Theory of quantum state control with solid-state qubits Research supervisor
... The potential to exploit quantum-mechanics in technology, from sensors to computers, is vast. Essential for these developments, however, is the ability to take a quantum system with a few discrete states, such as an exciton in a quantum dot or impurity state in a crystal, and control its wavefunctio ...
... The potential to exploit quantum-mechanics in technology, from sensors to computers, is vast. Essential for these developments, however, is the ability to take a quantum system with a few discrete states, such as an exciton in a quantum dot or impurity state in a crystal, and control its wavefunctio ...
By: 3rd Period Chemistry Actinide Ionization Energy Probability
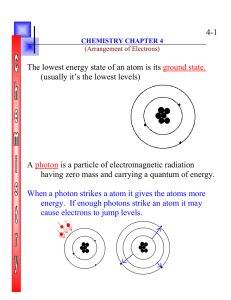
... Volume of space in which the electron is likely to be found nucleus Quantum Number Four values that completely describe an electron Atomic number ...
... Volume of space in which the electron is likely to be found nucleus Quantum Number Four values that completely describe an electron Atomic number ...
constructive - Purdue Physics
... positively charged and neutrons are neutral. The number of protons is called Z, the atomic number. The total number of protons and neutrons is called A, the mass number. The number of neutrons is therefore A-Z. The neutral atom has Z electrons which determine the chemical properties of the element. ...
... positively charged and neutrons are neutral. The number of protons is called Z, the atomic number. The total number of protons and neutrons is called A, the mass number. The number of neutrons is therefore A-Z. The neutral atom has Z electrons which determine the chemical properties of the element. ...
Historical Introduction to the Elementary Particles 2
... For example, p denotes the proton and p the antiproton; n the neutron and n the antineutron. However, in some cases it is more customary simply to specify the charge. Thus most people write e+ for the positron (not e) and m+ for the antimuon (not m). [But you must not mix conventions: e + is ambiguo ...
... For example, p denotes the proton and p the antiproton; n the neutron and n the antineutron. However, in some cases it is more customary simply to specify the charge. Thus most people write e+ for the positron (not e) and m+ for the antimuon (not m). [But you must not mix conventions: e + is ambiguo ...
Quantum Numbers
... 2s orbital is not degenerate (e.g., the same energy) with a 2p or a 1s orbital. The ml values are entirely dependent on the l values; each type of orbital has a set degeneracy. For an s-orbital, ml = 0, and degeneracy = 1. For a p-orbital, ml = -1, 0, +1, and degeneracy = 3. For a d-orbital, ml = -2 ...
... 2s orbital is not degenerate (e.g., the same energy) with a 2p or a 1s orbital. The ml values are entirely dependent on the l values; each type of orbital has a set degeneracy. For an s-orbital, ml = 0, and degeneracy = 1. For a p-orbital, ml = -1, 0, +1, and degeneracy = 3. For a d-orbital, ml = -2 ...
Document
... • Hamiltonian oracles are the continuum limit of the standard unitary quantum oracles. In this limit, the problem of finding the optimal query algorithm can be mapped into the problem of finding shortest paths on a manifold. Prove this trivially: ...
... • Hamiltonian oracles are the continuum limit of the standard unitary quantum oracles. In this limit, the problem of finding the optimal query algorithm can be mapped into the problem of finding shortest paths on a manifold. Prove this trivially: ...
The Transactional Interpretation
... • Theory needed to predict behavior of very small particles such as atoms, electrons, photons, and other subatomic particles. • QM works very well but what it actually tells us about reality is very unclear • An interpretation is intended to make clear what the theory tells us about reality ...
... • Theory needed to predict behavior of very small particles such as atoms, electrons, photons, and other subatomic particles. • QM works very well but what it actually tells us about reality is very unclear • An interpretation is intended to make clear what the theory tells us about reality ...
Chapter 2
... __ (e) If wave B represents visible radiation, is wave A or C more likely to be IR radiation? ...
... __ (e) If wave B represents visible radiation, is wave A or C more likely to be IR radiation? ...
lecture31
... • “Allowed” transitions between energy levels occur between states whose value of l differ by one: • Other, “forbidden,” transitions also occur but with much lower probability • Photon has a spin angular momentum of 1ħ ...
... • “Allowed” transitions between energy levels occur between states whose value of l differ by one: • Other, “forbidden,” transitions also occur but with much lower probability • Photon has a spin angular momentum of 1ħ ...
Slide 1
... functions - y) that incorporates the dual nature of the electron. 2) Y2 provides info about the electron’s location. 3) In the Quantum Mechanical Model, we speak of the probability (Y2) that the electron will be in a certain region of space at a given instant. 4) We call it probability density or el ...
... functions - y) that incorporates the dual nature of the electron. 2) Y2 provides info about the electron’s location. 3) In the Quantum Mechanical Model, we speak of the probability (Y2) that the electron will be in a certain region of space at a given instant. 4) We call it probability density or el ...
lecture31
... “Allowed” transitions between energy levels occur between states whose value of l differ by one: Other, “forbidden,” transitions also occur but with much lower probability. Photon has a spin angular momentum of 1ħ. ...
... “Allowed” transitions between energy levels occur between states whose value of l differ by one: Other, “forbidden,” transitions also occur but with much lower probability. Photon has a spin angular momentum of 1ħ. ...
Particle in a box

In quantum mechanics, the particle in a box model (also known as the infinite potential well or the infinite square well) describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trapped inside a large box, the particle can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than another. However, when the well becomes very narrow (on the scale of a few nanometers), quantum effects become important. The particle may only occupy certain positive energy levels. Likewise, it can never have zero energy, meaning that the particle can never ""sit still"". Additionally, it is more likely to be found at certain positions than at others, depending on its energy level. The particle may never be detected at certain positions, known as spatial nodes.The particle in a box model provides one of the very few problems in quantum mechanics which can be solved analytically, without approximations. This means that the observable properties of the particle (such as its energy and position) are related to the mass of the particle and the width of the well by simple mathematical expressions. Due to its simplicity, the model allows insight into quantum effects without the need for complicated mathematics. It is one of the first quantum mechanics problems taught in undergraduate physics courses, and it is commonly used as an approximation for more complicated quantum systems.