template strand
... • During translation, the codons are read in the 5’->3’ direction along the mRNA. • Each codon specifies which one of the 20 amino acids will be incorporated at the corresponding position along a polypeptide. • Because codons are base triplets, the number of nucleotides making up a genetic message ...
... • During translation, the codons are read in the 5’->3’ direction along the mRNA. • Each codon specifies which one of the 20 amino acids will be incorporated at the corresponding position along a polypeptide. • Because codons are base triplets, the number of nucleotides making up a genetic message ...
ppt
... on a medium containing nucleotide precursors labeled with a heavy isotope of nitrogen, 15N. The bacteria incorporated the heavy nitrogen into their DNA. The scientists then transferred the bacteria to a medium with only 14N, the lighter, more common isotope of nitrogen. Any new DNA that the bacteria ...
... on a medium containing nucleotide precursors labeled with a heavy isotope of nitrogen, 15N. The bacteria incorporated the heavy nitrogen into their DNA. The scientists then transferred the bacteria to a medium with only 14N, the lighter, more common isotope of nitrogen. Any new DNA that the bacteria ...
A single oligonucleotide can be used to rapidly isolate DNA
... optimize the MgCl2 concentration for each PCR substrate, and was most convenient to use the Taq polymerase buffer supplied with the enzyme by the manufacturer (1.5 mM MgCy. In addition to the more typical, smaller molecular weight 'primer dimer', a product of —0.5 kb (not shown) was observed in all ...
... optimize the MgCl2 concentration for each PCR substrate, and was most convenient to use the Taq polymerase buffer supplied with the enzyme by the manufacturer (1.5 mM MgCy. In addition to the more typical, smaller molecular weight 'primer dimer', a product of —0.5 kb (not shown) was observed in all ...
Inference of homologous recombination in bacteria using whole
... disperse, diversify and adapt because DNA contains information of how organisms are related. In bacteria and archaea, genomic DNA is replicated as part of reproduction by binary fission [1]. Changes in genomic DNA can accumulate because replication is unfaithful or due to DNA damage, but might also ...
... disperse, diversify and adapt because DNA contains information of how organisms are related. In bacteria and archaea, genomic DNA is replicated as part of reproduction by binary fission [1]. Changes in genomic DNA can accumulate because replication is unfaithful or due to DNA damage, but might also ...
to 3
... Defects in DNA repair or replication All are associated with a high frequency of chromosome and gene (base pair) mutations; most are also associated with a predisposition to cancer, particularly leukemias • Xeroderma pigmentosum • caused by mutations in genes involved in nucleotide excision repair ...
... Defects in DNA repair or replication All are associated with a high frequency of chromosome and gene (base pair) mutations; most are also associated with a predisposition to cancer, particularly leukemias • Xeroderma pigmentosum • caused by mutations in genes involved in nucleotide excision repair ...
Q1. (a) Describe what happens to chromosomes in meiosis
... Glycine-proline-proline is a series of amino acids found in a particular protein. Give the sequence of DNA bases for these three amino acids which contains the longest “slippery” ...
... Glycine-proline-proline is a series of amino acids found in a particular protein. Give the sequence of DNA bases for these three amino acids which contains the longest “slippery” ...
SCI 30 UA CH 2.3 DNA - Fort Saskatchewan High
... When a cell needs to multiply to aid in the growth or repair of an organism, its DNA must first be copied. It is important that each of the two daughter cells produced during mitosis receives an exact copy of the parent cell’s DNA. The process of making an extra copy of DNA for a new cell is called ...
... When a cell needs to multiply to aid in the growth or repair of an organism, its DNA must first be copied. It is important that each of the two daughter cells produced during mitosis receives an exact copy of the parent cell’s DNA. The process of making an extra copy of DNA for a new cell is called ...
Recombinant DNA
... Until recently plant and animal breeders could only work with variations that already exist in nature. Even when breeders tried to add variation by introducing mutations, the changes they produced were unpredictable. Today genetic engineers can transfer certain genes at will from one organism to ano ...
... Until recently plant and animal breeders could only work with variations that already exist in nature. Even when breeders tried to add variation by introducing mutations, the changes they produced were unpredictable. Today genetic engineers can transfer certain genes at will from one organism to ano ...
Recombinant DNA
... Until recently plant and animal breeders could only work with variations that already exist in nature. Even when breeders tried to add variation by introducing mutations, the changes they produced were unpredictable. Today genetic engineers can transfer certain genes at will from one organism to ano ...
... Until recently plant and animal breeders could only work with variations that already exist in nature. Even when breeders tried to add variation by introducing mutations, the changes they produced were unpredictable. Today genetic engineers can transfer certain genes at will from one organism to ano ...
Estimation of Circular DNA Size Using r
... treatment ((11,17); data not shown). The material remaining within the well probably corresponds to nicked circular H DNAs, as large open circular DNAs (>30 kb) do not enter the gel under the high voltage gradients utilized (6 V/cm; (11)). Following irradiation, progressively reduced levels of the s ...
... treatment ((11,17); data not shown). The material remaining within the well probably corresponds to nicked circular H DNAs, as large open circular DNAs (>30 kb) do not enter the gel under the high voltage gradients utilized (6 V/cm; (11)). Following irradiation, progressively reduced levels of the s ...
SHORT COMMUNICATION A Procedure for Isolating
... Spores prepared as described above are, with rare exceptions, fully susceptible to the lysis procedure. However, several batches of spores from strains which routinely lyse easily gave low yields of DNA. These spores were abnormally pigmented. Although older spores were more pigmented, I have been u ...
... Spores prepared as described above are, with rare exceptions, fully susceptible to the lysis procedure. However, several batches of spores from strains which routinely lyse easily gave low yields of DNA. These spores were abnormally pigmented. Although older spores were more pigmented, I have been u ...
The Regulatory Region of the Larabinose Operon: Its Isolation on a
... by a modification of the procedure of Petterson et al. (1973). A 1*7-cm internal diameter glass tubing was constricted at one end to 1.1 cm. The open end of about 2 cm of no. 32 dialysis tubing (Union Carbide) knotted at the other end w&s fitted over the constricted glsss tubing end and held in plac ...
... by a modification of the procedure of Petterson et al. (1973). A 1*7-cm internal diameter glass tubing was constricted at one end to 1.1 cm. The open end of about 2 cm of no. 32 dialysis tubing (Union Carbide) knotted at the other end w&s fitted over the constricted glsss tubing end and held in plac ...
DNA basics - Crop Genebank Knowledge Base
... These enzymes belong to a class that cleave (or cut) DNA at specific and unique internal locations along its length. As a consequence, they are also called endonucleases. These enzymes act as scissors, cutting the DNA of the phages and inactivating them. Of the three types of restriction enzymes, ty ...
... These enzymes belong to a class that cleave (or cut) DNA at specific and unique internal locations along its length. As a consequence, they are also called endonucleases. These enzymes act as scissors, cutting the DNA of the phages and inactivating them. Of the three types of restriction enzymes, ty ...
Rescue of arrested RNA polymerase II complexes
... related to TRCF (except for limited homology in the ATPase domains) (Eisen et al., 1995), it would thus have been reasonable for researchers interested in eukaryotic CSB/Rad26 not to pay too much attention to the lessons learnt from bacterial TRCF. However, two pieces of evidence should be mentioned ...
... related to TRCF (except for limited homology in the ATPase domains) (Eisen et al., 1995), it would thus have been reasonable for researchers interested in eukaryotic CSB/Rad26 not to pay too much attention to the lessons learnt from bacterial TRCF. However, two pieces of evidence should be mentioned ...
light - Microbiology
... fragments, also induces new donor bacteria. Other agents such as X-rays and methyl methansulphonate (MMS) do not stimulate the production of new donors but may enhance the recombination frequency since cells killed by them may continue to act as chromosome donors. The effect is not shown either by u ...
... fragments, also induces new donor bacteria. Other agents such as X-rays and methyl methansulphonate (MMS) do not stimulate the production of new donors but may enhance the recombination frequency since cells killed by them may continue to act as chromosome donors. The effect is not shown either by u ...
Ultraviolet Induction of Chromosome Transfer by
... fragments, also induces new donor bacteria. Other agents such as X-rays and methyl methansulphonate (MMS) do not stimulate the production of new donors but may enhance the recombination frequency since cells killed by them may continue to act as chromosome donors. The effect is not shown either by u ...
... fragments, also induces new donor bacteria. Other agents such as X-rays and methyl methansulphonate (MMS) do not stimulate the production of new donors but may enhance the recombination frequency since cells killed by them may continue to act as chromosome donors. The effect is not shown either by u ...
[4] Fologea, D., Brandin, E., Uplinger, J., Branton, D., Li, J
... for analyzing real DNA current drop signal. The measured mean pulse heights ∆Ib verses the pulse widths td are plotted in Fig. S1(D) (blue circles). This calibration shows that when the pulse width is less than 100 sec, the calculated mean pulse height will be attenuated, but the time durations (th ...
... for analyzing real DNA current drop signal. The measured mean pulse heights ∆Ib verses the pulse widths td are plotted in Fig. S1(D) (blue circles). This calibration shows that when the pulse width is less than 100 sec, the calculated mean pulse height will be attenuated, but the time durations (th ...
L - Bilkent CS.
... that multiplicity of a fragment can be detected, i.e., the number of restriction fragments of the same length can be determined (e.g., by observing twice as much fluorescence intensity for a double fragment than for a single fragment) ...
... that multiplicity of a fragment can be detected, i.e., the number of restriction fragments of the same length can be determined (e.g., by observing twice as much fluorescence intensity for a double fragment than for a single fragment) ...
Cryptography with DNA binary strands
... from the intercepted solution to be successful. After separation he or she can read out the message as described above. For the interceptor there is a rare chance to distinguish between the dummies and the message strand. The only way to get the message strand is to take it by chance or to guess the ...
... from the intercepted solution to be successful. After separation he or she can read out the message as described above. For the interceptor there is a rare chance to distinguish between the dummies and the message strand. The only way to get the message strand is to take it by chance or to guess the ...
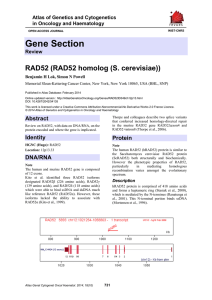
Gene Section RAD52 (RAD52 homolog (S. cerevisiae)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... protects them from exonuclease resection, and facilitates end-to-end interaction (Van Dyck et al., 1999). Furthermore, capture of the second DNA end in homologous recombination appears to involve RAD52-mediated annealing of RPAssDNA strands in biochemical reactions (Sugiyama et al., 2006). Although, ...
... protects them from exonuclease resection, and facilitates end-to-end interaction (Van Dyck et al., 1999). Furthermore, capture of the second DNA end in homologous recombination appears to involve RAD52-mediated annealing of RPAssDNA strands in biochemical reactions (Sugiyama et al., 2006). Although, ...
Chapter 1
... passed on from one generation of pea plants to the next. For convenience, Mendel’s laws of inheritance will be described using two modern biological terms, gene for a unit of heredity and chromosome for a structure bearing several linked genes. 1. The law of independent assortment — Specific physica ...
... passed on from one generation of pea plants to the next. For convenience, Mendel’s laws of inheritance will be described using two modern biological terms, gene for a unit of heredity and chromosome for a structure bearing several linked genes. 1. The law of independent assortment — Specific physica ...
DNA - Warren County Schools
... Helicase begin to unzip the double helix at many different places breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases creates a replication fork. Occurs in two different directions. Leading strand – read normal Lagging strand – upside down – reads in fragments ...
... Helicase begin to unzip the double helix at many different places breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases creates a replication fork. Occurs in two different directions. Leading strand – read normal Lagging strand – upside down – reads in fragments ...
DNA - Warren County Schools
... STEPS OF DNA REPLICATION 1. Helicase begin to unzip the double helix at many different places. The hydrogen bonds between the bases are broken. Occurs in two different directions. 2. Free floating in the cytoplasm nucleotides pair with the bases on the template. DNA polyermase bonds together the n ...
... STEPS OF DNA REPLICATION 1. Helicase begin to unzip the double helix at many different places. The hydrogen bonds between the bases are broken. Occurs in two different directions. 2. Free floating in the cytoplasm nucleotides pair with the bases on the template. DNA polyermase bonds together the n ...
Homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks. Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses.Although homologous recombination varies widely among different organisms and cell types, most forms involve the same basic steps. After a double-strand break occurs, sections of DNA around the 5' ends of the break are cut away in a process called resection. In the strand invasion step that follows, an overhanging 3' end of the broken DNA molecule then ""invades"" a similar or identical DNA molecule that is not broken. After strand invasion, the further sequence of events may follow either of two main pathways discussed below (see Models); the DSBR (double-strand break repair) pathway or the SDSA (synthesis-dependent strand annealing) pathway. Homologous recombination that occurs during DNA repair tends to result in non-crossover products, in effect restoring the damaged DNA molecule as it existed before the double-strand break.Homologous recombination is conserved across all three domains of life as well as viruses, suggesting that it is a nearly universal biological mechanism. The discovery of genes for homologous recombination in protists—a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms—has been interpreted as evidence that meiosis emerged early in the evolution of eukaryotes. Since their dysfunction has been strongly associated with increased susceptibility to several types of cancer, the proteins that facilitate homologous recombination are topics of active research. Homologous recombination is also used in gene targeting, a technique for introducing genetic changes into target organisms. For their development of this technique, Mario Capecchi, Martin Evans and Oliver Smithies were awarded the 2007 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine.















![[4] Fologea, D., Brandin, E., Uplinger, J., Branton, D., Li, J](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022017731_1-3d28463eccad2ba4cd92d75bb9791a40-300x300.png)