REVIEW ARTICLE
... This can be illustrated by the following example. Let us assume the DNA profile is based on six separate loci or genes, and that the suspect possesses alleles or versions of these that are present respectively in 8 percent, 1 percent, 5 percent, 10 percent, 10 percent and 2 percent of the total popu ...
... This can be illustrated by the following example. Let us assume the DNA profile is based on six separate loci or genes, and that the suspect possesses alleles or versions of these that are present respectively in 8 percent, 1 percent, 5 percent, 10 percent, 10 percent and 2 percent of the total popu ...
Activity Name - Science4Inquiry.com
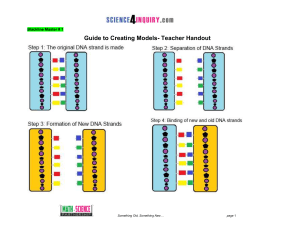
... a. Primase creates an RNA primer, helicase unzips the DNA, DNA polymerase adds nucleotides and creates new DNA, DNA polymerase fills in the gaps, DNA ligase seals the fragments of DNA, exonuclease removes the primers. b. Helicase unzips the DNA, primase creates an RNA primer, DNA polymerase adds nuc ...
... a. Primase creates an RNA primer, helicase unzips the DNA, DNA polymerase adds nucleotides and creates new DNA, DNA polymerase fills in the gaps, DNA ligase seals the fragments of DNA, exonuclease removes the primers. b. Helicase unzips the DNA, primase creates an RNA primer, DNA polymerase adds nuc ...
Chapter 12 Molecular Genetics
... cells. The cell may die or simply not perform its normal function. These mutations are not passed on to the next generation. When mutations occur in sex cells, they will be present in every cell of the offspring. ...
... cells. The cell may die or simply not perform its normal function. These mutations are not passed on to the next generation. When mutations occur in sex cells, they will be present in every cell of the offspring. ...
Divergent roles for the two PolI-like organelle DNA polymerases of
... (rice) (Kimura et al., 2002), Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis) (Mori et al., 2005) and tobacco (Ono et al., 2007). Full-length cDNAs were cloned and regions corresponding to the DNA polymerase domains of these enzymes were produced in bacteria and tested for template preference, biochemical proper ...
... (rice) (Kimura et al., 2002), Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis) (Mori et al., 2005) and tobacco (Ono et al., 2007). Full-length cDNAs were cloned and regions corresponding to the DNA polymerase domains of these enzymes were produced in bacteria and tested for template preference, biochemical proper ...
Geminivirus Replication Origins Have a Modular
... TGMV A (Figure 1, cf. lanes 2 and 3), while BGMV B only replicated in the presence of BGMV A (cf. lanes 6 and 7). These results established that BGMV is able to replicate efficiently in tobacco cells and that, similar to TGMV A (Rogers et al., 1986; Hayes and Buck, 1989), BGMV A provides all of the ...
... TGMV A (Figure 1, cf. lanes 2 and 3), while BGMV B only replicated in the presence of BGMV A (cf. lanes 6 and 7). These results established that BGMV is able to replicate efficiently in tobacco cells and that, similar to TGMV A (Rogers et al., 1986; Hayes and Buck, 1989), BGMV A provides all of the ...
10_lecture-dna
... – binding to receptors on a host’s target cell, – injecting viral genetic material into the cell, and – hijacking the cell’s own molecules and organelles to produce new copies of the virus. ...
... – binding to receptors on a host’s target cell, – injecting viral genetic material into the cell, and – hijacking the cell’s own molecules and organelles to produce new copies of the virus. ...
Dr. Mani Tagmount, as used
... To Save columns: If your plan is to pool your RNA samples. Pool first ...
... To Save columns: If your plan is to pool your RNA samples. Pool first ...
Stability of triple helices containing RNA and DNA strands
... and/or cleave long DNA fragments at single sites (see ref. 8 for a review). A pyrimidine oligonucleotide binds to the major groove of a double helix in a parallel orientation with respect to the purine strand, through formation of Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds between a T.A base pair and thymine and betw ...
... and/or cleave long DNA fragments at single sites (see ref. 8 for a review). A pyrimidine oligonucleotide binds to the major groove of a double helix in a parallel orientation with respect to the purine strand, through formation of Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds between a T.A base pair and thymine and betw ...
The Effects of Skeletal Preparation Techniques on DNA from Human
... Today it is not uncommon for forensic pathologists, morgue assistants, or anthropologists to clean skeletal material harboring putrefying material by boiling it in a bleach solution, which removes adhering soft tissue. While bleach is highly effective for defleshing bones, its drawbacks are far too ...
... Today it is not uncommon for forensic pathologists, morgue assistants, or anthropologists to clean skeletal material harboring putrefying material by boiling it in a bleach solution, which removes adhering soft tissue. While bleach is highly effective for defleshing bones, its drawbacks are far too ...
Chapter 21 - University of Hawaii
... 11. Mutations can be caused by: A.errors in the replication process B.exposure to environmental substances C.base substitutions D.All of the choices are correct. 12. Mutations are: A.changes in the base sequence within a gene B.always beneficial C.always harmful 13. In DNA function, the term "templa ...
... 11. Mutations can be caused by: A.errors in the replication process B.exposure to environmental substances C.base substitutions D.All of the choices are correct. 12. Mutations are: A.changes in the base sequence within a gene B.always beneficial C.always harmful 13. In DNA function, the term "templa ...
Therapeutic Targeting of the DNA Mismatch Repair Pathway
... nition is carried out by MutS. The MutS heterodimer does this task by recognizing distortions in the DNA double helix structure caused by mismatched bases (12). MutS initially binds double-stranded DNA at the site of a mismatch and then recruits MutL. MutL seems to act as the mediator for a series o ...
... nition is carried out by MutS. The MutS heterodimer does this task by recognizing distortions in the DNA double helix structure caused by mismatched bases (12). MutS initially binds double-stranded DNA at the site of a mismatch and then recruits MutL. MutL seems to act as the mediator for a series o ...
DNA - IPN-Kiel
... work. When they had garnered all the available information, they built models so that they could see what they were imagining more clearly. They finally succeeded in devising a structure that fitted all the data, and published their findings in Nature, a most prestigious scientific journal, in 1953. ...
... work. When they had garnered all the available information, they built models so that they could see what they were imagining more clearly. They finally succeeded in devising a structure that fitted all the data, and published their findings in Nature, a most prestigious scientific journal, in 1953. ...
Mechanisms of Transcription-Replication
... are virtually identical to those for the P7 promoter (compare Fig. 4B to Fig. 3D). Since very different promoters cause similar inhibitory effects on replication, it is likely that the act of transcription, rather than the nature of a promoter, is responsible for this effect. When the trc promoter w ...
... are virtually identical to those for the P7 promoter (compare Fig. 4B to Fig. 3D). Since very different promoters cause similar inhibitory effects on replication, it is likely that the act of transcription, rather than the nature of a promoter, is responsible for this effect. When the trc promoter w ...
Linear DNA Low Efficiency Transfection by Liposome Can - if
... enzyme activity was observed in Vero cells transfected with the linear DNA:liposome complexes. On the other hand, using a light microscope, the presence of transfected blue cells was estimated to be around 40% for circular DNA. A vacuolization of the cells was also observed, but not with the linear ...
... enzyme activity was observed in Vero cells transfected with the linear DNA:liposome complexes. On the other hand, using a light microscope, the presence of transfected blue cells was estimated to be around 40% for circular DNA. A vacuolization of the cells was also observed, but not with the linear ...
The nucleic acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... • DNA in the nucleus of the cell directs the sythesis of an RNA molecule. – The RNA will carry the sequence of amines found on a particular portion of the DNA • Only a portion of a DNA strand is used to make any given RNA. • There needs to be a way to start and stop transcription. • The DNA has syst ...
... • DNA in the nucleus of the cell directs the sythesis of an RNA molecule. – The RNA will carry the sequence of amines found on a particular portion of the DNA • Only a portion of a DNA strand is used to make any given RNA. • There needs to be a way to start and stop transcription. • The DNA has syst ...
Variable effects of DNA-synthesis inhibitors upon DNA methylation
... molecular weight DNA representing sites of initiated but incomplete DNA synthesis; and (4) occurred primarily within CpG dinucleotides, although other dinucleotides were overmethylated as well. Drug-induced CpG hypermethylation may be capable of silencing genes, an effect which may be relevant to th ...
... molecular weight DNA representing sites of initiated but incomplete DNA synthesis; and (4) occurred primarily within CpG dinucleotides, although other dinucleotides were overmethylated as well. Drug-induced CpG hypermethylation may be capable of silencing genes, an effect which may be relevant to th ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... bound to the promoter, the C-terminal domain causes transcriptional activation through contacts to the σ70 subunit of RNA polymerase (11,12). The function of Ada as a transcription factor is thus dependent on the methylation of Cys69, and the presence of the C-terminal domain (regardless of methylat ...
... bound to the promoter, the C-terminal domain causes transcriptional activation through contacts to the σ70 subunit of RNA polymerase (11,12). The function of Ada as a transcription factor is thus dependent on the methylation of Cys69, and the presence of the C-terminal domain (regardless of methylat ...
DNA structure 2008
... • Each strand of the double-helical DNA molecule must be copied in complementary fashion by DNA polymerase • Each strand can serve as a template for copying • DNA polymerase requires template and primer • Primer: an oligonucleotide that pairs with the end of the template molecule to form dsDNA • DNA ...
... • Each strand of the double-helical DNA molecule must be copied in complementary fashion by DNA polymerase • Each strand can serve as a template for copying • DNA polymerase requires template and primer • Primer: an oligonucleotide that pairs with the end of the template molecule to form dsDNA • DNA ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to DNA Recognition By Minor Groove
... proteins, while complex in their own right, are often altered by association with their target DNA sequence. Complex formation often involves more than one protein component and can result in gross distortions of the canonical B-form double helix.9 Attempts to engineer proteins with novel DNA bindin ...
... proteins, while complex in their own right, are often altered by association with their target DNA sequence. Complex formation often involves more than one protein component and can result in gross distortions of the canonical B-form double helix.9 Attempts to engineer proteins with novel DNA bindin ...
Reverse Transcription (cDNA Synthesis) | NEB
... use an RNA template and a short primer complementary to the 3' end of the RNA to direct the synthesis of the first strand cDNA, which can be used directly as a template for the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). This combination of reverse transcription and PCR (RT-PCR) allows the detection of low abu ...
... use an RNA template and a short primer complementary to the 3' end of the RNA to direct the synthesis of the first strand cDNA, which can be used directly as a template for the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). This combination of reverse transcription and PCR (RT-PCR) allows the detection of low abu ...
Identification and characterization of the DNA replication origin
... (Mus musculus ORC) core complex (containing Orc2p–5p) was highly expressed in adult mouse brain tissue, and knockdown using siRNA (small interfering RNA) reduced the dendrite and dendritic spine developments in postmitotic neurons [20]. ScOrc6 proteins contain a unique conserved domain named the Orc ...
... (Mus musculus ORC) core complex (containing Orc2p–5p) was highly expressed in adult mouse brain tissue, and knockdown using siRNA (small interfering RNA) reduced the dendrite and dendritic spine developments in postmitotic neurons [20]. ScOrc6 proteins contain a unique conserved domain named the Orc ...
a series of experiments
... growth, the blood cells became infected by M. pirum within 2-3 weeks. Similarly fluid containing HIV particles with a diameter of 100-120nM were not sterilised by 20nM filtration. When investigating these filtrates it was also discovered that if they were diluted and agitated in a specific way, they ...
... growth, the blood cells became infected by M. pirum within 2-3 weeks. Similarly fluid containing HIV particles with a diameter of 100-120nM were not sterilised by 20nM filtration. When investigating these filtrates it was also discovered that if they were diluted and agitated in a specific way, they ...
In vitro Selection for a Max 1s DNA Genetic Algorithm
... a rate of about 10,4 nucleotide per cycle when Taq DNA polymerase is used [12]. Special PCR protocols can be used to induce pointwise mutation at a rate of 10,2 to 10,4 [5, 6, 8, 19, 20, 35, 38]. One of the PCR primers (the complement of the tail), that is used to make the strands which are compleme ...
... a rate of about 10,4 nucleotide per cycle when Taq DNA polymerase is used [12]. Special PCR protocols can be used to induce pointwise mutation at a rate of 10,2 to 10,4 [5, 6, 8, 19, 20, 35, 38]. One of the PCR primers (the complement of the tail), that is used to make the strands which are compleme ...
Simple and inexpensive DNA extraction protocol for - Funpec-RP
... are subsequently purified. Many direct extraction methods combine chemical and enzymatic treatments and physical procedures, although some of these protocols are tedious and laborious, with numerous steps. In addition, the required enzymes are expensive and inefficient for most Gram-positive bacteri ...
... are subsequently purified. Many direct extraction methods combine chemical and enzymatic treatments and physical procedures, although some of these protocols are tedious and laborious, with numerous steps. In addition, the required enzymes are expensive and inefficient for most Gram-positive bacteri ...
DNA replication
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. This biological process occurs in all living organisms and is the basis for biological inheritance. DNA is made up of two strands and each strand of the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the production of the complementary strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. Cellular proofreading and error-checking mechanisms ensure near perfect fidelity for DNA replication.In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations, or origins of replication, in the genome. Unwinding of DNA at the origin and synthesis of new strands results in replication forks growing bidirectional from the origin. A number of proteins are associated with the replication fork which helps in terms of the initiation and continuation of DNA synthesis. Most prominently, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new DNA by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand.DNA replication can also be performed in vitro (artificially, outside a cell). DNA polymerases isolated from cells and artificial DNA primers can be used to initiate DNA synthesis at known sequences in a template DNA molecule. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common laboratory technique, cyclically applies such artificial synthesis to amplify a specific target DNA fragment from a pool of DNA.