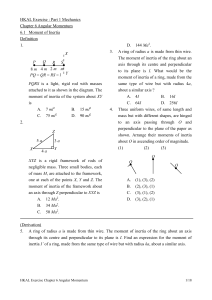
Momentum
... immediately before and after the collision if there isn’t net external force acting on the system. Two objects moving horizontally on a level rough table will not conserve momentum when they collide because of the force of kinetic friction. If the initial momentum was large and the collision lasted ...
... immediately before and after the collision if there isn’t net external force acting on the system. Two objects moving horizontally on a level rough table will not conserve momentum when they collide because of the force of kinetic friction. If the initial momentum was large and the collision lasted ...
Work, Energy, and Momentum
... • Impulse is a quantity in physics that is used to describe a force applied on an object during a given time interval, • Impulse is defined as the product of the force and the time over which the force acts on the object • The impulse-momentum theorem states that the impulse acting an object is equ ...
... • Impulse is a quantity in physics that is used to describe a force applied on an object during a given time interval, • Impulse is defined as the product of the force and the time over which the force acts on the object • The impulse-momentum theorem states that the impulse acting an object is equ ...
1 - PLK Vicwood KT Chong Sixth Form College
... photon whose energy is just enough for exciting it to a higher energy state. When the excited molecule returns to ground state, it re-emits light of the same wavelength of the photon but equally in all directions. So the intensity of the radiation in the direction of the incident photon is reduced. ...
... photon whose energy is just enough for exciting it to a higher energy state. When the excited molecule returns to ground state, it re-emits light of the same wavelength of the photon but equally in all directions. So the intensity of the radiation in the direction of the incident photon is reduced. ...
Lecture 14 - Purdue Physics
... Electromagnetic Spectrum • All em waves travel through a vacuum at the speed c • c = 2.99792458 x 108 m/s ~ 3.00 x 108 m/s • c is defined to have this value and the value of a meter is derived from this speed • Electromagnetic waves are classified according to ...
... Electromagnetic Spectrum • All em waves travel through a vacuum at the speed c • c = 2.99792458 x 108 m/s ~ 3.00 x 108 m/s • c is defined to have this value and the value of a meter is derived from this speed • Electromagnetic waves are classified according to ...
Rotational Motion Test Review
... 13. A comet orbiting the Sun can be considered an isolated system with no outside forces or torques acting on it. As the comet moves in its highly elliptical orbit, what remains constant? A. Its distant from the Sun B. Its angular speed C. Its linear speed D. Its angular momentum E. The gravitationa ...
... 13. A comet orbiting the Sun can be considered an isolated system with no outside forces or torques acting on it. As the comet moves in its highly elliptical orbit, what remains constant? A. Its distant from the Sun B. Its angular speed C. Its linear speed D. Its angular momentum E. The gravitationa ...
PHOTOELASTICITY
... An “ordinary” light is an electromagnetic wave that passes through transparent material in some direction the material’s atoms are excited in some direction, perpendicular to the light direction. Because the time interval of the excitation is about 1e-8 second and each atom is excited in some direct ...
... An “ordinary” light is an electromagnetic wave that passes through transparent material in some direction the material’s atoms are excited in some direction, perpendicular to the light direction. Because the time interval of the excitation is about 1e-8 second and each atom is excited in some direct ...
final-S06
... choose the best answers in the context of what we have learned in Physics I. On graphing and numerical questions (Parts B and C), show all work to receive credit. IMPORTANT REMINDER FOR PARTS B AND C: You are allowed to use only the formulas given with the exam and standard math (trigonometry, algeb ...
... choose the best answers in the context of what we have learned in Physics I. On graphing and numerical questions (Parts B and C), show all work to receive credit. IMPORTANT REMINDER FOR PARTS B AND C: You are allowed to use only the formulas given with the exam and standard math (trigonometry, algeb ...
PSB Final Review
... 8. Accelerated motion is represented by a(an) ____________________ line on a distance-time graph. 9. A car that increases its speed from 20 km/h to 100 km/h undergoes ____________________ acceleration. 10. A push or pull is an example of a(an) ____________________. 11. If the forces acting on an obj ...
... 8. Accelerated motion is represented by a(an) ____________________ line on a distance-time graph. 9. A car that increases its speed from 20 km/h to 100 km/h undergoes ____________________ acceleration. 10. A push or pull is an example of a(an) ____________________. 11. If the forces acting on an obj ...
PHY131 Physics Exam Ch 7
... through the center of mass of a 8.00 kg block initially at rest. The bullet emerges from the block moving directly upward at 400 m/s. To what maximum height does the block then rise above its initial position if the block rests inside a box full of compressible green ooze? (The force applied by the ...
... through the center of mass of a 8.00 kg block initially at rest. The bullet emerges from the block moving directly upward at 400 m/s. To what maximum height does the block then rise above its initial position if the block rests inside a box full of compressible green ooze? (The force applied by the ...
Is the electron a photon with toroidal topology?
... Moving backwards or forwards along the strip represents a transformation in space, but equally well a transformation in time (i.e. x ct). This works for the photon illustrated in Fig. 1a, either moving along the strip, or waiting for the strip to pass you by, will give a rotation of the eld compone ...
... Moving backwards or forwards along the strip represents a transformation in space, but equally well a transformation in time (i.e. x ct). This works for the photon illustrated in Fig. 1a, either moving along the strip, or waiting for the strip to pass you by, will give a rotation of the eld compone ...