certain radii, which in the language of quantum mechanics is the expectation value
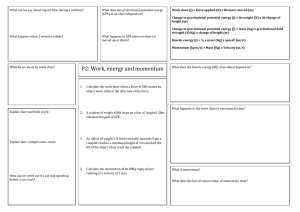
AP Physics I - Southern Regional School District
... Marking Period 2 Topics/Units to be covered: • Vocabulary, key terms, and proper S.I. units ...
... Marking Period 2 Topics/Units to be covered: • Vocabulary, key terms, and proper S.I. units ...