PHYS_2326_022609
... In electrostatic situations – no E-field inside There is no net current. But charges (electrons) still move chaotically, they are not on rest. On the other side, electrons do not move with ...
... In electrostatic situations – no E-field inside There is no net current. But charges (electrons) still move chaotically, they are not on rest. On the other side, electrons do not move with ...
Norton`s Theorems
... Definitions for Norton’s Theorem Input resistance is the resistance seen by the load when IN = 0A. ...
... Definitions for Norton’s Theorem Input resistance is the resistance seen by the load when IN = 0A. ...
Name: Record Responses in med blue bold font Module 8 Lesson 2
... The net movement of electric charges in a single direction is an ______. In a metal wire, or any material, electrons are in ______ _______in all directions. As a result, there is no net movement of electrons in one direction. When an electric current flows in the wire, electrons continue their rando ...
... The net movement of electric charges in a single direction is an ______. In a metal wire, or any material, electrons are in ______ _______in all directions. As a result, there is no net movement of electrons in one direction. When an electric current flows in the wire, electrons continue their rando ...
– Simple turn-off description of Trench- Field-stop IGBT IGBT
... simple equivalent circuit contains the output characteristics, CGC-, CGE-, and the new CCEcapacitance. This circuit describes principal switching and control characteristics. Characterization of these elements is done by special test configurations, which allow excluding parasitic capacitance of the ...
... simple equivalent circuit contains the output characteristics, CGC-, CGE-, and the new CCEcapacitance. This circuit describes principal switching and control characteristics. Characterization of these elements is done by special test configurations, which allow excluding parasitic capacitance of the ...
CAPACITANCE
... In a 20V RC circuit, if 20V is measured across the resistor and 40V across the capacitor, the applied voltage is A. 50V B. 55V C. 60V D. 45V ...
... In a 20V RC circuit, if 20V is measured across the resistor and 40V across the capacitor, the applied voltage is A. 50V B. 55V C. 60V D. 45V ...
Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) notes
... Silicon Controlled Rectifiers, almost exclusively referred to as SCRs, are one of a small group of devices known as Thyristors. They (SCRs) are three terminal devices that perform in a manner similar to a silicon diode with an ‘On’ switch but no ‘Off’ switch. That is, they will not conduct even if f ...
... Silicon Controlled Rectifiers, almost exclusively referred to as SCRs, are one of a small group of devices known as Thyristors. They (SCRs) are three terminal devices that perform in a manner similar to a silicon diode with an ‘On’ switch but no ‘Off’ switch. That is, they will not conduct even if f ...
The circuit in this problem has two resistors, one capacitor,... The power supply is a sinusoidal voltage source with an...
... The circuit in this problem has two resistors, one capacitor, and one inductor. The power supply is a sinusoidal voltage source with an amplitude of 4 volts and a frequency of 3,000 radians per second. We want to find the apparent power absorbed by the load in the circuit. If we can find the voltage ...
... The circuit in this problem has two resistors, one capacitor, and one inductor. The power supply is a sinusoidal voltage source with an amplitude of 4 volts and a frequency of 3,000 radians per second. We want to find the apparent power absorbed by the load in the circuit. If we can find the voltage ...
Document
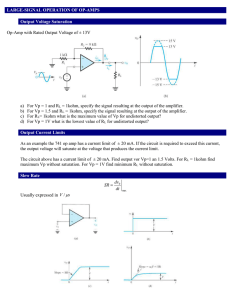
... For Vp = 1 and RL = 1kohm, specify the signal resulting at the output of the amplifier. For Vp = 1.5 and RL = 1kohm, specify the signal resulting at the output of the amplifier. For RL= 1kohm what is the maximum value of Vp for undistorted output? For Vp = 1V what is the lowest value of RL for undis ...
... For Vp = 1 and RL = 1kohm, specify the signal resulting at the output of the amplifier. For Vp = 1.5 and RL = 1kohm, specify the signal resulting at the output of the amplifier. For RL= 1kohm what is the maximum value of Vp for undistorted output? For Vp = 1V what is the lowest value of RL for undis ...
The IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference, APEC, is in
... The IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference, APEC, is in Tampa, FL, March 26 to 30. Complimentary registration for the Exhibit Hall is available. For details please see here: GMW will be showing examples of: •AKM PCB mounting Current Sensors for electrically isolated control of current from +/-20A ...
... The IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference, APEC, is in Tampa, FL, March 26 to 30. Complimentary registration for the Exhibit Hall is available. For details please see here: GMW will be showing examples of: •AKM PCB mounting Current Sensors for electrically isolated control of current from +/-20A ...
Power supply require..
... V drain-to-gate. A possible reason for the failures of the 50 ohm LNAs is static charge build-up on the feed arms. There’s a DC-block capacitor on the input that will protect for this, but if the voltage becomes too high this capacitor can break down or the electrons could decide to jump over the ed ...
... V drain-to-gate. A possible reason for the failures of the 50 ohm LNAs is static charge build-up on the feed arms. There’s a DC-block capacitor on the input that will protect for this, but if the voltage becomes too high this capacitor can break down or the electrons could decide to jump over the ed ...
V R I
... 1. What are the differences between an insulator and a conductor? What types of material make good insulators? Good conductors? Insulator: any material that doesn’t allow the flow of electricity through it. Dull and brittle. Good insulators include plastic, rubber, and glass Conductor: any device th ...
... 1. What are the differences between an insulator and a conductor? What types of material make good insulators? Good conductors? Insulator: any material that doesn’t allow the flow of electricity through it. Dull and brittle. Good insulators include plastic, rubber, and glass Conductor: any device th ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.