Life Goes On Molecular Genetics Components of DNA
... backbone of the daughter strand creating one long complementary DNA strand ...
... backbone of the daughter strand creating one long complementary DNA strand ...
2014 DNA Replication ppt
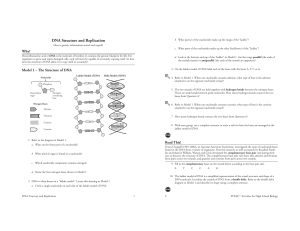
... separates into two strands. Each strand of the double helix of DNA serves as a template for the new strand. This is carried out by an enzyme, DNA helicase, that “unzips” a molecule of DNA at the Hydrogen bonds between base pairs and the two strands of DNA unwind. ...
... separates into two strands. Each strand of the double helix of DNA serves as a template for the new strand. This is carried out by an enzyme, DNA helicase, that “unzips” a molecule of DNA at the Hydrogen bonds between base pairs and the two strands of DNA unwind. ...
18 DNA Structure and Replication-S
... assembling a living organism. The DNA blueprint carries its instructions in the form of genes. In most cases the genes direct the production of a polypeptide, from which other more complex proteins, such as enzymes or hormones, may be constructed. These polypeptides and other molecules run the organ ...
... assembling a living organism. The DNA blueprint carries its instructions in the form of genes. In most cases the genes direct the production of a polypeptide, from which other more complex proteins, such as enzymes or hormones, may be constructed. These polypeptides and other molecules run the organ ...
DNA - jacybiology
... gene and at least 65 kb of flanking DNA were amplified, an average of 2.6-fold. Six other regions of DNA were co-amplified in all 33 mutants, but sometimes to a different extent than CAD. Novel joints, marking recombinations which link amplified regions to each other, were found surprisingly rarely. ...
... gene and at least 65 kb of flanking DNA were amplified, an average of 2.6-fold. Six other regions of DNA were co-amplified in all 33 mutants, but sometimes to a different extent than CAD. Novel joints, marking recombinations which link amplified regions to each other, were found surprisingly rarely. ...
C - SchoolRack
... • DNA is found inside the nucleus • Proteins, however, are made in the cytoplasm of cells by organelles called ribosomes • Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
... • DNA is found inside the nucleus • Proteins, however, are made in the cytoplasm of cells by organelles called ribosomes • Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
DNA:RNA PACKETPkt_
... 6. Place the blunt end of a wooden skewer into the center of the white, stringy mass. Slowly rotate (DO NOT STIR) the skewer in one direction. The DNA should spool onto the wooden skewer (Figure 4). Remove the skewer and observe the DNA that you have extracted. Analysis Questions: Answer using ...
... 6. Place the blunt end of a wooden skewer into the center of the white, stringy mass. Slowly rotate (DO NOT STIR) the skewer in one direction. The DNA should spool onto the wooden skewer (Figure 4). Remove the skewer and observe the DNA that you have extracted. Analysis Questions: Answer using ...
Hammer
... Ability to form repetitive hydrogen bonding structures in DNA and RNA is due to the isostructural (isomorphic) nature of the C-G and A-T(U) basepairs. That is, the fact that a C-G, G-C, A-T, and T-A basepairs have same geometries provides the template to make a polymeric duplex structure with differ ...
... Ability to form repetitive hydrogen bonding structures in DNA and RNA is due to the isostructural (isomorphic) nature of the C-G and A-T(U) basepairs. That is, the fact that a C-G, G-C, A-T, and T-A basepairs have same geometries provides the template to make a polymeric duplex structure with differ ...
II. Building a Model of DNA
... 3. Each type of tRNA can carry only one type of amino acid. There are enough different types of tRNA molecules to carry all the different types of amino acids needed to make your body’s proteins. 4. Where do the tRNA molecules take the amino acids? They take them to ribosomes, organelles in the cyto ...
... 3. Each type of tRNA can carry only one type of amino acid. There are enough different types of tRNA molecules to carry all the different types of amino acids needed to make your body’s proteins. 4. Where do the tRNA molecules take the amino acids? They take them to ribosomes, organelles in the cyto ...
Chapter 6 DNA Replication
... In a population, genetic variation is important to allow organisms to evolve in response to changing environment. These DNA rearrangements are cause by a class Of mechanisms called genetic recombination. ...
... In a population, genetic variation is important to allow organisms to evolve in response to changing environment. These DNA rearrangements are cause by a class Of mechanisms called genetic recombination. ...
DNA Structure and Replication
... DNA must replicate (copy) itself so that each resulting cell after mitosis and cell division has the same DNA as the parent cell. DNA replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle, before mitosis and cell division. The base pairing rules are crucial for the process of replication. DNA repl ...
... DNA must replicate (copy) itself so that each resulting cell after mitosis and cell division has the same DNA as the parent cell. DNA replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle, before mitosis and cell division. The base pairing rules are crucial for the process of replication. DNA repl ...
Name
... b. DNA has stored information, that can be copied and passed on. c. DNA has information wrapped in an identifying cover. d. DNA has information that is periodically updated. ...
... b. DNA has stored information, that can be copied and passed on. c. DNA has information wrapped in an identifying cover. d. DNA has information that is periodically updated. ...
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... Science Education. The Kansas Board of Education and the Colorado State Board of Education, for mandating that children should not believe in Darwin's theory of evolution. Medicine. Arvid Vatle of Norway, for carefully collecting, classifying, and contemplating which kinds of containers his patients ...
... Science Education. The Kansas Board of Education and the Colorado State Board of Education, for mandating that children should not believe in Darwin's theory of evolution. Medicine. Arvid Vatle of Norway, for carefully collecting, classifying, and contemplating which kinds of containers his patients ...
DNA as genetic material chemistry of genetic neuclic acid
... • DNA uses four bases in its structure: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). • The order of the bases in a DNA molecule—the genetic code—determines the amino acid sequence of a protein. • In the cells of most organisms, two long strands of DNA join in a single molecule that resem ...
... • DNA uses four bases in its structure: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). • The order of the bases in a DNA molecule—the genetic code—determines the amino acid sequence of a protein. • In the cells of most organisms, two long strands of DNA join in a single molecule that resem ...
PPT
... Multiple scientists conducted experiments that helped determine that DNA is responsible for storing, copying, and carries genetic information. Those scientists are: 1. Griffith – Bacterial Transformation in Mice Experiments ...
... Multiple scientists conducted experiments that helped determine that DNA is responsible for storing, copying, and carries genetic information. Those scientists are: 1. Griffith – Bacterial Transformation in Mice Experiments ...
Unit 4
... - Each three bases of mRNA are called a codon, these codons line up with the amino acids picked up by the tRNA. 12. Explain the process of transcription including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. - Initiation: polymerase attaches to promoter regions on the DNA and be ...
... - Each three bases of mRNA are called a codon, these codons line up with the amino acids picked up by the tRNA. 12. Explain the process of transcription including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. - Initiation: polymerase attaches to promoter regions on the DNA and be ...
DNA Synthesis aka DNA Replication
... 1. Replication fork made when Helicase separates parent strands Helicase “unzips” the two sides 2. DNA polymerase links new nucleotides to the growing strand (only on the 3’ end) 3. Leading strand made as single polymer ...
... 1. Replication fork made when Helicase separates parent strands Helicase “unzips” the two sides 2. DNA polymerase links new nucleotides to the growing strand (only on the 3’ end) 3. Leading strand made as single polymer ...
Document
... • Dispersive-would produce two DNA molecule with sections of both old and new along each strand. • Semiconservative –would produce DNA molecule with both one old strand and one new strand. ...
... • Dispersive-would produce two DNA molecule with sections of both old and new along each strand. • Semiconservative –would produce DNA molecule with both one old strand and one new strand. ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Review WITH ANSWERS
... catastrophic effect on the functioning of a protein? A) a base substitution near the start of the coding sequence but not in the start codon B) a base deletion near the beginning of the coding sequence but not in the start codon C) a base deletion near the end of the coding sequence, but not in the ...
... catastrophic effect on the functioning of a protein? A) a base substitution near the start of the coding sequence but not in the start codon B) a base deletion near the beginning of the coding sequence but not in the start codon C) a base deletion near the end of the coding sequence, but not in the ...
BI0029
... rho factor. This protein binds and runs along the mRNA towards the RNA polymerase. When ρ-factor reaches the RNAP, it causes RNAP to dissociate from the DNA, terminating transcription. Explanation for Rho-independent termination of transcription ...
... rho factor. This protein binds and runs along the mRNA towards the RNA polymerase. When ρ-factor reaches the RNAP, it causes RNAP to dissociate from the DNA, terminating transcription. Explanation for Rho-independent termination of transcription ...
Biochemical Analysis of the Human Mismatch Repair Proteins
... is the nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) activity, which catalyzes transfer of γ-phosphate between nucleoside triphosphates and diphosphates. The second one is the 3'-5' exonuclease activity, which is involved in repair of UV-induced DNA damage in yeasts. UV radiation is one of the most widesprea ...
... is the nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) activity, which catalyzes transfer of γ-phosphate between nucleoside triphosphates and diphosphates. The second one is the 3'-5' exonuclease activity, which is involved in repair of UV-induced DNA damage in yeasts. UV radiation is one of the most widesprea ...
DNA Structure Notes PPT
... made of two chains of sugar and phosphate held together by nitrogenous bases. • Watson and Crick also proposed that DNA is shaped like a long zipper that is twisted into a coil like a spring. ...
... made of two chains of sugar and phosphate held together by nitrogenous bases. • Watson and Crick also proposed that DNA is shaped like a long zipper that is twisted into a coil like a spring. ...
Entry task
... • HOW DO YOU THINK SCIENTISTS WERE ABLE TO DETERMINE THAT DNA WAS THE INHERITANCE MOLECULE THAT WAS PASSED FROM PARENTS TO OFFSPRING? (12.1) ...
... • HOW DO YOU THINK SCIENTISTS WERE ABLE TO DETERMINE THAT DNA WAS THE INHERITANCE MOLECULE THAT WAS PASSED FROM PARENTS TO OFFSPRING? (12.1) ...
dna isolation
... Nucleic acids are the most polar of the biopolymers and are therefore soluble in polar solvents and precipitated by nonpolar solvents. In prokaryotes, DNA is double stranded and circular and is found throughout the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, DNA is located in the nucleus and in mitochondria or chloro ...
... Nucleic acids are the most polar of the biopolymers and are therefore soluble in polar solvents and precipitated by nonpolar solvents. In prokaryotes, DNA is double stranded and circular and is found throughout the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, DNA is located in the nucleus and in mitochondria or chloro ...
Helicase

Helicases are a class of enzymes vital to all living organisms. Their main function is to unpackage an organism's genes. They are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separating two annealed nucleic acid strands (i.e., DNA, RNA, or RNA-DNA hybrid) using energy derived from ATP hydrolysis. There are many helicases resulting from the great variety of processes in which strand separation must be catalyzed. Approximately 1% of eukaryotic genes code for helicases. The human genome codes for 95 non-redundant helicases: 64 RNA helicases and 31 DNA helicases. Many cellular processes, such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, recombination, DNA repair, and ribosome biogenesis involve the separation of nucleic acid strands that necessitates the use of helicases.