The Hebrew Bible - A Global Ethic Now
... Around these scriptures there gradually arose a body of traditional rabbinic interpretations of the biblical texts, especially of the provisions of the law. These commentaries Midrash (= “study”, “interpretation”) to individual books of the Bible came to be committed to writing after the destruction ...
... Around these scriptures there gradually arose a body of traditional rabbinic interpretations of the biblical texts, especially of the provisions of the law. These commentaries Midrash (= “study”, “interpretation”) to individual books of the Bible came to be committed to writing after the destruction ...
Hebrew Religion and Ethics
... King Solomon 962-922 BCE, built Temple to contain Ark of Covenant Northern kingdom of Israel, Southern kingdom of Judah (I Kings) 727-722 BCE Babylonians destroyed Jerusalem and Temple, deported Jewish people of Judea to Babylon (II Chronicles) Late 7th, early 6th c. BCE Prophets Nahum, Zephaniah, H ...
... King Solomon 962-922 BCE, built Temple to contain Ark of Covenant Northern kingdom of Israel, Southern kingdom of Judah (I Kings) 727-722 BCE Babylonians destroyed Jerusalem and Temple, deported Jewish people of Judea to Babylon (II Chronicles) Late 7th, early 6th c. BCE Prophets Nahum, Zephaniah, H ...
Parashat Pinchas - Congregation Agudas Israel
... story in 165 B.C.E. and the unsuccessful revolt against Rome in 70 C.E. had elements of civil war between various factions of Jews over the proper course of action. In the 20th century there were zealous actions taken to establish the modern State of Israel that are now being reevaluated. Begin’s Ir ...
... story in 165 B.C.E. and the unsuccessful revolt against Rome in 70 C.E. had elements of civil war between various factions of Jews over the proper course of action. In the 20th century there were zealous actions taken to establish the modern State of Israel that are now being reevaluated. Begin’s Ir ...
File - Seton Campus Ministry
... 4. Ethical and moral systems, as set forth in the Torah and Ten Commandments ...
... 4. Ethical and moral systems, as set forth in the Torah and Ten Commandments ...
Slide 1
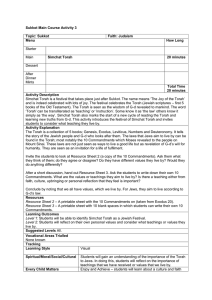
... The Jewish ritual of preparing the dead for burial is called Taharah. The Jewish community has a voluntary burial society called the Chevra Kadisha. They believe that performing a Taharah is the ultimate mitzvah or worthy deed. A group of three or four people (usually women), prepares the body with ...
... The Jewish ritual of preparing the dead for burial is called Taharah. The Jewish community has a voluntary burial society called the Chevra Kadisha. They believe that performing a Taharah is the ultimate mitzvah or worthy deed. A group of three or four people (usually women), prepares the body with ...
Chapter Title Headline text: arial bold 27pt
... The Beliefs of Judaism Unlike most ancient peoples, who were polytheistic, the Israelites believed in only one god. They believed that God delivered the Ten Commandments to them, as well as other laws set forth in the Torah. They also believed in prophets who spoke for God, explaining the code of et ...
... The Beliefs of Judaism Unlike most ancient peoples, who were polytheistic, the Israelites believed in only one god. They believed that God delivered the Ten Commandments to them, as well as other laws set forth in the Torah. They also believed in prophets who spoke for God, explaining the code of et ...
Appendix to: Judaism Group I Ner Tamid – lamps which always
... are kept. They represent the menorah lamps, burning all day in Temple times. Sefer Torah – The text of the Torah was kept in the synagogue, held in reverence as a person, not an object, since worshipping objects in Judaism is forbidden. Sefer Torah was written by a sofer (a scribe) with a goose quil ...
... are kept. They represent the menorah lamps, burning all day in Temple times. Sefer Torah – The text of the Torah was kept in the synagogue, held in reverence as a person, not an object, since worshipping objects in Judaism is forbidden. Sefer Torah was written by a sofer (a scribe) with a goose quil ...
Glossary of Jewish definitions
... outgrowth of Conservative that does not believe in a personified deity and believes that Jewish law was created by men. The Sabbath (or Shabbat, as it is called in Hebrew) is a precious gift from God, a day of great joy eagerly awaited throughout the week, a time when we can set aside all of our wee ...
... outgrowth of Conservative that does not believe in a personified deity and believes that Jewish law was created by men. The Sabbath (or Shabbat, as it is called in Hebrew) is a precious gift from God, a day of great joy eagerly awaited throughout the week, a time when we can set aside all of our wee ...
Judaism - WordPress.com
... Jews are understood to be God’s Chosen People Exchange for the Covenant, Jewish people keep God’s laws and try to bring holiness to every aspect of their lives ...
... Jews are understood to be God’s Chosen People Exchange for the Covenant, Jewish people keep God’s laws and try to bring holiness to every aspect of their lives ...
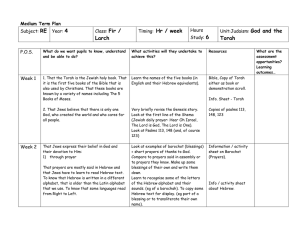
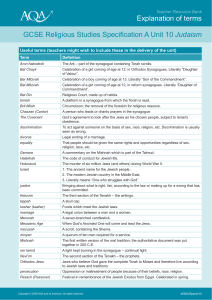
Teacher guidance Explanation of terms: Unit 10 - Judaism
... Copyright © 2008 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and QualiÞcations Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723) and a registered charity (registered charity number 1073334). Registered address: AQA, Devas Street, ...
... Copyright © 2008 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and QualiÞcations Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (company number 3644723) and a registered charity (registered charity number 1073334). Registered address: AQA, Devas Street, ...
World History / Geography
... and the Origins of Judaism Terms Locate as many of the following terms as you can in your Reading or Activity Notes and highlight them. For each term not already in your notes, define and explain its significance on a separate sheet of paper. Judaism (p. 101) Torah (p. 101) Old Testament (p. 101) Je ...
... and the Origins of Judaism Terms Locate as many of the following terms as you can in your Reading or Activity Notes and highlight them. For each term not already in your notes, define and explain its significance on a separate sheet of paper. Judaism (p. 101) Torah (p. 101) Old Testament (p. 101) Je ...
Hebrew Religion and Ethics
... ca. 500 C.E. Babylonian Talmud gave rabbinical discussion on ethics and religious observance. Law (halachah) and Folklore (agadah) In the medieval period, the Babylonian Talmud was authoritative for individual rabbi’s interpretation of law and custom in scattered Jewish communities. It gave guidance ...
... ca. 500 C.E. Babylonian Talmud gave rabbinical discussion on ethics and religious observance. Law (halachah) and Folklore (agadah) In the medieval period, the Babylonian Talmud was authoritative for individual rabbi’s interpretation of law and custom in scattered Jewish communities. It gave guidance ...
Judaism - Bakersfield College
... II. Judaism as the Chosen People a. The Covenant as basis for “Chosenness” i. Before Exodus (Covenant with Abraham and his descendants) Age of the Patriarchs: Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, 12 sons(1900-1600 BCE) ii. After Exodus (Renewal at Sinai with Moses) Covenant established with “the people” and “ ...
... II. Judaism as the Chosen People a. The Covenant as basis for “Chosenness” i. Before Exodus (Covenant with Abraham and his descendants) Age of the Patriarchs: Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, 12 sons(1900-1600 BCE) ii. After Exodus (Renewal at Sinai with Moses) Covenant established with “the people” and “ ...
Judaism - Bloomer High School
... They follow written as well as oral law. Written Law – Torah/Pentateuch ( generally the most important) The first five books of the Old Testament - the Jewish Hebrew version called the Tanakh - of the Bible. Also known as the Books of Moses ...
... They follow written as well as oral law. Written Law – Torah/Pentateuch ( generally the most important) The first five books of the Old Testament - the Jewish Hebrew version called the Tanakh - of the Bible. Also known as the Books of Moses ...
What is Judaism? - Avery County Schools
... Jacob (“I srael”) – origins of the Hebrew people (more than 3800 years ago) Enslaved in ancient Egypt and f reed by Moses (more than 3300 years ago) Hebrew monarchy in the “Promised Land” (The Land of I srael), ends 6th century BC ...
... Jacob (“I srael”) – origins of the Hebrew people (more than 3800 years ago) Enslaved in ancient Egypt and f reed by Moses (more than 3300 years ago) Hebrew monarchy in the “Promised Land” (The Land of I srael), ends 6th century BC ...
1. What is the correct order of the events in the list? 1. David was
... 2. Who unified Israel and Judah? David 3. What should a historian keep in mind when using the Torah as an artifact? It was written as a historical record of the ancient Hebrews. 4. The word exodus means departure. Which departure does the Exodus refer to? the departure from Egypt 5. What did David p ...
... 2. Who unified Israel and Judah? David 3. What should a historian keep in mind when using the Torah as an artifact? It was written as a historical record of the ancient Hebrews. 4. The word exodus means departure. Which departure does the Exodus refer to? the departure from Egypt 5. What did David p ...
Read as Doc file
... absolute precision were careful to hand down the tradition in the most exact manner possible. Possessing this sort of tradition is as good as having seen with our own eyes the giving of the Torah at Mount Sinai and the miraculous Exodus from Egypt. ...
... absolute precision were careful to hand down the tradition in the most exact manner possible. Possessing this sort of tradition is as good as having seen with our own eyes the giving of the Torah at Mount Sinai and the miraculous Exodus from Egypt. ...
Judaism: Beliefs and Rites of Passage
... More of a way of life than a set of beliefs. 1.) There is 1 God who created the universe. 2.) He revealed the Torah to Moses as a guide to life. 3.) Still waiting for the Messiah ...
... More of a way of life than a set of beliefs. 1.) There is 1 God who created the universe. 2.) He revealed the Torah to Moses as a guide to life. 3.) Still waiting for the Messiah ...
The Mitzvah of Keruv - The Rabbinical Assembly
... In any discussion of religious statesmanship, it is important to bear in mind that Torah embraces in depth and scope far more than halakhah. The concept of Torah includes general principles as well as specific laws- such as the love of God, the love of man, the quest for holiness, walking in the way ...
... In any discussion of religious statesmanship, it is important to bear in mind that Torah embraces in depth and scope far more than halakhah. The concept of Torah includes general principles as well as specific laws- such as the love of God, the love of man, the quest for holiness, walking in the way ...
Section One-Judaism - Immaculateheartacademy.org
... The belief in the existence of God. God's unity. God's spirituality and incorporeality. God's eternity and timelessness. God alone should be the object of worship and prayer. Revelation through God's prophets. The preeminence of Moses among the prophets. God's law given on Mount Sinai. The immutabil ...
... The belief in the existence of God. God's unity. God's spirituality and incorporeality. God's eternity and timelessness. God alone should be the object of worship and prayer. Revelation through God's prophets. The preeminence of Moses among the prophets. God's law given on Mount Sinai. The immutabil ...
Simchat Torah - faithtutorials.co.uk
... Simchat Torah is a festival that takes place just after Sukkot. The name means ‘The Joy of the Torah’ and is indeed celebrated with lots of joy. The festival celebrates the Torah (Jewish scriptures – first 5 books of the Old Testament). The Torah is seen as the wisdom of G-d revealed to mankind. The ...
... Simchat Torah is a festival that takes place just after Sukkot. The name means ‘The Joy of the Torah’ and is indeed celebrated with lots of joy. The festival celebrates the Torah (Jewish scriptures – first 5 books of the Old Testament). The Torah is seen as the wisdom of G-d revealed to mankind. The ...
Ch. 6 Sec. 1: Origins of Judaism PowerPoint
... caused a split into two kingdoms: Israel and Judah. These people became known as the Jews. The diaspora (dy-AS-pruh) is the scattering of Jews out of Israel and Judah. The Romans conquered the Jews who returned to Jerusalem. ...
... caused a split into two kingdoms: Israel and Judah. These people became known as the Jews. The diaspora (dy-AS-pruh) is the scattering of Jews out of Israel and Judah. The Romans conquered the Jews who returned to Jerusalem. ...
Ch. 2 Judaism
... • Mishnah or “teaching” is the oral Torah that was eventually translated. Divided into six sections: agriculture (land of Israel), holidays, family life, relations with other people, sacrifices and dietary laws, and ritual purity. ...
... • Mishnah or “teaching” is the oral Torah that was eventually translated. Divided into six sections: agriculture (land of Israel), holidays, family life, relations with other people, sacrifices and dietary laws, and ritual purity. ...
December 2003: The Practice of Jewish Law is Forbidden!
... the second century BCE, when Antiochus IV forbade the observance of Judaism, placed idols in the Temple, and forced people to bow down to images of the pig in public. Circumcision was forbidden, and the laws of the Torah suspended. Some Jews went along with the decrees. But a few, led by Mattathias ...
... the second century BCE, when Antiochus IV forbade the observance of Judaism, placed idols in the Temple, and forced people to bow down to images of the pig in public. Circumcision was forbidden, and the laws of the Torah suspended. Some Jews went along with the decrees. But a few, led by Mattathias ...