AD5246 数据手册DataSheet下载
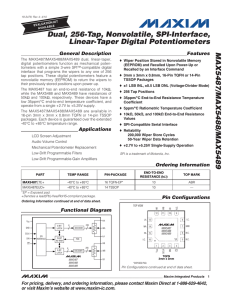
... solution for 128-position adjustment applications. This device performs the same electronic adjustment function as a variable resistor. Available in four different end-to-end resistance values (5 kΩ, 10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ), these low temperature coefficient devices are ideal for high accuracy and sta ...
... solution for 128-position adjustment applications. This device performs the same electronic adjustment function as a variable resistor. Available in four different end-to-end resistance values (5 kΩ, 10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ), these low temperature coefficient devices are ideal for high accuracy and sta ...
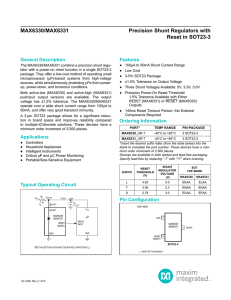
MAX1816/MAX1994 Dual Step-Down Controllers Plus Linear- Regulator Controller for Notebook Computers General Description
... for notebook computer applications. BUCK1 is a CPU core regulator with dynamically adjustable output, ultrafast transient response, high DC accuracy, and high efficiency. BUCK2 is an adjustable step-down regulator for I/O and memory supplies. Both regulators employ Maxim’s proprietary Quick-PWM™ con ...
... for notebook computer applications. BUCK1 is a CPU core regulator with dynamically adjustable output, ultrafast transient response, high DC accuracy, and high efficiency. BUCK2 is an adjustable step-down regulator for I/O and memory supplies. Both regulators employ Maxim’s proprietary Quick-PWM™ con ...
Line filter design of parallel interleaved VSCs for high power
... of the wind turbine. The parallel connected VSCs can be operated with interleaved carriers to reduce the value of the filter components [12]–[18]. However, the carrier interleaving results in common-mode voltage difference across the parallel VSCs. If the conventional three limb three-phase differen ...
... of the wind turbine. The parallel connected VSCs can be operated with interleaved carriers to reduce the value of the filter components [12]–[18]. However, the carrier interleaving results in common-mode voltage difference across the parallel VSCs. If the conventional three limb three-phase differen ...
testing of amptector, digitrip rms or optim trip
... the output. Timer should read less than dial setting but not under 2/3 of the setting, i.e., if set at 36 it should be more than 24 seconds. 3. Any other multiple of sensor may be checked, if desired – see performance curves for approximate trip time to be expected. D. TO CHECK INSTANTANEOUS (Turn T ...
... the output. Timer should read less than dial setting but not under 2/3 of the setting, i.e., if set at 36 it should be more than 24 seconds. 3. Any other multiple of sensor may be checked, if desired – see performance curves for approximate trip time to be expected. D. TO CHECK INSTANTANEOUS (Turn T ...
MAX8552 High-Speed, Wide-Input, Single-Phase MOSFET Driver General Description
... the Low-Side MOSFET At high input voltages, fast turn-on of the high-side MOSFET can momentarily turn on the low-side MOSFET due to the high dV/dt appearing at the drain of the low-side MOSFET. The high dV/dt causes a current flow through the Miller capacitance (CRSS) and the input capacitance (CISS ...
... the Low-Side MOSFET At high input voltages, fast turn-on of the high-side MOSFET can momentarily turn on the low-side MOSFET due to the high dV/dt appearing at the drain of the low-side MOSFET. The high dV/dt causes a current flow through the Miller capacitance (CRSS) and the input capacitance (CISS ...
The LM3900 A New Current-Differencing Quad of Plus or Minus
... All of the voltage gain is provided by the gain transistor, Q2, and an output emitter-follower transistor, Q1, serves to isolate the load impedance from the high impedance that exists at the collector of the gain transistor, Q2. Closed-loop stability is guaranteed by an on-chip capacitor C e 3 pF, w ...
... All of the voltage gain is provided by the gain transistor, Q2, and an output emitter-follower transistor, Q1, serves to isolate the load impedance from the high impedance that exists at the collector of the gain transistor, Q2. Closed-loop stability is guaranteed by an on-chip capacitor C e 3 pF, w ...
R EE - Ateneonline
... from the two inverting amplifiers. • Interstage coupling capacitors C3 and C5 transfer ac signals between amplifiers but provide isolation at dc, and prevent Q-points of the transistors from being affected. 2 Microelettronica – Circuiti integrati analogici 2/ed Richard C. Jaeger, Travis N. Blalock ...
... from the two inverting amplifiers. • Interstage coupling capacitors C3 and C5 transfer ac signals between amplifiers but provide isolation at dc, and prevent Q-points of the transistors from being affected. 2 Microelettronica – Circuiti integrati analogici 2/ed Richard C. Jaeger, Travis N. Blalock ...
TRANSIENT RECOVERY VOLTAGE (TRV) FOR HIGH
... In a similar way, interruption in a L-C series circuit produces initially a high frequency TRV of small amplitude (the voltage prior to interruption tends toward the supply voltage value) called the voltage jump, followed by the 1 - cos waveshape shown on figure 4 for a capacitive circuit. An open c ...
... In a similar way, interruption in a L-C series circuit produces initially a high frequency TRV of small amplitude (the voltage prior to interruption tends toward the supply voltage value) called the voltage jump, followed by the 1 - cos waveshape shown on figure 4 for a capacitive circuit. An open c ...
LT1789-1/LT1789-10 - Micropower, Single Supply Rail-to-Rail Output Instrumentation Amplifier
... 1kHz Voltage Noise: 48nV/√Hz 0.1Hz to 10Hz Noise: 1.5μVP-P ...
... 1kHz Voltage Noise: 48nV/√Hz 0.1Hz to 10Hz Noise: 1.5μVP-P ...
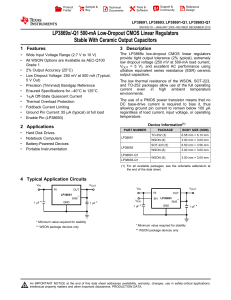
38 V, 2 A synchronous step-down switching regulator with 30 A
... The L6986 device is a step-down monolithic switching regulator able to deliver up to 2 A DC. The output voltage adjustability ranges from 0.85 V to VIN. Thanks to the P-channel MOSFET high-side power element, the device features 100% duty cycle operation. The wide input voltage range meets the speci ...
... The L6986 device is a step-down monolithic switching regulator able to deliver up to 2 A DC. The output voltage adjustability ranges from 0.85 V to VIN. Thanks to the P-channel MOSFET high-side power element, the device features 100% duty cycle operation. The wide input voltage range meets the speci ...
MAX5487/MAX5488/MAX5489 Dual, 256-Tap, Nonvolatile, SPI-Interface, Linear-Taper Digital Potentiometers General Description
... Note 1: All devices are production tested at TA = +85°C and are guaranteed by design and characterization for -40°C < TA < +85°C. Note 2: DNL and INL are measured with the potentiometer configured as a voltage-divider with H_ = VDD and L_ = 0. The wiper terminal is unloaded and measured with an idea ...
... Note 1: All devices are production tested at TA = +85°C and are guaranteed by design and characterization for -40°C < TA < +85°C. Note 2: DNL and INL are measured with the potentiometer configured as a voltage-divider with H_ = VDD and L_ = 0. The wiper terminal is unloaded and measured with an idea ...
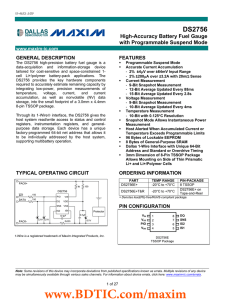
DS2756 High-Accuracy Battery Fuel Gauge with Programmable Suspend Mode
... Continuous offset cancellation corrects offset errors in the current measurement system. Individual values reported by the Current register have a maximum offset of ±0.5 LSb’s (±7.8125V). Individual values reported in the Average Current register have a maximum offset of ±2 LSb’s (±7.8125V). Curre ...
... Continuous offset cancellation corrects offset errors in the current measurement system. Individual values reported by the Current register have a maximum offset of ±0.5 LSb’s (±7.8125V). Individual values reported in the Average Current register have a maximum offset of ±2 LSb’s (±7.8125V). Curre ...
WCL488 Series 402828 Rev B1
... Mandatory Customer Information Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful int ...
... Mandatory Customer Information Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful int ...
2300 Exam 1 Spring 2003
... 8) {15 Points} Four loads are connected in parallel across a voltage source that has an rms voltage of 100[Vrms] and a frequency of 30[Hz]. The circuit is in steady state. The first load absorbs 1500[W] and delivers 2000[VAR]. The second load absorbs 900[VA] at 0.8 pf lagging. The third load is pure ...
... 8) {15 Points} Four loads are connected in parallel across a voltage source that has an rms voltage of 100[Vrms] and a frequency of 30[Hz]. The circuit is in steady state. The first load absorbs 1500[W] and delivers 2000[VAR]. The second load absorbs 900[VA] at 0.8 pf lagging. The third load is pure ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.