Organizing Information Digitally
... • Data in this format often called “flat files.” • Can be used as a way of getting data “into” a database: make a list into a database table ...
... • Data in this format often called “flat files.” • Can be used as a way of getting data “into” a database: make a list into a database table ...
Lecture 3
... • Relation is a table of n columns and m rows., Referred to as: m x n • rows define CARDINALITY (m), cols define DEGREE (n) • relations are represented as: • relation (attribute names..) • ex; • STUDENT (student name, student ss#, student address, GPA) ...
... • Relation is a table of n columns and m rows., Referred to as: m x n • rows define CARDINALITY (m), cols define DEGREE (n) • relations are represented as: • relation (attribute names..) • ex; • STUDENT (student name, student ss#, student address, GPA) ...
Database Introduction - YSU Computer Science & Information Systems
... Database vs Flat Files • Flat Files – Characters-fields-records-files • Files are not designed to work together – Each file is an independent entity – No design rules followed – Updates can be hairy ...
... Database vs Flat Files • Flat Files – Characters-fields-records-files • Files are not designed to work together – Each file is an independent entity – No design rules followed – Updates can be hairy ...
Database
... 1986: SQL standardized 90s: Object-relational databases, object-oriented databases Late 90s: XML databases 1999: SQL incorporates some OO features 2003, 2006: SQL incorporates support for XML data ...
... 1986: SQL standardized 90s: Object-relational databases, object-oriented databases Late 90s: XML databases 1999: SQL incorporates some OO features 2003, 2006: SQL incorporates support for XML data ...
syllabus template - Cumberland County College
... analysis. Students gain hands-on experience in the design and creation of databases and retrieval from a database. SQL will be introduced. Learning Outcomes Upon successful completion of this course, the student should be able to: Demonstrate knowledge of fundamental data design and relational datab ...
... analysis. Students gain hands-on experience in the design and creation of databases and retrieval from a database. SQL will be introduced. Learning Outcomes Upon successful completion of this course, the student should be able to: Demonstrate knowledge of fundamental data design and relational datab ...
CENG 302 Introduction to Database Management
... Objectives & Content • Objectives: • This course involves students in real-life problems and theory on database systems and encourages them to design and implement databases. ...
... Objectives & Content • Objectives: • This course involves students in real-life problems and theory on database systems and encourages them to design and implement databases. ...
Chapter 1
... 2. To retrieve or update the data in a database, the client sends a/an _____________________ to the database. 3. A relational database consists of one or more __________________. 4. A/An _______________________ uniquely identifies each row in a table. 5. The intersection of a row and a column is com ...
... 2. To retrieve or update the data in a database, the client sends a/an _____________________ to the database. 3. A relational database consists of one or more __________________. 4. A/An _______________________ uniquely identifies each row in a table. 5. The intersection of a row and a column is com ...
CSC 3110 Database Management Systems II
... database management systems. Operational aspects like speed and se- curity are to be extensively addressed. Internal operations of database management systems like indexing, query processing and transactions are to be covered. These are to create a strong basis for future advanced studies/research. ...
... database management systems. Operational aspects like speed and se- curity are to be extensively addressed. Internal operations of database management systems like indexing, query processing and transactions are to be covered. These are to create a strong basis for future advanced studies/research. ...
Application Software Practical 1
... Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) – software that uses related data stored in different tables Table is made up of rows (records) and columns (fields) ...
... Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) – software that uses related data stored in different tables Table is made up of rows (records) and columns (fields) ...
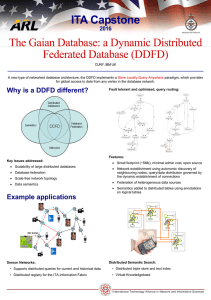
The Gaian Database: a Dynamic Distributed Federated Database
... A new type of networked database architecture, the DDFD implements a Store Locally Query Anywhere paradigm, which provides for global access to data from any vertex in the database network. ...
... A new type of networked database architecture, the DDFD implements a Store Locally Query Anywhere paradigm, which provides for global access to data from any vertex in the database network. ...
LECTURE NOTES #5
... Need standardized data definition Advantages of DBMS require careful design Define data correctly and the rest is much easier It especially makes it easier to expand database later Method applies to most models and most DBMS Similar to Entity-Relationship Similar to Objects (without inheritan ...
... Need standardized data definition Advantages of DBMS require careful design Define data correctly and the rest is much easier It especially makes it easier to expand database later Method applies to most models and most DBMS Similar to Entity-Relationship Similar to Objects (without inheritan ...
Chapter 1: Why Study Computers and Digital Technology?
... Name, number, or combination of characters that describes some aspect of an object Record Collection of related fields File Collection of related records Database Collection of integrated and related files ...
... Name, number, or combination of characters that describes some aspect of an object Record Collection of related fields File Collection of related records Database Collection of integrated and related files ...
A brief history of computing databases
... The earliest “databases” (organized collections of information) may date as early as 3300 BCE (BC) with the beginning of writing (Cuneiform). ...
... The earliest “databases” (organized collections of information) may date as early as 3300 BCE (BC) with the beginning of writing (Cuneiform). ...
Job Description – System Support Analyst Description The
... information systems across the College and the production of core and ad-hoc information and reporting requirements. As part of the role they will be responsible for implementing data dashboards to all levels of the organisation. Responsibilities ...
... information systems across the College and the production of core and ad-hoc information and reporting requirements. As part of the role they will be responsible for implementing data dashboards to all levels of the organisation. Responsibilities ...
Object Summary
... particular Data Subject (DS) in a database. Comprise a more complete and therefore semantically meaningful set of information about the enquired DS ...
... particular Data Subject (DS) in a database. Comprise a more complete and therefore semantically meaningful set of information about the enquired DS ...
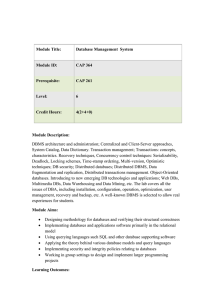
Database Management System Module Title: CAP 364 Module ID
... techniques; DB security; Distributed databases; Distributed DBMS, Data fragmentation and replication, Distributed transactions management. Object-Oriented databases. Introducing to new emerging DB technologies and applications; Web DBs, Multimedia DBs, Data Warehousing and Data Mining, etc. The lab ...
... techniques; DB security; Distributed databases; Distributed DBMS, Data fragmentation and replication, Distributed transactions management. Object-Oriented databases. Introducing to new emerging DB technologies and applications; Web DBs, Multimedia DBs, Data Warehousing and Data Mining, etc. The lab ...
Document
... description of the data in a database Specifies data types and ranges Assists programmers in understanding the data ...
... description of the data in a database Specifies data types and ranges Assists programmers in understanding the data ...
Fundamental_of_RDBMS.pdf
... Problems with traditional file processing system. Objectives of database management system. Data Independence Data integrity Relational Database Name database approaches : Relational, Hierarchical Network What is Relational database approach Terminology : Relational, entity, attributes Tuples, entit ...
... Problems with traditional file processing system. Objectives of database management system. Data Independence Data integrity Relational Database Name database approaches : Relational, Hierarchical Network What is Relational database approach Terminology : Relational, entity, attributes Tuples, entit ...
Database Systems
... Consequences Commercial systems followed CODASYL DBTG propoal, but none fully implemented it. IDMS system by B.F. Goodrich, Honeywell’s IDS II, UNIVAC’s DMS 1100, Burroughs’s DMS-II, CDC’s DMS 170, Phillip’s PHOLAS and Digital’s DBMS 11. Several integrated DB/ DC Systems: Cincom’s TOTAL plus ENVIRON ...
... Consequences Commercial systems followed CODASYL DBTG propoal, but none fully implemented it. IDMS system by B.F. Goodrich, Honeywell’s IDS II, UNIVAC’s DMS 1100, Burroughs’s DMS-II, CDC’s DMS 170, Phillip’s PHOLAS and Digital’s DBMS 11. Several integrated DB/ DC Systems: Cincom’s TOTAL plus ENVIRON ...
RELATIONAL DATABASE Computer database in which all data is
... Computer database in which all data is stored in Relations which (to the user) are tables with rows and columns. Each table is composed of records (called Tuples) and each record is identified by a field (attribute) containing a unique value. Every table shares at least one field with another table ...
... Computer database in which all data is stored in Relations which (to the user) are tables with rows and columns. Each table is composed of records (called Tuples) and each record is identified by a field (attribute) containing a unique value. Every table shares at least one field with another table ...
Database model

A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database and fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized, and manipulated. The most popular example of a database model is the relational model, which uses a table-based format.