Topic 11.5: Polarization
... • The reflected ray contains more vibrations parallel to the reflecting surface while the transmitted beam contains more vibrations at right angles to these. ...
... • The reflected ray contains more vibrations parallel to the reflecting surface while the transmitted beam contains more vibrations at right angles to these. ...
feb18_rg
... Since the galactic plane is thin, face-on galaxies seldom exhibit evidence for significant optical thickness: the vast majority of the atomic gas is in optically thin clouds. As disks approach the edge-on aspect, velocity spread to a large extent prevents optical depth to increase significantly. As ...
... Since the galactic plane is thin, face-on galaxies seldom exhibit evidence for significant optical thickness: the vast majority of the atomic gas is in optically thin clouds. As disks approach the edge-on aspect, velocity spread to a large extent prevents optical depth to increase significantly. As ...
Slide 1
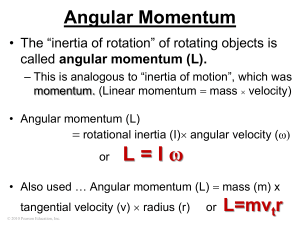
... momentum . mass, but carries ______________ and ________________ Its energy is given by: ...
... momentum . mass, but carries ______________ and ________________ Its energy is given by: ...
Purdue University PHYS221 EXAM II Solutions are
... 15.You are standing one meter front of a short flat mirror which is placed too high, so you can see above your head, but only down to your knees. To see your shoes you must: (a) move 0.5 m closer to the mirror (b) move so close to the mirror yo are almost touching it. (c) move further from the mirro ...
... 15.You are standing one meter front of a short flat mirror which is placed too high, so you can see above your head, but only down to your knees. To see your shoes you must: (a) move 0.5 m closer to the mirror (b) move so close to the mirror yo are almost touching it. (c) move further from the mirro ...