Ch. 4 Objectives
... Chapter 4 World Geography Objectives Contrast Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources & identify examples of each. ...
... Chapter 4 World Geography Objectives Contrast Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources & identify examples of each. ...
Economic Systems Review An economic system is the method used
... →In theory, a free market system has no government intervention. However, since there does not exist a country with absolutely no government in control, we consider a free market economy to have very minimal government interference. →Free market economic systems are characterized by a large urban ...
... →In theory, a free market system has no government intervention. However, since there does not exist a country with absolutely no government in control, we consider a free market economy to have very minimal government interference. →Free market economic systems are characterized by a large urban ...
Assignment I Haitham F. AlMubarak 200600045 Introduction to
... A schedule showing the quantity of a good that suppliers in a given market desire to sell at each price, holding other things equal. ...
... A schedule showing the quantity of a good that suppliers in a given market desire to sell at each price, holding other things equal. ...
Economic Systems
... What economic goods will be produced? How will goods be produced? For whom will the economic goods be produced? ...
... What economic goods will be produced? How will goods be produced? For whom will the economic goods be produced? ...
Command & Traditional Economies - Hamburg Central School District
... a. consumer goods because low consumer confidence worsened the Great Depression b. government goods because government spending is large part of the economy c. investment because it fluctuated and was linked to the spending multiplier effect d. net exports because they were related to a favorable ba ...
... a. consumer goods because low consumer confidence worsened the Great Depression b. government goods because government spending is large part of the economy c. investment because it fluctuated and was linked to the spending multiplier effect d. net exports because they were related to a favorable ba ...
free market
... ability of others to use it. In addition, the lighthouse owner cannot restrict individuals from using the light. ...
... ability of others to use it. In addition, the lighthouse owner cannot restrict individuals from using the light. ...
Chapter 4, Section 5
... exchange of goods and services among a group of people • The way people choose to produce and exchange goods is called as economic system – Traditional Economy - trade without money, or “barter” – Command Economy – production determined by government, who also owns the means of production, and does ...
... exchange of goods and services among a group of people • The way people choose to produce and exchange goods is called as economic system – Traditional Economy - trade without money, or “barter” – Command Economy – production determined by government, who also owns the means of production, and does ...
The Circular Flow Model
... • Money that is transferred from one person to another (or group or business). Usually government is doing the redistribution. • Key characteristic --- no good or service or factor of production is exchanged in return (purely financial ...
... • Money that is transferred from one person to another (or group or business). Usually government is doing the redistribution. • Key characteristic --- no good or service or factor of production is exchanged in return (purely financial ...
Review: Introduction
... 4. "All systems either of preference or of restraint, therefore, being thus completely taken away, the obvious and simple system of natural liberty establishes itself of its own accord. Every man, as long as he does not violate the laws of justice, is left perfectly free to pursue his own interest h ...
... 4. "All systems either of preference or of restraint, therefore, being thus completely taken away, the obvious and simple system of natural liberty establishes itself of its own accord. Every man, as long as he does not violate the laws of justice, is left perfectly free to pursue his own interest h ...
19th Century Economics
... distribution of products is in the hands of private individuals or corporations who operate these businesses for profit • Evolved out of statesponsored mercantilism ...
... distribution of products is in the hands of private individuals or corporations who operate these businesses for profit • Evolved out of statesponsored mercantilism ...
POL 4410: Week 10 Domestic Development Structure Inward vs
... Self-sufficiency in all goods, including highend goods. But what if you can’t produce everything? Develop own capital stocks, human capital stocks, and technology. Capital stock must come from domestic savings Cannot import educated workers Cannot import technology ...
... Self-sufficiency in all goods, including highend goods. But what if you can’t produce everything? Develop own capital stocks, human capital stocks, and technology. Capital stock must come from domestic savings Cannot import educated workers Cannot import technology ...
Economics - Crossword Labs
... 15. the ability of a firm or individual to produce goods and/or services at a lower opportunity cost than other firms 16. a political theory derived from Karl Marx 17. the level of employment rates where there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment 18. an economic system where few restricti ...
... 15. the ability of a firm or individual to produce goods and/or services at a lower opportunity cost than other firms 16. a political theory derived from Karl Marx 17. the level of employment rates where there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment 18. an economic system where few restricti ...
Guide 3
... Census- A government count of the U.S population taken every 10 years Dow Jones Industrial Average- Represents 30 stocks in the New York Stock Exchange to monitor market price changes Bull Market- A stock Market where most prices are rising ...
... Census- A government count of the U.S population taken every 10 years Dow Jones Industrial Average- Represents 30 stocks in the New York Stock Exchange to monitor market price changes Bull Market- A stock Market where most prices are rising ...
honors economics chapter 2
... b. Capitalism is based chiefly on private ownership of property. Most means of production and distribution are privately owned and operated. 3. Freedom of Enterprise a. a system in which individuals are free to own and control the factors of production b. Pillars of a Free Enterprise: private proper ...
... b. Capitalism is based chiefly on private ownership of property. Most means of production and distribution are privately owned and operated. 3. Freedom of Enterprise a. a system in which individuals are free to own and control the factors of production b. Pillars of a Free Enterprise: private proper ...
Unit 4 Powerpoint
... – the special interest effect from lobbyists, – the short-sightedness of politicians. Taxation and spending by the government make the economy less stable. A uniform flat ax with no deductions is more fair than a progressive income tax. Social welfare programs don't help the poor; they reward povert ...
... – the special interest effect from lobbyists, – the short-sightedness of politicians. Taxation and spending by the government make the economy less stable. A uniform flat ax with no deductions is more fair than a progressive income tax. Social welfare programs don't help the poor; they reward povert ...
THE SCIENCE OF ECONOMICS Economics is the social science
... Analysis of change in a single market often proceeds from the simplifying assumption that relations in other markets remain unchanged, that is, partial-equilibrium analysis. Generalequilibrium theory allows for changes in different markets and aggregates across all markets, including their movements ...
... Analysis of change in a single market often proceeds from the simplifying assumption that relations in other markets remain unchanged, that is, partial-equilibrium analysis. Generalequilibrium theory allows for changes in different markets and aggregates across all markets, including their movements ...
The Nature and Methods of Economics
... The Nature and Methods of Economics Krugman Section 1 Module 1 ...
... The Nature and Methods of Economics Krugman Section 1 Module 1 ...
The World`s People
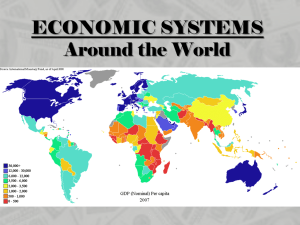
... Develop and Developing Countries o Developed countries have strong economies and a high quality of life; usually have high per capita GDP o Developing countries have less productive economies and a lower quality of life; usually have lower per capita GDP ...
... Develop and Developing Countries o Developed countries have strong economies and a high quality of life; usually have high per capita GDP o Developing countries have less productive economies and a lower quality of life; usually have lower per capita GDP ...
Economics Talk Show Links Economy: from Greek words oikos
... Wealth of Nations. The book identified land, labor, and capital as the three factors of production and the major contributors to a nation's wealth. In Smith's view, the ideal economy is a self-regulating market system that automatically satisfies the economic needs of the populace. He described the ...
... Wealth of Nations. The book identified land, labor, and capital as the three factors of production and the major contributors to a nation's wealth. In Smith's view, the ideal economy is a self-regulating market system that automatically satisfies the economic needs of the populace. He described the ...
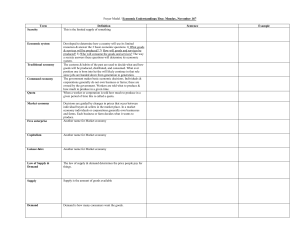
Frayer Model / Economic Understandings
... & services will be produced? 2) How will goods and services be produced? 3) Who will consume the goods and services? The way a society answers these questions will determine its economic system. The customs & habits of the past are used to decide what and how goods will be produced, distributed, and ...
... & services will be produced? 2) How will goods and services be produced? 3) Who will consume the goods and services? The way a society answers these questions will determine its economic system. The customs & habits of the past are used to decide what and how goods will be produced, distributed, and ...
The U.S. Economy
... Social security 23%, interest on debt 15%, medicare and medicaid 18%, others 11% ...
... Social security 23%, interest on debt 15%, medicare and medicaid 18%, others 11% ...
The Economic Questions
... 2. __________ should those goods and services be produced? 3. __________ should those goods and services be produced? Each nation’s economic system is determined by how the country answers these three economic questions. ...
... 2. __________ should those goods and services be produced? 3. __________ should those goods and services be produced? Each nation’s economic system is determined by how the country answers these three economic questions. ...
Unit 1 BASICS - Kenston Local Schools
... Russia & other nations have transitioned to mixed market economies. North Korea, Cuba, Iran, Libya, Laos, Belarus remain command systems. ...
... Russia & other nations have transitioned to mixed market economies. North Korea, Cuba, Iran, Libya, Laos, Belarus remain command systems. ...