Chromosome and Human Genetics
... • The basic building block of DNA is a nucleotide. • Each nucleotide is made of 3 sub-units: * Phosphate – P * Deoxyribose – R (5-C-compoud) * One of 4 bases: A, T, C, or G (A-Adenine, TThymine, C-Cytosine, G-Guanine) * How many different nucleotides are there? ...
... • The basic building block of DNA is a nucleotide. • Each nucleotide is made of 3 sub-units: * Phosphate – P * Deoxyribose – R (5-C-compoud) * One of 4 bases: A, T, C, or G (A-Adenine, TThymine, C-Cytosine, G-Guanine) * How many different nucleotides are there? ...
Biology Final Exam
... 1. The amount of guanine (G) in an organism’s DNA always equals the amount of ____________. The amount of adenine (A) in DNA always equals the amount of ___________________. 2. A nucleotide (the basic unit of DNA) consists of _______________, _______________ and _______________. 3. Genes in DNA → RN ...
... 1. The amount of guanine (G) in an organism’s DNA always equals the amount of ____________. The amount of adenine (A) in DNA always equals the amount of ___________________. 2. A nucleotide (the basic unit of DNA) consists of _______________, _______________ and _______________. 3. Genes in DNA → RN ...
Old exam 2 from 2002
... ____ 12. What is the name for the phenomenon of a chromosome breaking into several pieces and rejoining, but a piece is lost in the process? A. monosomic B. nullosomic C. duplication D. deletion E. inversion. ____ 13. How many origins of replication are found in a mitochondrial chromosome? A. many B ...
... ____ 12. What is the name for the phenomenon of a chromosome breaking into several pieces and rejoining, but a piece is lost in the process? A. monosomic B. nullosomic C. duplication D. deletion E. inversion. ____ 13. How many origins of replication are found in a mitochondrial chromosome? A. many B ...
DNA - Canyon ISD
... • Each cell has about ______________. • The average human has _______________. • The average human has enough DNA to go from the earth to the sun ...
... • Each cell has about ______________. • The average human has _______________. • The average human has enough DNA to go from the earth to the sun ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... The charge on DNA and the component that gives it that charge ...
... The charge on DNA and the component that gives it that charge ...
Concept 20.1 A. -Plasmid is the cloning vector.
... - The bacterial will recognize the promotor and express the foreign gene. b) Presence of introns (non-coding regions), in most Eukaryotic genes. These make it hard to correct expression of the gene by bacteria, as they do not have RNA splicing machinery. - Use a cDNA form of the gene which only incl ...
... - The bacterial will recognize the promotor and express the foreign gene. b) Presence of introns (non-coding regions), in most Eukaryotic genes. These make it hard to correct expression of the gene by bacteria, as they do not have RNA splicing machinery. - Use a cDNA form of the gene which only incl ...
Advanced Biology
... Chapter 16: Molecular Basis of Inheritance transformation thymine bacteriophage guanine Griffith’s expt (S cells, cytosine R cells) purine Avery, McCarty, pyrimidine McLeod expt Watson & Crick Hershey/Chase expt. double helix DNA base pair RNA hydrogen bonding prote ...
... Chapter 16: Molecular Basis of Inheritance transformation thymine bacteriophage guanine Griffith’s expt (S cells, cytosine R cells) purine Avery, McCarty, pyrimidine McLeod expt Watson & Crick Hershey/Chase expt. double helix DNA base pair RNA hydrogen bonding prote ...
File
... How do nitrogenous bases bind to each other? Which part of a nucleotide makes up the actual “code” that DNA is said to contain? Who were the two men who discovered the structure of DNA? What did Rosalind Franklin do that greatly helped the men in question 4 prove that they had discovered the structu ...
... How do nitrogenous bases bind to each other? Which part of a nucleotide makes up the actual “code” that DNA is said to contain? Who were the two men who discovered the structure of DNA? What did Rosalind Franklin do that greatly helped the men in question 4 prove that they had discovered the structu ...
Genes to Proteins Nucleic Acid Structure
... – H‐bonding in RNA structure – Reactions of catalytic RNA (rare) – Hydrolysis ...
... – H‐bonding in RNA structure – Reactions of catalytic RNA (rare) – Hydrolysis ...
KUPSHO
... In DNA the base A (adenine) forms a bond with the base____. In RNA the base A (adenine) forms a bond with the base ____. In DNA the base C (Cytosine) forms a bond with the base ____. In DNA the bases A and T are held together by a ___ bond. a. single b. double c. triple In DNA the bases G (Guanine) ...
... In DNA the base A (adenine) forms a bond with the base____. In RNA the base A (adenine) forms a bond with the base ____. In DNA the base C (Cytosine) forms a bond with the base ____. In DNA the bases A and T are held together by a ___ bond. a. single b. double c. triple In DNA the bases G (Guanine) ...
Biology 218 Microbial Metabolism and Genetics Chapter Six
... Prokaryotic Genetics Review Vocabulary Phenotype: physical traits Genotype: genetic make-up Mutations: replication errors, single base pairs Recombination: rearranging or acquiring genes ...
... Prokaryotic Genetics Review Vocabulary Phenotype: physical traits Genotype: genetic make-up Mutations: replication errors, single base pairs Recombination: rearranging or acquiring genes ...
Chapter 3,
... A cancer-inducing virus, HTLV-1, inserts itself into a human chromosome, where it remains. How can a laboratory technician prove that a patient is infected with HTLV-1? The technician can design a DNA probe—a radioactive or fluorescent DNA strand that is complimentary to a specific sequence found in ...
... A cancer-inducing virus, HTLV-1, inserts itself into a human chromosome, where it remains. How can a laboratory technician prove that a patient is infected with HTLV-1? The technician can design a DNA probe—a radioactive or fluorescent DNA strand that is complimentary to a specific sequence found in ...
Biology 12 – Review Sheet
... 2. Compare and contrast the nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. 3. What is the importance of hydrogen bonds in the explanation of the DNA model? 4. Define complimentary base pairing and its significance with respect to DNA 5. At what point during cell division does DNA replicate? Why? 6. What are the basic ...
... 2. Compare and contrast the nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. 3. What is the importance of hydrogen bonds in the explanation of the DNA model? 4. Define complimentary base pairing and its significance with respect to DNA 5. At what point during cell division does DNA replicate? Why? 6. What are the basic ...
(KEY).
... 6. Create a template strand of 5 codons. Next replicate them to make a new strand. Be sure to follow the proper DNA-DNA “base pair rules”. Template strand: AAA TTT GGG CCC ACT New strand: TTT AAA CCC GGG TGA DNA VS. RNA 7. Describe the differences and characteristics of DNA vs. RNA using the table b ...
... 6. Create a template strand of 5 codons. Next replicate them to make a new strand. Be sure to follow the proper DNA-DNA “base pair rules”. Template strand: AAA TTT GGG CCC ACT New strand: TTT AAA CCC GGG TGA DNA VS. RNA 7. Describe the differences and characteristics of DNA vs. RNA using the table b ...
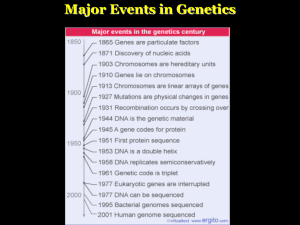
Major Events in Genetics
... – Already determined that the sugar-phosphate ladder was on the outside of the molecule – Wilkins received Nobel Prize in 1962 – Franklin –and Chargaff- did not. ...
... – Already determined that the sugar-phosphate ladder was on the outside of the molecule – Wilkins received Nobel Prize in 1962 – Franklin –and Chargaff- did not. ...
Study Guide 7 - The Blueprint of Life Chpt. 7
... Distinguish between replication, transcription, and translation. Describe the basic structure of a deoxynucleotide (i.e. name the three general parts). Which 4 bases are found in DNA? What are the "base pairing rules"? Describe the basic structure of a DNA molecule. How is RNA different from DNA? Wh ...
... Distinguish between replication, transcription, and translation. Describe the basic structure of a deoxynucleotide (i.e. name the three general parts). Which 4 bases are found in DNA? What are the "base pairing rules"? Describe the basic structure of a DNA molecule. How is RNA different from DNA? Wh ...
DNA
... i. The bases of DNA always pair as A with T and C with G. h. The information is stored in DNA as the order of the bases which is a code. 3. The process where DNA is copied is called DNA replication. a. Replication occurs in the nucleus. b. Helicase is the enzyme that “unzips” the DNA strands by brea ...
... i. The bases of DNA always pair as A with T and C with G. h. The information is stored in DNA as the order of the bases which is a code. 3. The process where DNA is copied is called DNA replication. a. Replication occurs in the nucleus. b. Helicase is the enzyme that “unzips” the DNA strands by brea ...
Deoxyribonucleic acid from calf thymus Product Number D4522
... Protein synthesis occurs with the intermediate messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) as well as participation by another form of RNA, ribosomal RNA. DNA provides the means of transmitting heritable information from one generation of cells or higher organism to the next via the gene and genome. A gene is ...
... Protein synthesis occurs with the intermediate messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) as well as participation by another form of RNA, ribosomal RNA. DNA provides the means of transmitting heritable information from one generation of cells or higher organism to the next via the gene and genome. A gene is ...
NAME CH11 In class assignment Due 2/18/14 Across 1. Initials of
... for these single stranded sections is: a) “single ends” b) “lonely ends” c) “sticky ends” d) “fragmented ends” 3) In order to produce a transgenic animal, DNA must be injected into the __________________. a) unfertilized egg b) unfertilized sperm c) zygote (fertilized egg) d) fetus during the 3rd tr ...
... for these single stranded sections is: a) “single ends” b) “lonely ends” c) “sticky ends” d) “fragmented ends” 3) In order to produce a transgenic animal, DNA must be injected into the __________________. a) unfertilized egg b) unfertilized sperm c) zygote (fertilized egg) d) fetus during the 3rd tr ...
Biology Summary Sheet
... Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell. Genes are located on chromosomes and are made of DNA. DNA is a molecule that consists of two strands connected together by bases. DNA is described as a double-stranded helix. There are 4 bases named; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine ...
... Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell. Genes are located on chromosomes and are made of DNA. DNA is a molecule that consists of two strands connected together by bases. DNA is described as a double-stranded helix. There are 4 bases named; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine ...
Unit 2 – Genetics Content Map
... A. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. B. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. C. Using Mendel’s laws, explain the role of meiosis in reproductive variability. D. Describe the relationships between changes in DNA and potential appearance of new traits including: -Al ...
... A. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. B. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. C. Using Mendel’s laws, explain the role of meiosis in reproductive variability. D. Describe the relationships between changes in DNA and potential appearance of new traits including: -Al ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.