Unit Objectives
... 6. Distinguish between a scalar and a vector physical quantity. (Chapter one) Be able to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector Be able to determine the components of a vector Know how to add and subtract vectors graphically and mathematically 7. Be able to use multiple representati ...
... 6. Distinguish between a scalar and a vector physical quantity. (Chapter one) Be able to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector Be able to determine the components of a vector Know how to add and subtract vectors graphically and mathematically 7. Be able to use multiple representati ...
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum
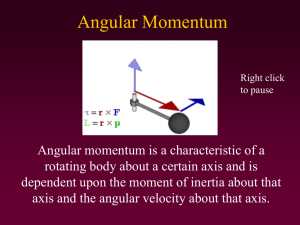
... • From the previous, the relations among the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation ...
... • From the previous, the relations among the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation ...
CHAPTER 3: The Experimental Basis of Quantum Theory
... Classical theory predicts that the total amount of energy in a light wave increases as the light intensity increases. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends on the value of the light frequency f and not on the intensity. The existence of a threshold frequency is completely inexplic ...
... Classical theory predicts that the total amount of energy in a light wave increases as the light intensity increases. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends on the value of the light frequency f and not on the intensity. The existence of a threshold frequency is completely inexplic ...
Jovian Planet Systems
... • It occurs during a supernova. While the supernova is in the process of ripping apart a star, the stellar material is flooded with neutrons. • During the few seconds (or milliseconds) of the explosion neutrons are absorbed much faster then the atoms can decay, so the isotopes are pushed far to the ...
... • It occurs during a supernova. While the supernova is in the process of ripping apart a star, the stellar material is flooded with neutrons. • During the few seconds (or milliseconds) of the explosion neutrons are absorbed much faster then the atoms can decay, so the isotopes are pushed far to the ...
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
... A bowling ball of mass m and radius R is initially thrown down an alley with an initial speed v0 and backspin with angular speed 0 , such that v0 R 0 . The moment of inertia of the ball about its center of mass is Icm (2 / 5)mR2 . Your goal is to determine the speed vf of the bowling ball wh ...
... A bowling ball of mass m and radius R is initially thrown down an alley with an initial speed v0 and backspin with angular speed 0 , such that v0 R 0 . The moment of inertia of the ball about its center of mass is Icm (2 / 5)mR2 . Your goal is to determine the speed vf of the bowling ball wh ...
The Fresnel Equations and Brewster`s Law
... Brewster’s Law may be understood by the following intuitive argument: the electric field vector is transverse to the forward direction. However, at the point where the light polarized in the plane of incidence starts to enter the glass the vibrations in the transmitted wave happen to be parallel to ...
... Brewster’s Law may be understood by the following intuitive argument: the electric field vector is transverse to the forward direction. However, at the point where the light polarized in the plane of incidence starts to enter the glass the vibrations in the transmitted wave happen to be parallel to ...
The present status of the problem of neutrino theory is briefly
... antineutrinos, i.e. a right-handed "neutrino" would be an antineutrino. Particles of this sort are called Majorana particles. As long as the neutrino is massless, its helicity is completely defined, and a Majorana neutrino would be a different particle from its antineutrino. But if neutrinos have ma ...
... antineutrinos, i.e. a right-handed "neutrino" would be an antineutrino. Particles of this sort are called Majorana particles. As long as the neutrino is massless, its helicity is completely defined, and a Majorana neutrino would be a different particle from its antineutrino. But if neutrinos have ma ...
Outline Mechanical Systems Kinematics Example Projectile Motion
... • Perfectly inelastic collision – Example - two lumps of clay – Conserve momentum and the two objects stick together ...
... • Perfectly inelastic collision – Example - two lumps of clay – Conserve momentum and the two objects stick together ...
PH212Chapter11_15
... • From the previous, the relations among the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation ...
... • From the previous, the relations among the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation ...