Blank Jeopardy - Workforce3One
... Process of correcting faulty DNA codes that causes genetic diseases. Carry normal gene into cells containing ...
... Process of correcting faulty DNA codes that causes genetic diseases. Carry normal gene into cells containing ...
Slide
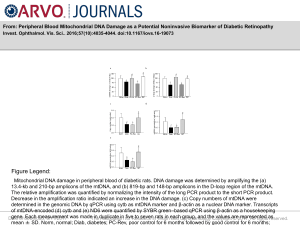
... 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of the long PCR product to the short PCR product. Decrease in the amplification ratio indicated an increase in the ...
... 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of the long PCR product to the short PCR product. Decrease in the amplification ratio indicated an increase in the ...
Unit D : DNA -Functions of DNA - Mr. Lesiuk
... 2. New complimentary nucleotides, always present in the nucleus, move into place and pair with complementary bases on the exposed strands. - T joins to A ...
... 2. New complimentary nucleotides, always present in the nucleus, move into place and pair with complementary bases on the exposed strands. - T joins to A ...
Gene Technology
... Gene cloning – many copies of the gene of interest are made by the vector copying its DNA with the gene in it Screening – cells that have the gene you want are separated from those that don’t ...
... Gene cloning – many copies of the gene of interest are made by the vector copying its DNA with the gene in it Screening – cells that have the gene you want are separated from those that don’t ...
Smurfs, Trolls & Elves
... • As railroads and development swept through, the blue Fugates started moving out of Troublesome Creek and marrying other people • The inherited blue began to disappear as the recessive gene spread to families where it is unlikely to be paired to a similar gene ...
... • As railroads and development swept through, the blue Fugates started moving out of Troublesome Creek and marrying other people • The inherited blue began to disappear as the recessive gene spread to families where it is unlikely to be paired to a similar gene ...
Slide 1
... Nucleotides - are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of DNA and RNA (A-G-T-C). Gene - is a code of nucleotides within DNA. Target DNA – The piece of DNA strand that is the focus of the test, i.e. Contains the genes involved in CML. Primer –a short nucleic acid that bi ...
... Nucleotides - are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of DNA and RNA (A-G-T-C). Gene - is a code of nucleotides within DNA. Target DNA – The piece of DNA strand that is the focus of the test, i.e. Contains the genes involved in CML. Primer –a short nucleic acid that bi ...
Biology: Genetic Technology questions
... 8. How is reproductive cloning achieved? (list as steps). ...
... 8. How is reproductive cloning achieved? (list as steps). ...
DNA Technology
... use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific in explaining how the technique was used. Cite your sources – not the textbook. This is the major part of your report. DO NOT USE INSULIN or INDENTIFYING CRIMINALS as examples. Find something less common. 3. If this is a controversia ...
... use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific in explaining how the technique was used. Cite your sources – not the textbook. This is the major part of your report. DO NOT USE INSULIN or INDENTIFYING CRIMINALS as examples. Find something less common. 3. If this is a controversia ...
DNA and RNA
... Griffith hypothesized… • when the live, harmless bacteria and the heat-killed bacteria were mixed, some factor was transferred from the heat-killed cells into the live cells • The ability to cause disease was inherited by the transformed bacteria’s offspring, the transforming factor might be a gene ...
... Griffith hypothesized… • when the live, harmless bacteria and the heat-killed bacteria were mixed, some factor was transferred from the heat-killed cells into the live cells • The ability to cause disease was inherited by the transformed bacteria’s offspring, the transforming factor might be a gene ...
7.1 - DNA Structure
... 7.1 - DNA Structure 7.1.1 - Describe the structure of DNA, including the antiparallel strands, 3'-5' linkages and hydrogen bonding between purines and pyrimidines DNA has a uniform diameter along its entire length due to complementary base pairing. The two polynucleotide chains are antiparallel, wit ...
... 7.1 - DNA Structure 7.1.1 - Describe the structure of DNA, including the antiparallel strands, 3'-5' linkages and hydrogen bonding between purines and pyrimidines DNA has a uniform diameter along its entire length due to complementary base pairing. The two polynucleotide chains are antiparallel, wit ...
Non-Mendelian Genetics Test Review
... What is chromosomal analysis? Chromosomal analysis is a procedure that isolates the chromosome pairs so that they may be visualized to determine abnormalities. ...
... What is chromosomal analysis? Chromosomal analysis is a procedure that isolates the chromosome pairs so that they may be visualized to determine abnormalities. ...
Ch - TeacherWeb
... C. tRNA- the supplier. Transfers rna delivers amino acids to ribosomes to be assembled. ...
... C. tRNA- the supplier. Transfers rna delivers amino acids to ribosomes to be assembled. ...
chapter 12 test review key
... mutation will be the daughter cells of that one cell. Only a certain group of cells will carry the incorrect information. If a mutation or change of information occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries th ...
... mutation will be the daughter cells of that one cell. Only a certain group of cells will carry the incorrect information. If a mutation or change of information occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries th ...
Human Genomics - Mrs Smith`s Biology
... • What were the aims of the human genome project? • To identify all the approximately 20,000-25,000 genes in human DNA. • To find where each gene is located • To determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA. • Store this information in databases. • Estimated t ...
... • What were the aims of the human genome project? • To identify all the approximately 20,000-25,000 genes in human DNA. • To find where each gene is located • To determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA. • Store this information in databases. • Estimated t ...
Problem Set 3A
... chromosome as replication is occurring through that region. Give yourself plenty of room and make the replication bubble stretch most of the way from one side of your paper to the other. Show both replication forks and a bit of DNA at each end that has not yet been replicated. Use single long arrows ...
... chromosome as replication is occurring through that region. Give yourself plenty of room and make the replication bubble stretch most of the way from one side of your paper to the other. Show both replication forks and a bit of DNA at each end that has not yet been replicated. Use single long arrows ...
Nucleic Acid and Protein - Seattle Central College
... 2. Write a complementary DNA strand to the single strand below to show what a double strand will contain. P = phosphate D = deoxyribose sugar P-D-P-D-P-D-P-D ...
... 2. Write a complementary DNA strand to the single strand below to show what a double strand will contain. P = phosphate D = deoxyribose sugar P-D-P-D-P-D-P-D ...
The genome is an organism`s complete set of DNA
... rejoinings (translocations), can be detected by microscopic examination. Most changes in DNA, however, are more subtle and require a closer analysis of the DNA molecule to find perhaps single-base differences. Each chromosome contains many genes, the basic physical and functional units of heredity. ...
... rejoinings (translocations), can be detected by microscopic examination. Most changes in DNA, however, are more subtle and require a closer analysis of the DNA molecule to find perhaps single-base differences. Each chromosome contains many genes, the basic physical and functional units of heredity. ...
Name
... 19. A cooperative unit of many similar cells that perform a specific function within a multi-cellular organism. 20. A protein that serves as a biological catalyst, changing the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being changed into a different molecule in the process. Down 1. A discipline tha ...
... 19. A cooperative unit of many similar cells that perform a specific function within a multi-cellular organism. 20. A protein that serves as a biological catalyst, changing the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being changed into a different molecule in the process. Down 1. A discipline tha ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... Name the enzyme involved in protein synthesis which manufactures mRNA using DNA as a template. DNA polymerase ...
... Name the enzyme involved in protein synthesis which manufactures mRNA using DNA as a template. DNA polymerase ...
Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen bonds 9. You have separated the nucleotides in a piece of DNA ...
... 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen bonds 9. You have separated the nucleotides in a piece of DNA ...
Road To Discovery of DNA
... Timeline to DNA • Mendel (1865) – performed and recorded crosses with pea plants to study aspects of heredity. • Sutton & Boveri (1902) – identified similarities between Mendel’s factors and the behavior of chromosomes. ...
... Timeline to DNA • Mendel (1865) – performed and recorded crosses with pea plants to study aspects of heredity. • Sutton & Boveri (1902) – identified similarities between Mendel’s factors and the behavior of chromosomes. ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis lesson
... mRNA in 3-base sequences called codons. Specific amino acids are added to a growing protein chain. They are matched up with an anticodon found on a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule. ...
... mRNA in 3-base sequences called codons. Specific amino acids are added to a growing protein chain. They are matched up with an anticodon found on a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule. ...
Journey Into dna
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? Intestines: Is the DNA code from cell to cell in the human body the same? Cells: ...
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? Intestines: Is the DNA code from cell to cell in the human body the same? Cells: ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.