Glossary of Jewish Terminology (MSWord)
... Lit. house of study. A place set aside for study of sacred texts such as the Torah and the Talmud, generally a part of the synagogue or attached to it. Beit Shammai (BAYT SHAH-mahy) Lit. House of Shammai. A school of thought during the Talmudic period, generally contrasted with the more lenient, hu ...
... Lit. house of study. A place set aside for study of sacred texts such as the Torah and the Talmud, generally a part of the synagogue or attached to it. Beit Shammai (BAYT SHAH-mahy) Lit. House of Shammai. A school of thought during the Talmudic period, generally contrasted with the more lenient, hu ...
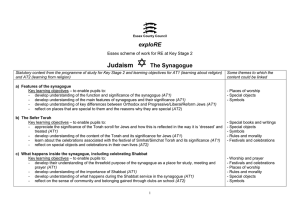
KS2 Judaism The Synagogue
... Background notes for teachers Teachers may wish to draw on some of the following information when enabling pupils to learn about synagogues. It is not intended that the subject matter will be presented to children as it appears below. It is intended that teachers will use a variety of pedagogies whe ...
... Background notes for teachers Teachers may wish to draw on some of the following information when enabling pupils to learn about synagogues. It is not intended that the subject matter will be presented to children as it appears below. It is intended that teachers will use a variety of pedagogies whe ...
Oral Law 3 - Beth David Messianic Congregation
... law, or “tradition of the elders” (cf. Matt. 15: 1– 9). Gradually the supplemental code displaced the primary code of Moses, prompting Jesus to decry a religion that neglected the law of God to cling to the traditions of men (cf. Mark 7: 1– 9). The idea of Hebrew exclusiveness fostered by Ezra sl ...
... law, or “tradition of the elders” (cf. Matt. 15: 1– 9). Gradually the supplemental code displaced the primary code of Moses, prompting Jesus to decry a religion that neglected the law of God to cling to the traditions of men (cf. Mark 7: 1– 9). The idea of Hebrew exclusiveness fostered by Ezra sl ...
Mark scheme - Unit G579 - AS Judaism - June
... Candidates may start their answer by describing weekday worship services and practices in the home and synagogue and use this as a way of outlining the importance of these acts of weekday worship. They may consider textual sources which outline the obligation of worship. In considering the argument, ...
... Candidates may start their answer by describing weekday worship services and practices in the home and synagogue and use this as a way of outlining the importance of these acts of weekday worship. They may consider textual sources which outline the obligation of worship. In considering the argument, ...
A RABBI LOOKS AT JESUS
... Jesus...represents a point of development running unbroken from the Hebrew Bible and linked to it through an interpretive supplement that is characteristic of the great literary creation of the Rabbis, the Oral Torah. As Yehezkel Kaufmann put it: "The attitude of Jesus to the Torah is the very same ...
... Jesus...represents a point of development running unbroken from the Hebrew Bible and linked to it through an interpretive supplement that is characteristic of the great literary creation of the Rabbis, the Oral Torah. As Yehezkel Kaufmann put it: "The attitude of Jesus to the Torah is the very same ...
Imperialism And Jewish Society, 200 BCE To 640
... In part three, Schwartz traces the development of synagogue and community from 350-640 C.E. In chapter six, he argues that the Christianization of the Roman Empire in the fourth century had widespread effects on Jewish life. First, Christianization marginalized Jews as it "excluded [them] from ...
... In part three, Schwartz traces the development of synagogue and community from 350-640 C.E. In chapter six, he argues that the Christianization of the Roman Empire in the fourth century had widespread effects on Jewish life. First, Christianization marginalized Jews as it "excluded [them] from ...
Maimonides` Mishneh Torah
... were currently in force. Thus in Isaac Alfasi’s eleventh-century code of Jewish Law the Halakhot was mainly based on the laws found in the Talmudic orders of Mo’ed (festivals), Nashim (women), and Nezikin (damages), plus the tractate Berakhot (blessings) from the order Zera’im (seeds) and Niddah (th ...
... were currently in force. Thus in Isaac Alfasi’s eleventh-century code of Jewish Law the Halakhot was mainly based on the laws found in the Talmudic orders of Mo’ed (festivals), Nashim (women), and Nezikin (damages), plus the tractate Berakhot (blessings) from the order Zera’im (seeds) and Niddah (th ...
A New Look at the Torah and the LAW of God
... The English word "charity" denotes giving to the poor, whereas the Hebrew chesed denotes "love" and "mercy." The person showing chesed does so because of his love and mercy toward those he seeks to help, while "charity" does not necessarily convey the impact of a deep emotional love and attachment f ...
... The English word "charity" denotes giving to the poor, whereas the Hebrew chesed denotes "love" and "mercy." The person showing chesed does so because of his love and mercy toward those he seeks to help, while "charity" does not necessarily convey the impact of a deep emotional love and attachment f ...
Noahidism - www.BahaiStudies.net
... saying, of every tree of the garden thou mayest freely eat." in Gen 2:16.[12] Historically, some rabbinic opinions consider non-Jews not only not obligated to adhere to all the laws of the Torah, but are actually forbidden to observe them.[13] The Noachide Laws are regarded as the way through which ...
... saying, of every tree of the garden thou mayest freely eat." in Gen 2:16.[12] Historically, some rabbinic opinions consider non-Jews not only not obligated to adhere to all the laws of the Torah, but are actually forbidden to observe them.[13] The Noachide Laws are regarded as the way through which ...
Nature in the Sources of Judaism
... Even miracles, in which God directly intervenes in the created order, are understood to exhibit both the orderliness of God’s creation and God’s control over the created order.12 The greatest miracles of all, however, are to be found not in the natural world but in the way God operates in human hist ...
... Even miracles, in which God directly intervenes in the created order, are understood to exhibit both the orderliness of God’s creation and God’s control over the created order.12 The greatest miracles of all, however, are to be found not in the natural world but in the way God operates in human hist ...
Haredi Construction of Rabbinic Authority: A Case Study
... Haredi Jews are becoming increasingly powerful culture brokers. In many ways, they maintain “a hegemonic position, insofar as they are figured as the ‘competent,’ ‘authentic,’ ‘legitimate,’ and ‘loyal’ bearers of tradition.”1 These concepts are being further pressed since Haredi Jews have become con ...
... Haredi Jews are becoming increasingly powerful culture brokers. In many ways, they maintain “a hegemonic position, insofar as they are figured as the ‘competent,’ ‘authentic,’ ‘legitimate,’ and ‘loyal’ bearers of tradition.”1 These concepts are being further pressed since Haredi Jews have become con ...
The Ẓaddiq as Axis Mundi in Later Judaism Author(s): Arthur Green
... Judentums of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries depicted a religious civilization which seemed to have little in common with those societies to which the emerging methodology of the history of religions was first being applied in that same time period. With the exception of certain minor " ...
... Judentums of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries depicted a religious civilization which seemed to have little in common with those societies to which the emerging methodology of the history of religions was first being applied in that same time period. With the exception of certain minor " ...
Denominations in Judaism
... that right, and how, when, and to what extent does change take place in Judaism? A third major question is of interpretation: Who should interpret Judaism, and how? How should one study Torah? Is it subject to historical, literary, and philosophical analysis like other books? And finally, students s ...
... that right, and how, when, and to what extent does change take place in Judaism? A third major question is of interpretation: Who should interpret Judaism, and how? How should one study Torah? Is it subject to historical, literary, and philosophical analysis like other books? And finally, students s ...
Parshat Behar-Behukotai
... that already Rabbi Hillel allowed the procedure of the Prozbul, or assignment of debts to the Beit Din which could then collect them after the Shmita year. Otherwise credit would have dried up towards the end of the Shmita cycle. But the Jubilee, can you imagine the scene? Did it really ever take pl ...
... that already Rabbi Hillel allowed the procedure of the Prozbul, or assignment of debts to the Beit Din which could then collect them after the Shmita year. Otherwise credit would have dried up towards the end of the Shmita cycle. But the Jubilee, can you imagine the scene? Did it really ever take pl ...
The Torah Story
... jewish history (or the history of the jewish people) is the history of the jews, and their religion and culture, as it developed and interacted with other peoples ... THETORAH - A HISTORICAL AND CONTEXTUAL APPROACH Sun, 23 Apr 2017 13:03:00 GMT a premier site about torah and biblical scholarship . t ...
... jewish history (or the history of the jewish people) is the history of the jews, and their religion and culture, as it developed and interacted with other peoples ... THETORAH - A HISTORICAL AND CONTEXTUAL APPROACH Sun, 23 Apr 2017 13:03:00 GMT a premier site about torah and biblical scholarship . t ...
The Greco-roman World
... Central Purpose: The Proclamation and Exposition of the Law Oriented toward the laity Rectangular building facing toward Jerusalem Board of Directors (3); Archisynagogus; 10 minimum Service: Shema, prayer, and Torah Meeting on Monday and Thursday as well as Sabbath Early Judaism ...
... Central Purpose: The Proclamation and Exposition of the Law Oriented toward the laity Rectangular building facing toward Jerusalem Board of Directors (3); Archisynagogus; 10 minimum Service: Shema, prayer, and Torah Meeting on Monday and Thursday as well as Sabbath Early Judaism ...
Professional Learning Paper about Judaism
... authoritative and objective account of Judaism. Care should be taken to ensure that the speaker approaches his/her presentation in an unbiased and balanced way and that practitioners are aware of the speaker’s background and views. It is also important to stress that learners in class who are Jewish ...
... authoritative and objective account of Judaism. Care should be taken to ensure that the speaker approaches his/her presentation in an unbiased and balanced way and that practitioners are aware of the speaker’s background and views. It is also important to stress that learners in class who are Jewish ...
Gr10 LO2 AS4 Judaism Explained
... What is the Torah? Do Jews use any other sacred texts? Technically it refers to the Five Books of Moses (Pentateuch). This is the Written Torah (Torah SheBiktav). The scroll upon which it is written and which is kept in the Holy Ark of the synagogue is called a Scroll of the Torah (Sefer Torah). In ...
... What is the Torah? Do Jews use any other sacred texts? Technically it refers to the Five Books of Moses (Pentateuch). This is the Written Torah (Torah SheBiktav). The scroll upon which it is written and which is kept in the Holy Ark of the synagogue is called a Scroll of the Torah (Sefer Torah). In ...
in the talmud and the midrash
... Another quality of life case involving intractable pain is that recorded in the Talmud as follows: One of Rabbi Akiva's disciples fell sick and none of his fellow students visited him. So Rabbi Akiva himself entered (his house) to visit him and provided necessary care. liMy master, you have revived ...
... Another quality of life case involving intractable pain is that recorded in the Talmud as follows: One of Rabbi Akiva's disciples fell sick and none of his fellow students visited him. So Rabbi Akiva himself entered (his house) to visit him and provided necessary care. liMy master, you have revived ...
The Torah
... the body of wisdom and law contained in jewish scripture and oral tradition and narrowly defined as the first five books of the bible, english translations of the torah portions reformjudaism org - these english translations from the torah a modern commentary are provided courtesy of the central con ...
... the body of wisdom and law contained in jewish scripture and oral tradition and narrowly defined as the first five books of the bible, english translations of the torah portions reformjudaism org - these english translations from the torah a modern commentary are provided courtesy of the central con ...
Creativity and Cultural Influence in Early Jewish
... Jewish religious law, known as halakhah, has been influenced by cultural developments both within the Jewish community and outside of it. Cultural analysis reminds us that cultures are not hermetically sealed but continuously interact with the world around them. This reality is especially true with ...
... Jewish religious law, known as halakhah, has been influenced by cultural developments both within the Jewish community and outside of it. Cultural analysis reminds us that cultures are not hermetically sealed but continuously interact with the world around them. This reality is especially true with ...
FREE Full Text - Rambam Maimonides Medical Journal
... Judaism and is known as the Written Law. It includes 613 commandments which religiously observant Jews believe are absolutely binding. The second source is the Talmud, also known as the Oral Law. It includes interpretation of the written law using logical reasoning and rabbinic insights and teaching ...
... Judaism and is known as the Written Law. It includes 613 commandments which religiously observant Jews believe are absolutely binding. The second source is the Talmud, also known as the Oral Law. It includes interpretation of the written law using logical reasoning and rabbinic insights and teaching ...
Judaism 101 Questions - Beth El Congregation
... Why should we follow the mitzvot? What will happen if we don’t? What are the Ten Commandments? How many commandments are there? What is a mitzvah? ...
... Why should we follow the mitzvot? What will happen if we don’t? What are the Ten Commandments? How many commandments are there? What is a mitzvah? ...
Why was the Torah given to us in the wilderness?
... dissuade them nor encourage them (Midrash Rut Rabati 2:17), but ask them: “What did you see to make such a choice? Do you not know we are a people that has been brutalized and downtrodden and unpopular, and our ways are very different from the ways of the rest of the world?” We do this in order to t ...
... dissuade them nor encourage them (Midrash Rut Rabati 2:17), but ask them: “What did you see to make such a choice? Do you not know we are a people that has been brutalized and downtrodden and unpopular, and our ways are very different from the ways of the rest of the world?” We do this in order to t ...
Why Study Talmud in the Twenty-first Century?
... The editor has grouped the writers into four sections: “Women’s Voices,” “Teaching Talmud,” “Academics Respond,” and “A Philosopher’s Approach.” In his introduction, Socken acknowledges that the female contributors are also academics, but he wants to emphasize how they engage the Talmud specifically ...
... The editor has grouped the writers into four sections: “Women’s Voices,” “Teaching Talmud,” “Academics Respond,” and “A Philosopher’s Approach.” In his introduction, Socken acknowledges that the female contributors are also academics, but he wants to emphasize how they engage the Talmud specifically ...