Example: PMOS Circuit Analysis
... A: It’s not possible! The solution is either VGS=0.24 V or VGS = -4.23 V. Q: But how can we tell which solution is correct? A: We must choose a solution that is consistent with our original ASSUMPTION. Note that neither of the solutions must be consistent with the saturation ASSUMPTION, an event mea ...
... A: It’s not possible! The solution is either VGS=0.24 V or VGS = -4.23 V. Q: But how can we tell which solution is correct? A: We must choose a solution that is consistent with our original ASSUMPTION. Note that neither of the solutions must be consistent with the saturation ASSUMPTION, an event mea ...
ch20_sol
... out, charges will not be able to flow around the circuit, and neither headlight will stay on. On the other hand, if the bulbs are J connected in parallel, as shown at the right, the current will split at the junction J. Charges will be able to flow through the branch of the circuit that contains the ...
... out, charges will not be able to flow around the circuit, and neither headlight will stay on. On the other hand, if the bulbs are J connected in parallel, as shown at the right, the current will split at the junction J. Charges will be able to flow through the branch of the circuit that contains the ...
LTM4606 - High Efficiency Buck-Boost DC/DC uModule
... input decoupling capacitance directly between VIN pins and PGND pins. VOUT (Bank 3): Power Output Pins. Apply output load between these pins and PGND pins. Recommend placing output decoupling capacitance directly between these pins and PGND pins (see figure below). PGND (Bank 2): Power Ground Pins f ...
... input decoupling capacitance directly between VIN pins and PGND pins. VOUT (Bank 3): Power Output Pins. Apply output load between these pins and PGND pins. Recommend placing output decoupling capacitance directly between these pins and PGND pins (see figure below). PGND (Bank 2): Power Ground Pins f ...
Dual 256-Position SPI Digital Potentiometer AD5162
... device performs the same electronic adjustment function as a 3-terminal mechanical potentiometer. Available in four different end-to-end resistance values (2.5 kΩ, 10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ), this low temperature coefficient device is ideal for high accuracy and stability variable resistance adjustments. ...
... device performs the same electronic adjustment function as a 3-terminal mechanical potentiometer. Available in four different end-to-end resistance values (2.5 kΩ, 10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ), this low temperature coefficient device is ideal for high accuracy and stability variable resistance adjustments. ...
LTC5100 - 3.3V, 3.2Gbps VCSEL Driver.
... Note 20: Serial interface timing is guaranteed by design from –40°C to 85°C. Note 21: The LTC5100 has 100µA nominal pull-up current sources on the SCL and SDA pins to eliminate the need for external pull-up resistors when connected to a single EEPROM device. The LTC5100 meets the maximum rise time s ...
... Note 20: Serial interface timing is guaranteed by design from –40°C to 85°C. Note 21: The LTC5100 has 100µA nominal pull-up current sources on the SCL and SDA pins to eliminate the need for external pull-up resistors when connected to a single EEPROM device. The LTC5100 meets the maximum rise time s ...
LM4120 - Texas Instruments
... about 1 µF. However, values above 0.047 µF must be tantalum. With tantalum capacitors in the 1-µF range, a small capacitor between the output and the reference pin is required. This capacitor will typically be in the 50-pF range. Care must be taken when using output capacitors of 1 µF or larger. The ...
... about 1 µF. However, values above 0.047 µF must be tantalum. With tantalum capacitors in the 1-µF range, a small capacitor between the output and the reference pin is required. This capacitor will typically be in the 50-pF range. Care must be taken when using output capacitors of 1 µF or larger. The ...
OKY-T/3,T/5-D12 Series
... resistor close to the converter with very short leads or use a surface mount trim resistor. In the tables below, the calculated resistance is given. Do not exceed the specified limits of the output voltage or the converter’s maximum power rating when applying these resistors. Also, avoid high noise a ...
... resistor close to the converter with very short leads or use a surface mount trim resistor. In the tables below, the calculated resistance is given. Do not exceed the specified limits of the output voltage or the converter’s maximum power rating when applying these resistors. Also, avoid high noise a ...
Power Factor Correction Handbook
... is the product of the rms value of current times the rms value of voltage. If both current and voltage are sinusoidal and in phase, the power factor is 1.0. If both are sinusoidal but not in phase, the power factor is the cosine of the phase angle. In elementary courses in electricity this is someti ...
... is the product of the rms value of current times the rms value of voltage. If both current and voltage are sinusoidal and in phase, the power factor is 1.0. If both are sinusoidal but not in phase, the power factor is the cosine of the phase angle. In elementary courses in electricity this is someti ...
WATTrouter M - user manual - SOLAR controls sro
... If the power output of the PV-plant decreases, or if another load - not connected to the WATTrouter device is switched on, the switched (active) outputs are disconnected - again according to preset priorities but in reverse order (the load with lower priority is disconnected first). For relay output ...
... If the power output of the PV-plant decreases, or if another load - not connected to the WATTrouter device is switched on, the switched (active) outputs are disconnected - again according to preset priorities but in reverse order (the load with lower priority is disconnected first). For relay output ...
Chapter 24 Electric Circuits
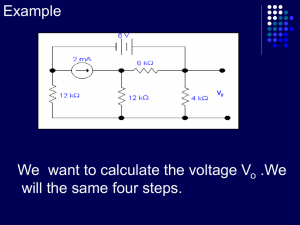
... Three identical 3 resistors are connected into a circuit as shown above. Find the readings of the voltmeter and the ammeter respectively. Voltmeter 3V 3V 4.5 V 4.5 V ...
... Three identical 3 resistors are connected into a circuit as shown above. Find the readings of the voltmeter and the ammeter respectively. Voltmeter 3V 3V 4.5 V 4.5 V ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.