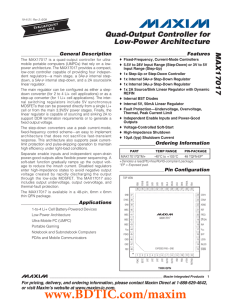
MAX17017 Quad-Output Controller for Low-Power Architecture General Description
... The main regulator can be configured as either a stepdown converter (for 2 to 4 Li+ cell applications) or as a step-up converter (for 1 Li+ cell applications). The internal switching regulators include 5V synchronous MOSFETs that can be powered directly from a single Li+ cell or from the main 3.3V/5 ...
... The main regulator can be configured as either a stepdown converter (for 2 to 4 Li+ cell applications) or as a step-up converter (for 1 Li+ cell applications). The internal switching regulators include 5V synchronous MOSFETs that can be powered directly from a single Li+ cell or from the main 3.3V/5 ...
Novel Advancements in Solid-State Magnet Control
... Common discharge loads utilized are resistors or varistors. The problem with conventional magnet controllers is that the rapid change in magnet current (di/dt), caused when the load is switched across the magnet, induces a very high magnitude voltage spike into the supply. These discharge voltage sp ...
... Common discharge loads utilized are resistors or varistors. The problem with conventional magnet controllers is that the rapid change in magnet current (di/dt), caused when the load is switched across the magnet, induces a very high magnitude voltage spike into the supply. These discharge voltage sp ...
MAX17017 - Part Number Search
... The main regulator can be configured as either a stepdown converter (for 2 to 4 Li+ cell applications) or as a step-up converter (for 1 Li+ cell applications). The internal switching regulators include 5V synchronous MOSFETs that can be powered directly from a single Li+ cell or from the main 3.3V/5 ...
... The main regulator can be configured as either a stepdown converter (for 2 to 4 Li+ cell applications) or as a step-up converter (for 1 Li+ cell applications). The internal switching regulators include 5V synchronous MOSFETs that can be powered directly from a single Li+ cell or from the main 3.3V/5 ...
to this file.
... end of the lead protruding from the top of the battery, click left to start placement, then drag the pencil to the end of the lead at the top of the resistor. As you drag, a dashed line follows. Click left when you reach the resistor lead. This places the wire. (To help control routing, you can clic ...
... end of the lead protruding from the top of the battery, click left to start placement, then drag the pencil to the end of the lead at the top of the resistor. As you drag, a dashed line follows. Click left when you reach the resistor lead. This places the wire. (To help control routing, you can clic ...
32-Position Manual Up/Down Control Potentiometer AD5228
... switches. The AD5228 is designed with a built-in adaptive debouncer that ignores invalid bounces due to contact bounce commonly found in mechanical switches. The debouncer is adaptive, accommodating a variety of pushbutton tactile switches that generally have less than 10 ms of bounce time during co ...
... switches. The AD5228 is designed with a built-in adaptive debouncer that ignores invalid bounces due to contact bounce commonly found in mechanical switches. The debouncer is adaptive, accommodating a variety of pushbutton tactile switches that generally have less than 10 ms of bounce time during co ...
PTH04T220W,
... A low-leakage (<100 nA), open-drain device, such as MOSFET or voltage supervisor IC, is recommended to control pin 9. The open-circuit voltage is less than VI. This control pin has an internal pull-up. Do not place an external pull-up on this pin. If it is left open-circuit, the module operates when ...
... A low-leakage (<100 nA), open-drain device, such as MOSFET or voltage supervisor IC, is recommended to control pin 9. The open-circuit voltage is less than VI. This control pin has an internal pull-up. Do not place an external pull-up on this pin. If it is left open-circuit, the module operates when ...
ADM1276 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... the load current—is maintained below the preset maximum. The ADM1276 protects the external FET by limiting the time that the FET remains on while the current is at its maximum value. This current-limit time is set by the choice of capacitor connected to the TIMER pin. In addition, a foldback resisto ...
... the load current—is maintained below the preset maximum. The ADM1276 protects the external FET by limiting the time that the FET remains on while the current is at its maximum value. This current-limit time is set by the choice of capacitor connected to the TIMER pin. In addition, a foldback resisto ...
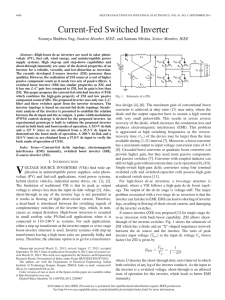
Current-Fed Switched Inverter
... diode and the output capacitor have to sustain a high current with very small pulsewidth. This results in severe reverse recovery of the diode, which increases the conduction loss and produces electromagnetic interference (EMI). This problem is aggravated at high switching frequencies as the reverse ...
... diode and the output capacitor have to sustain a high current with very small pulsewidth. This results in severe reverse recovery of the diode, which increases the conduction loss and produces electromagnetic interference (EMI). This problem is aggravated at high switching frequencies as the reverse ...
Bates
... the potentiometer. The variable V is output between the variable arm and an end terminal. Fig. 2-18: Potentiometer connected across voltage source to function as a voltage divider. (a) Wiring diagram. (b) Schematic diagram. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reprod ...
... the potentiometer. The variable V is output between the variable arm and an end terminal. Fig. 2-18: Potentiometer connected across voltage source to function as a voltage divider. (a) Wiring diagram. (b) Schematic diagram. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reprod ...
DC/DC converter testing with Fast Load Transient
... This can be done in two ways: - Increase the output capacitance to get equivalent 44µF total capacitance at 3.3Vdc and low AC ripple. - Reduce the compensation resistor RCOMP in same ratio as the output capacitance reduction. Let’s reduce the compensation resistor to reduce loop bandwidth. No other ...
... This can be done in two ways: - Increase the output capacitance to get equivalent 44µF total capacitance at 3.3Vdc and low AC ripple. - Reduce the compensation resistor RCOMP in same ratio as the output capacitance reduction. Let’s reduce the compensation resistor to reduce loop bandwidth. No other ...
Atmel LED Drivers MSL2160/MSL2161 MSL2164/MSL2166
... Gate Output 4: External MOSFET Gate Drive Output for LED string 4. Connect G4 to the gate of the external MOSFET driving LED string 4. If unused, leave G4 unconnected. Drain Sense Input 4: External MOSFET Drain Sense Input for LED string 4. Connect D4 through a 10MΩ resistor to the drain of the exte ...
... Gate Output 4: External MOSFET Gate Drive Output for LED string 4. Connect G4 to the gate of the external MOSFET driving LED string 4. If unused, leave G4 unconnected. Drain Sense Input 4: External MOSFET Drain Sense Input for LED string 4. Connect D4 through a 10MΩ resistor to the drain of the exte ...
Manual - Geist
... The Geist CM-3 current meter is a low-power, high accuracy meter capable of measuring true RMS Current. The value of current per output circuit is shown on an easy to read, 4-digit LED Display. The display continuously scrolls through the three different measured values of output circuit current. Th ...
... The Geist CM-3 current meter is a low-power, high accuracy meter capable of measuring true RMS Current. The value of current per output circuit is shown on an easy to read, 4-digit LED Display. The display continuously scrolls through the three different measured values of output circuit current. Th ...
HOW TO CHECK SERVOPACK
... that the fan is bad, the motor can be checked with an ohmmeter. Using an ohmmeter, measure across the fan motor terminals. If the measured value is 0 ohms, we can conclude that the motor is shorted, or if the measured value is infinite ohms, we can conclude that the motor is burned open. If the fan ...
... that the fan is bad, the motor can be checked with an ohmmeter. Using an ohmmeter, measure across the fan motor terminals. If the measured value is 0 ohms, we can conclude that the motor is shorted, or if the measured value is infinite ohms, we can conclude that the motor is burned open. If the fan ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.