3. Preformance of CMOS Circuits
... – Negligible for older processes – Approaches subthreshold leakage at 65 nm and below in some processes An order of magnitude less for pMOS than nMOS Control leakage in the process using tox > 10.5 Å – High-k gate dielectrics help – Some processes provide multiple tox • e.g. thicker oxide for 3. ...
... – Negligible for older processes – Approaches subthreshold leakage at 65 nm and below in some processes An order of magnitude less for pMOS than nMOS Control leakage in the process using tox > 10.5 Å – High-k gate dielectrics help – Some processes provide multiple tox • e.g. thicker oxide for 3. ...
chapter 3—electricity
... a. in series, the currents are different for each component (e.g., resistors) b. in series, the voltages are the same for each component c. in parallel, the currents are equal for all paths of the circuit d. in parallel, the voltages are equal for all paths of the circuit ANS: D ...
... a. in series, the currents are different for each component (e.g., resistors) b. in series, the voltages are the same for each component c. in parallel, the currents are equal for all paths of the circuit d. in parallel, the voltages are equal for all paths of the circuit ANS: D ...
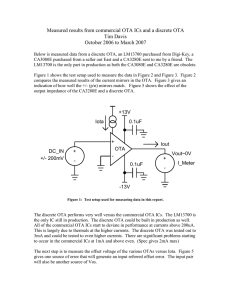
Discrete OTA Measurement Report #1
... The CA3280 measured for this Vos data is the better of the two CA3280s that have been measured thus far. At this point, only one discrete OTA has been built and tested. At the time of this writing, a second one is almost complete. Figure 8 shows that the offset voltage of the CA3280 is definitely be ...
... The CA3280 measured for this Vos data is the better of the two CA3280s that have been measured thus far. At this point, only one discrete OTA has been built and tested. At the time of this writing, a second one is almost complete. Figure 8 shows that the offset voltage of the CA3280 is definitely be ...
LTC6993-1/LTC6993-2/LTC6993-3/LTC6993-4
... Note 6: The TRIG pin has hysteresis to accommodate slow rising or falling signals. The threshold voltages are proportional to V+. Typical values can be estimated at any supply voltage using: VTRIG(RISING) ≈ 0.55 • V+ + 185mV and VTRIG(FALLING) ≈ 0.48 • V+ – 155mV Note 7: To conform to the Logic IC ...
... Note 6: The TRIG pin has hysteresis to accommodate slow rising or falling signals. The threshold voltages are proportional to V+. Typical values can be estimated at any supply voltage using: VTRIG(RISING) ≈ 0.55 • V+ + 185mV and VTRIG(FALLING) ≈ 0.48 • V+ – 155mV Note 7: To conform to the Logic IC ...
ST8024L
... Supply supervisor for spike-killing during power-on and power-off and power-on reset (threshold fixed internally or externally by a resistor bridge) ...
... Supply supervisor for spike-killing during power-on and power-off and power-on reset (threshold fixed internally or externally by a resistor bridge) ...
Aalborg Universitet Autonomous Control of Inverter-Interfaced Distributed Generation Units for Harmonic
... droop relationship between the output harmonic power of the DG inverter and the controlled harmonic resistance is built in [12]. However, it has been found that only the output voltage of the DG inverter can be regulated in this way, whereas the voltage at the Point of Connection (PoC) may be undamp ...
... droop relationship between the output harmonic power of the DG inverter and the controlled harmonic resistance is built in [12]. However, it has been found that only the output voltage of the DG inverter can be regulated in this way, whereas the voltage at the Point of Connection (PoC) may be undamp ...
JOSLYN Arresters
... voltages resulting from the surge current will damage electrical wiring or equipment. Surge Tec arresters are designed to limit surge voltages by discharging (bypassing) surge current to ground. Individuals should assess their risk by evaluating the potential impact that a power surge may have on t ...
... voltages resulting from the surge current will damage electrical wiring or equipment. Surge Tec arresters are designed to limit surge voltages by discharging (bypassing) surge current to ground. Individuals should assess their risk by evaluating the potential impact that a power surge may have on t ...
Residual Current Protective Devices / Arc Fault Detection Devices SENTRON
... DC residual currents make type A devices increasingly insensitive to AC residual currents and pulsating DC residual currents. If a fault occurs, there is therefore no tripping and the desired protective function is no longer assured. UC-sensitive residual current protective devices of types B and B+ ...
... DC residual currents make type A devices increasingly insensitive to AC residual currents and pulsating DC residual currents. If a fault occurs, there is therefore no tripping and the desired protective function is no longer assured. UC-sensitive residual current protective devices of types B and B+ ...
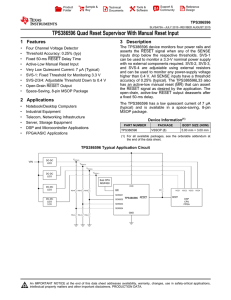
TPS386596 Quad Reset Supervisor With Manual Reset Input (Rev. A)
... The TPS386596L33 multi-channel reset supervisor provides a complete single reset function for a four power supply system. The design of the SVS is based on the TPS386000 quad supervisor device series. The TPS386596 is designed to assert the RESET signal following the logic in Table 1. The RESET outp ...
... The TPS386596L33 multi-channel reset supervisor provides a complete single reset function for a four power supply system. The design of the SVS is based on the TPS386000 quad supervisor device series. The TPS386596 is designed to assert the RESET signal following the logic in Table 1. The RESET outp ...
Analytical and Practical Analysis of Switched-Capacitor DC
... used must be controlled. Level-shifting circuitry is often used to translate the clock to drive each switch at the correct voltage level. Additionally, the power required to drive the switches (the gating loss) is considered. Each capacitor and switch also has parasitic elements: stray capacitance t ...
... used must be controlled. Level-shifting circuitry is often used to translate the clock to drive each switch at the correct voltage level. Additionally, the power required to drive the switches (the gating loss) is considered. Each capacitor and switch also has parasitic elements: stray capacitance t ...
2007
... (either analog or digital) is described in the second chapter, also with the benefits from a parallel first stage to reduce the load on digital circuits and produce a more compact design. At the heart of the optical-flow computation is the evaluation of convolutions with known kernels. The third cha ...
... (either analog or digital) is described in the second chapter, also with the benefits from a parallel first stage to reduce the load on digital circuits and produce a more compact design. At the heart of the optical-flow computation is the evaluation of convolutions with known kernels. The third cha ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... this outgoing current from the source and entering current into the source. So that two are equal. That is why the current which is seen here is IC+IB or that is equal to IE. One part of this current will flow to the base. That is the base current. The other part will flow into the collector and th ...
... this outgoing current from the source and entering current into the source. So that two are equal. That is why the current which is seen here is IC+IB or that is equal to IE. One part of this current will flow to the base. That is the base current. The other part will flow into the collector and th ...
Institutionen för systemteknik technology Department of Electrical Engineering
... Addition is one of the critical and fundamental binary logic operations carried in digital circuits. Most electronic devices such as mobile phones, personal computers and tablet PCs, which are equipped with microprocessors contain Arithmetic and Logic Units (ALU). Being part of ALU, addition circuit ...
... Addition is one of the critical and fundamental binary logic operations carried in digital circuits. Most electronic devices such as mobile phones, personal computers and tablet PCs, which are equipped with microprocessors contain Arithmetic and Logic Units (ALU). Being part of ALU, addition circuit ...
ECE 2110 Lab Manual - Clemson University
... Ammeters are used to measure the flow of electrical current in a circuit. Theoretically, measuring devices should not affect the circuit being studied. Thus, for ammeters, it is important that their internal resistance be very small (ideally near zero) so they will not constrict the flow of current. ...
... Ammeters are used to measure the flow of electrical current in a circuit. Theoretically, measuring devices should not affect the circuit being studied. Thus, for ammeters, it is important that their internal resistance be very small (ideally near zero) so they will not constrict the flow of current. ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.