Retreating Blade Stall - Front Range Helicopters
... condition that will cause the nose to pitch up. This is due to gyroscopic precession, stall on the right side, reaction is 90 degrees later causing loss of lift over the tail and the nose to pitch up. At this point the helicopter may start to roll, usually to the left but not always. ...
... condition that will cause the nose to pitch up. This is due to gyroscopic precession, stall on the right side, reaction is 90 degrees later causing loss of lift over the tail and the nose to pitch up. At this point the helicopter may start to roll, usually to the left but not always. ...
Civil Aviation
... Aerofoil — Chord, span, camber, twist and centre of pressure Rotor system — Articulated, rigid, semi-rigid, rotor disc, pitch angle, coning and angle of attack ...
... Aerofoil — Chord, span, camber, twist and centre of pressure Rotor system — Articulated, rigid, semi-rigid, rotor disc, pitch angle, coning and angle of attack ...
Fundamentals of Flight - Aviation Training Network
... In forward flight, air flows opposite the flight path of the aircraft. The velocity of the flow of air equals the forward speed of the helicopter. Because the blades of the helicopter turn in a circular pattern, the velocity of the airflow across a blade depends on the position of the blade in the r ...
... In forward flight, air flows opposite the flight path of the aircraft. The velocity of the flow of air equals the forward speed of the helicopter. Because the blades of the helicopter turn in a circular pattern, the velocity of the airflow across a blade depends on the position of the blade in the r ...
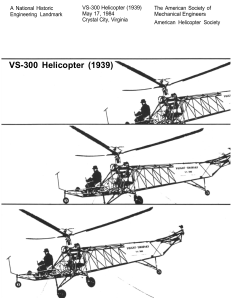
VS-300 Helicopter (1939) - American Society of Mechanical Engineers
... mounted on outriggers were used for the Focke-Achgelis Fw-61 which was initially flown in Germany in 1936 and is considered to be the world’s first practical helicopter. Another German helicopter, the Flettner synchrocopter was produced for military use between 1942 and 1945. This aircraft, sometime ...
... mounted on outriggers were used for the Focke-Achgelis Fw-61 which was initially flown in Germany in 1936 and is considered to be the world’s first practical helicopter. Another German helicopter, the Flettner synchrocopter was produced for military use between 1942 and 1945. This aircraft, sometime ...
Antaris 9.5 kW - West Coast Solar and Wind
... Extremely strong permanent magnets for a high level of efficiency (NdFeBo permanent magnets, resistent to temperatures up to 150° C) ...
... Extremely strong permanent magnets for a high level of efficiency (NdFeBo permanent magnets, resistent to temperatures up to 150° C) ...
Centrifugation
... the speed of the rotor in revolutions per minute (rpm) and the radius of rotation (ie the distance from the axis of rotation). The equations that permit calculation of the RCF from a known rpm and radius of rotation, and calculation of the rpm from a known RCF and radius are shown in Table 1. The RC ...
... the speed of the rotor in revolutions per minute (rpm) and the radius of rotation (ie the distance from the axis of rotation). The equations that permit calculation of the RCF from a known rpm and radius of rotation, and calculation of the rpm from a known RCF and radius are shown in Table 1. The RC ...
Blade Element Theory for Rotor in Hover and Climb
... Consider a typical element or strip shown below. The blade “sees” an in-plane velocity UT, that is tangential to the plane of rotation. The magnitude of U T is, of course, r, where r is the radial position of the strip. This element has a pitch angle equal to . That is, the angle between the plane ...
... Consider a typical element or strip shown below. The blade “sees” an in-plane velocity UT, that is tangential to the plane of rotation. The magnitude of U T is, of course, r, where r is the radial position of the strip. This element has a pitch angle equal to . That is, the angle between the plane ...
PoF LO5 p2
... The Yaw Pedals Moving the Yaw Pedals will alter Blade Pitch equally on all the Tail Rotor Blades Yaw Pedals ...
... The Yaw Pedals Moving the Yaw Pedals will alter Blade Pitch equally on all the Tail Rotor Blades Yaw Pedals ...
Propellers
... If a helicopter was designed with a single rotor it would be very difficult to control. The rotor, spinning in one direction, sends the body twisting in the opposite direction. To overcome this effect, some helicopters are designed with two rotors, each turning in the opposite direction; this ...
... If a helicopter was designed with a single rotor it would be very difficult to control. The rotor, spinning in one direction, sends the body twisting in the opposite direction. To overcome this effect, some helicopters are designed with two rotors, each turning in the opposite direction; this ...
Helicopter rotor

A helicopter main rotor or rotor system is the combination of several rotary wings (rotor blades) and a control system that generates the aerodynamic lift force that supports the weight of the helicopter, and the thrust that counteracts aerodynamic drag in forward flight. Each main rotor is mounted on a vertical mast over the top of the helicopter, as opposed to a helicopter tail rotor, which connects through a combination of drive shaft(s) and gearboxes along the tail boom. The blade pitch is typically controlled by a swashplate connected to the helicopter flight controls. Helicopters are one example of rotary-wing aircraft (rotorcraft).