4.04 Workfile
... Scientists and investigators count on DNA fingerprinting for its accuracy. That’s because DNA is similar to a fingerprint— everybody’s DNA is different. (The only exception is identical twins. They have the exact same DNA.) This unique genetic code can be found in all body cells, including hair, ski ...
... Scientists and investigators count on DNA fingerprinting for its accuracy. That’s because DNA is similar to a fingerprint— everybody’s DNA is different. (The only exception is identical twins. They have the exact same DNA.) This unique genetic code can be found in all body cells, including hair, ski ...
Deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA
... In 1928, British scientist Fredrick Griffith was trying to learn how certain types of bacteria caused pneumonia. He isolated two different strains of pneumonia bacteria from mice and grew them in his lab. Griffith made two observations: (1) The disease-causing strain of bacteria grew into smooth col ...
... In 1928, British scientist Fredrick Griffith was trying to learn how certain types of bacteria caused pneumonia. He isolated two different strains of pneumonia bacteria from mice and grew them in his lab. Griffith made two observations: (1) The disease-causing strain of bacteria grew into smooth col ...
Fire Kit – TDS - DNA Custom Paints
... or purchasing some training materials on the subject to help learn this extremely popular technique properly. When done correctly, this technique is stunning, dramatic and very popular. In saying that however, we have included a few tips in the steps below which we are sure you will find helpful. Re ...
... or purchasing some training materials on the subject to help learn this extremely popular technique properly. When done correctly, this technique is stunning, dramatic and very popular. In saying that however, we have included a few tips in the steps below which we are sure you will find helpful. Re ...
DNA Replication lab
... 1. Using the model of DNA you made from activity 1, carefully “unzip” the DNA. Use only the side that codes C,T,G,A,G,C. This is the gene coding sequence. 2. The mRNA will now bond to the exposed DNA bases, copying the code in the sequence of bases. To do this, tape the mRNA nucleotides together as ...
... 1. Using the model of DNA you made from activity 1, carefully “unzip” the DNA. Use only the side that codes C,T,G,A,G,C. This is the gene coding sequence. 2. The mRNA will now bond to the exposed DNA bases, copying the code in the sequence of bases. To do this, tape the mRNA nucleotides together as ...
REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION, TRANSLATION, Oh My!
... 1. Using the model of DNA you made from activity 1, carefully “unzip” the DNA. Use only the side that codes C,T,G,A,G,C. This is the gene coding sequence. 2. The mRNA will now bond to the exposed DNA bases, copying the code in the sequence of bases. To do this, tape the mRNA nucleotides together as ...
... 1. Using the model of DNA you made from activity 1, carefully “unzip” the DNA. Use only the side that codes C,T,G,A,G,C. This is the gene coding sequence. 2. The mRNA will now bond to the exposed DNA bases, copying the code in the sequence of bases. To do this, tape the mRNA nucleotides together as ...
DNA Brochures
... Index can link crime scenes together, possibly identifying serial offenders. Based on a match, police in multiple jurisdictions can coordinate their respective investigations and share the leads they developed independently. Matches made between the Forensic and Offender Indexes provide investigator ...
... Index can link crime scenes together, possibly identifying serial offenders. Based on a match, police in multiple jurisdictions can coordinate their respective investigations and share the leads they developed independently. Matches made between the Forensic and Offender Indexes provide investigator ...
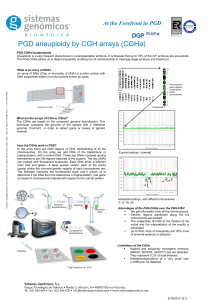
At the Forefront in PGD
... balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many cases, infertility. PGD using FISH techniques allows detect altered embryos (unbalanced) for a specific chromosomal rearrangement. However, the main limitation is that it does not provide information of the rest of chromosomes. Comb ...
... balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many cases, infertility. PGD using FISH techniques allows detect altered embryos (unbalanced) for a specific chromosomal rearrangement. However, the main limitation is that it does not provide information of the rest of chromosomes. Comb ...
Note 6.2 - DNA Structure and Function
... Experiment 2, heated the S-strain, destroying the capsule killing the bacteria. Injecting mice with the dead S-strain no longer killed the mice, they remained healthy similar to those mice injected with the R-strain. Experiment 3, Griffith mixed the dead S-strain version with the R-strain version p ...
... Experiment 2, heated the S-strain, destroying the capsule killing the bacteria. Injecting mice with the dead S-strain no longer killed the mice, they remained healthy similar to those mice injected with the R-strain. Experiment 3, Griffith mixed the dead S-strain version with the R-strain version p ...
Activity 1: Indescribable
... complementary ssDNA fragments will begin to re-anneal with each other. A high concentration of primers, and the tendency of the shorter primer strands to anneal more readily, ensures primer binding. The temperature is then raised again to about 72°C for primer extension. Underscoring the importance ...
... complementary ssDNA fragments will begin to re-anneal with each other. A high concentration of primers, and the tendency of the shorter primer strands to anneal more readily, ensures primer binding. The temperature is then raised again to about 72°C for primer extension. Underscoring the importance ...
ch 16 clicker questions
... c) The lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together. d) The leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucle ...
... c) The lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together. d) The leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucle ...
Chapter 6 DNA Replication
... have profound consequences. A mutation affecting just a single nucleotide pair can severely compromise an organism’s fitness if the change occurs in vital position in the DNA sequence. Because the structure and the activity of each protein depend on its amino acid composition, a protein with altered ...
... have profound consequences. A mutation affecting just a single nucleotide pair can severely compromise an organism’s fitness if the change occurs in vital position in the DNA sequence. Because the structure and the activity of each protein depend on its amino acid composition, a protein with altered ...
Conservation and Diversification of Three
... What is Myb ? Myb is derived from “myeloblastosis”, which is a name for a specific type of leukemia. This gene was first recognized as the v-Myb oncogene of the avian myeloblastosis virus. Family of transcription factors containing 2 or 3 repeat sequences in the DNA-binding domain (Myb domain ...
... What is Myb ? Myb is derived from “myeloblastosis”, which is a name for a specific type of leukemia. This gene was first recognized as the v-Myb oncogene of the avian myeloblastosis virus. Family of transcription factors containing 2 or 3 repeat sequences in the DNA-binding domain (Myb domain ...
Nucleic Acids
... Phosphate – allows more nucleotides to be added to the chain, forming long strands; ionized, partially responsible for solubility of nucleic acids in water ...
... Phosphate – allows more nucleotides to be added to the chain, forming long strands; ionized, partially responsible for solubility of nucleic acids in water ...
Objective Questions
... 31) The necessary ingredients for DNA synthesis can be mixed together in a test tube. The DNA polymerase is from Thermus aquaticus and the template is from a human cell. The DNA synthesized would be most similar to A) Human DNA. B) T. aquaticus DNA. C) A mixture of human and T. aquaticus DNA. D) Hum ...
... 31) The necessary ingredients for DNA synthesis can be mixed together in a test tube. The DNA polymerase is from Thermus aquaticus and the template is from a human cell. The DNA synthesized would be most similar to A) Human DNA. B) T. aquaticus DNA. C) A mixture of human and T. aquaticus DNA. D) Hum ...
Discovering DNA Fingerprinting
... occur in the non-coding regions of DNA – often called junk DNA. These regions of DNA have more variation than coding DNA as any changes do not have an impact on survival in the way a genetic mutation would have. The reason for these repeated regions is not fully understood. Sometimes they are found ...
... occur in the non-coding regions of DNA – often called junk DNA. These regions of DNA have more variation than coding DNA as any changes do not have an impact on survival in the way a genetic mutation would have. The reason for these repeated regions is not fully understood. Sometimes they are found ...
Campbell`s Biology, 9e (Reece et al.)
... A) it is heat stable and can withstand the temperature changes of the cycler. B) only minute amounts are needed for each cycle of PCR. C) it binds more readily than other polymerases to primer. D) it has regions that are complementary to primers. E) All of these are correct. 49) Which of the followi ...
... A) it is heat stable and can withstand the temperature changes of the cycler. B) only minute amounts are needed for each cycle of PCR. C) it binds more readily than other polymerases to primer. D) it has regions that are complementary to primers. E) All of these are correct. 49) Which of the followi ...
Document
... • Bacteria and eukaryotes have differences in details of processes. • Eukaryotic RNA polymerases differ from prokaryotic; require transcription factors. ...
... • Bacteria and eukaryotes have differences in details of processes. • Eukaryotic RNA polymerases differ from prokaryotic; require transcription factors. ...
7.014 Problem Set 3
... (b) You have created an in vitro (in the test tube) DNA replication system using yeast proteins and yeast DNA. One day you accidentally add human DNA polymerase instead of yeast DNA polymerase. You still get DNA replication! Provide an explanation for why human polymerase can substitute for yeast po ...
... (b) You have created an in vitro (in the test tube) DNA replication system using yeast proteins and yeast DNA. One day you accidentally add human DNA polymerase instead of yeast DNA polymerase. You still get DNA replication! Provide an explanation for why human polymerase can substitute for yeast po ...
Watermarking sexually reproducing diploid organisms
... be encrypted into DNA is first modified by a mutation correction code, the Hamming-code, to correct mutations within the DNA sequences. A header, containing the length of the original file, is produced and linked to the modified binary sequence. The composition of the header and the file is translat ...
... be encrypted into DNA is first modified by a mutation correction code, the Hamming-code, to correct mutations within the DNA sequences. A header, containing the length of the original file, is produced and linked to the modified binary sequence. The composition of the header and the file is translat ...
DNA Model
... phosphate unit joined to deoxyribose, a five-carbon sugar and a nitrogencontaining base. The DNA molecule is a double strand of posSlbly thousands of nucleotides bonded by their bases. There are four types of bases in DNA. Two arc purines, either adenine or guanine. TIle other two are pryimidiIJes. ...
... phosphate unit joined to deoxyribose, a five-carbon sugar and a nitrogencontaining base. The DNA molecule is a double strand of posSlbly thousands of nucleotides bonded by their bases. There are four types of bases in DNA. Two arc purines, either adenine or guanine. TIle other two are pryimidiIJes. ...
Notes
... 2. RNA primase adds an RNA primer (short segment of RNA) to each strand of DNA 3. DNA polymerase attaches to separated strand, helping add complementary nucleotides to the new DNA strand ...
... 2. RNA primase adds an RNA primer (short segment of RNA) to each strand of DNA 3. DNA polymerase attaches to separated strand, helping add complementary nucleotides to the new DNA strand ...
Chapter 5 - FIU Faculty Websites
... mammal genome ~ 3-4 billion base pairs of DNA one gene ~ 10 kbp It would be unpractical to isolate 1 gene Preparation of genomic DNA library Isolating total DNA – Aplying shotgun cloning Digesting total DNA into fragments of suitable size (the fragments do not corresponds to the individual genes) In ...
... mammal genome ~ 3-4 billion base pairs of DNA one gene ~ 10 kbp It would be unpractical to isolate 1 gene Preparation of genomic DNA library Isolating total DNA – Aplying shotgun cloning Digesting total DNA into fragments of suitable size (the fragments do not corresponds to the individual genes) In ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.