EE 101 Lab 4 Digital Signals
... A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor circuit element that allows electrical current to pass in only one direction. In effect it functions as a “flow valve” – current is allowed to pass in one direction through the diode, but is prevented from passing through in the opposite direction. Diodes are ...
... A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor circuit element that allows electrical current to pass in only one direction. In effect it functions as a “flow valve” – current is allowed to pass in one direction through the diode, but is prevented from passing through in the opposite direction. Diodes are ...
POWER ELECTRONICS NOTES 10ES45
... 90% of its initial value is called the gate controlled / trigger delay time tgd . It is also defined as the duration between 90% of the gate trigger pulse and the instant at which the anode current rises to 10% of its peak value. tgd is usually in the range of 1 sec. Once tgd has lapsed, the current ...
... 90% of its initial value is called the gate controlled / trigger delay time tgd . It is also defined as the duration between 90% of the gate trigger pulse and the instant at which the anode current rises to 10% of its peak value. tgd is usually in the range of 1 sec. Once tgd has lapsed, the current ...
ALS Storage Ring RF System Upgrade
... circulator and magic-tee transmission system. The klystron has operated well beyond its expected lifetime and even though replacement klystrons are available from a different manufacturer, we have opted to build the replacement amplifier with a system of four Inductive Output Tubes, (IOT). The new a ...
... circulator and magic-tee transmission system. The klystron has operated well beyond its expected lifetime and even though replacement klystrons are available from a different manufacturer, we have opted to build the replacement amplifier with a system of four Inductive Output Tubes, (IOT). The new a ...
Note 1
... thermionic diode a heated cathode emits electrons, which flow across the intervening vacuum to the anode when a positive potential is applied to it. The device permits flow of current in one direction only as a negative potential applied to the anode repels the electrons. This property of diodes was ...
... thermionic diode a heated cathode emits electrons, which flow across the intervening vacuum to the anode when a positive potential is applied to it. The device permits flow of current in one direction only as a negative potential applied to the anode repels the electrons. This property of diodes was ...
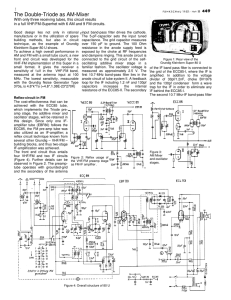
Voltage-controlled Oscillators (VCO), Phase Locked Loop, and
... Voltage-controlled Oscillators (VCO), Phase Locked Loop, and Frequency Converters Voltage-controlled oscillators are specialized oscillators in which the oscillation frequency varies with a control voltage. VCOs are used in many communication applications such as frequency modulation, in the phase l ...
... Voltage-controlled Oscillators (VCO), Phase Locked Loop, and Frequency Converters Voltage-controlled oscillators are specialized oscillators in which the oscillation frequency varies with a control voltage. VCOs are used in many communication applications such as frequency modulation, in the phase l ...
Accelerator Physics for pedestrians - Helmholtz
... of an electron accelerator is the television. Within the tube of such, a device a metal rod is heated which causes electrons to be ejected out of the rod. These electrons are then accelerated by means of an electric potential (voltage). As such a simple 1.5 Volt battery is sufficient to accelerate t ...
... of an electron accelerator is the television. Within the tube of such, a device a metal rod is heated which causes electrons to be ejected out of the rod. These electrons are then accelerated by means of an electric potential (voltage). As such a simple 1.5 Volt battery is sufficient to accelerate t ...
Slides
... Vfdbk chain, when we tried the other chain the system did not work. loop instabilities, what does the VLOOP light really mean lots of vibrations from blower in SF6 tank. Can we find a different fan, or a variable speed drive so we can tune it away from the tank resonance, which is close to 30 Hz? ou ...
... Vfdbk chain, when we tried the other chain the system did not work. loop instabilities, what does the VLOOP light really mean lots of vibrations from blower in SF6 tank. Can we find a different fan, or a variable speed drive so we can tune it away from the tank resonance, which is close to 30 Hz? ou ...
transistor theory
... Electrons cannot recombine with holes. This makes an open circuit. Open circuits allow no current to flow. What electrical component do we have that works like this? This is the working model for our diodes. ...
... Electrons cannot recombine with holes. This makes an open circuit. Open circuits allow no current to flow. What electrical component do we have that works like this? This is the working model for our diodes. ...
Linear Accelerators
... closed ended, precision crafted copper cavities where the electrical power provides momentum to the low-level electron stream mixed with the microwaves. Alternating positive and negative electric charge accelerates the electrons toward the treatment head, the negative voltage repels electrons while ...
... closed ended, precision crafted copper cavities where the electrical power provides momentum to the low-level electron stream mixed with the microwaves. Alternating positive and negative electric charge accelerates the electrons toward the treatment head, the negative voltage repels electrons while ...
Cavity magnetron

The cavity magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field while moving past a series of open metal cavities (cavity resonators). Bunches of electrons passing by the openings to the cavities excite radio wave oscillations in the cavity, much as a guitar's strings excite sound in its sound box. The frequency of the microwaves produced, the resonant frequency, is determined by the cavities' physical dimensions. Unlike other microwave tubes, such as the klystron and traveling-wave tube (TWT), the magnetron cannot function as an amplifier, increasing the power of an applied microwave signal, it serves solely as an oscillator, generating a microwave signal from direct current power supplied to the tube.The first form of magnetron tube, the split-anode magnetron, was invented by Albert Hull in 1920, but it wasn't capable of high frequencies and was little used. Similar devices were experimented with by many teams through the 1920s and 30s. On November 27, 1935, Hans Erich Hollmann applied for a patent for the first multiple cavities magnetron, which he received on July 12, 1938, but the more stable klystron was preferred for most German radars during World War II. The cavity magnetron tube was later improved by John Randall and Harry Boot in 1940 at the University of Birmingham, England. The high power of pulses from their device made centimeter-band radar practical for the Allies of World War II, with shorter wavelength radars allowing detection of smaller objects from smaller antennas. The compact cavity magnetron tube drastically reduced the size of radar sets so that they could be installed in anti-submarine aircraft and escort ships.In the post-war era the magnetron became less widely used in the radar role. This was because the magnetron's output changes from pulse to pulse, both in frequency and phase. This makes the signal unsuitable for pulse-to-pulse comparisons, which is widely used for detecting and removing ""clutter"" from the radar display. The magnetron remains in use in some radars, but has become much more common as a low-cost microwave source for microwave ovens. In this form, approximately one billion magnetrons are in use today.