Document
... Fraser governments. The authors give a blow-byblow account of policy decisions, economic events and party in-fighting, much in the manner of the financial press. But once again the basic argument is submerged by the detail. Essentially, they argue that Labor got in by formulating a "rival package wh ...
... Fraser governments. The authors give a blow-byblow account of policy decisions, economic events and party in-fighting, much in the manner of the financial press. But once again the basic argument is submerged by the detail. Essentially, they argue that Labor got in by formulating a "rival package wh ...
Economic Ups & Downs Activity
... What is real gross domestic product? O Total market value of all final goods and ...
... What is real gross domestic product? O Total market value of all final goods and ...
The Economic Perspective
... such as aggregate employment, output, growth, and inflation • Most important is GDP – Gross domestic product ...
... such as aggregate employment, output, growth, and inflation • Most important is GDP – Gross domestic product ...
International development - Institute for Governance and Policy
... individuals; profit seeking rather than subsistence and self sufficiency; Shift from commodity to human approach with investment in education and skill training ...
... individuals; profit seeking rather than subsistence and self sufficiency; Shift from commodity to human approach with investment in education and skill training ...
In `Brexit` and Trump, a populist farewell to laissez
... kind of meddlesome big government she loathed. Brussels was merely a stand-in for something deeper: the very globalization that Thatcher as Britain’s prime minister so enthusiastically promoted. ...
... kind of meddlesome big government she loathed. Brussels was merely a stand-in for something deeper: the very globalization that Thatcher as Britain’s prime minister so enthusiastically promoted. ...
Review of Course
... Means of production and distribution are privately or corporately owned, and Pure development is Democracy proportionate to the accumulation and reinvestment of profits gained in a free market. ...
... Means of production and distribution are privately or corporately owned, and Pure development is Democracy proportionate to the accumulation and reinvestment of profits gained in a free market. ...
SSEF6 - Productivity, Economic Growth and Standard of Living
... incomes of the population as measured by real per capita GDP, and also improvements in health and education, some social protection from poverty, freedom, a rule of law and other social goals. Standard of living is defined as the level of subsistence of a nation, social class or individual with refe ...
... incomes of the population as measured by real per capita GDP, and also improvements in health and education, some social protection from poverty, freedom, a rule of law and other social goals. Standard of living is defined as the level of subsistence of a nation, social class or individual with refe ...
Study Guide Europe Economics ANSWER KEY
... 17. How do entrepreneurs help increase a country’s GDP? They bring new ideas and jobs to the economy 18. In Germany, who decides which goods will be produced and sold? Businesses 19. What problems will occur in a country that does not invest in human capital? Workers will not be as productive 20. Th ...
... 17. How do entrepreneurs help increase a country’s GDP? They bring new ideas and jobs to the economy 18. In Germany, who decides which goods will be produced and sold? Businesses 19. What problems will occur in a country that does not invest in human capital? Workers will not be as productive 20. Th ...
Political economy
... Focus on “demand side” by manipulating independent variables such as government spending & taxes If people demand a product, producers will supply it, hence getting money into people’s hands will rise production Spending increases more effective than tax cuts: All of spending is consumption but some ...
... Focus on “demand side” by manipulating independent variables such as government spending & taxes If people demand a product, producers will supply it, hence getting money into people’s hands will rise production Spending increases more effective than tax cuts: All of spending is consumption but some ...
Good Morning! - Pennsylvania State University
... What about Real wages?? What about profits and thus the value of the stock market? What about labor market conditions? What about economic growth? What about inflation? ...
... What about Real wages?? What about profits and thus the value of the stock market? What about labor market conditions? What about economic growth? What about inflation? ...
The Economic Perspective
... – Which refers to the techniques of production – The results of new technology created, can include new ways of doing things, new product choices, and new uses for resources. ...
... – Which refers to the techniques of production – The results of new technology created, can include new ways of doing things, new product choices, and new uses for resources. ...
02. economic systems - Development of e
... for inputs and that for outputs. In the input markets, households offer their labour, land and capital. Firms buy these inputs at prices set in the markets. In the output markets, the enterprises sell out the goods and services to the consumers or households. ii) Types of Economy An economy might b ...
... for inputs and that for outputs. In the input markets, households offer their labour, land and capital. Firms buy these inputs at prices set in the markets. In the output markets, the enterprises sell out the goods and services to the consumers or households. ii) Types of Economy An economy might b ...
Economic Systems - Swan Hills School
... In a mixed economy, the market is still controlled by the mechanisms of a market economy (S+D+P, Competition), but also by the government or a central planning authority. In some cases, the government may allow or encourage a monopoly to exist—this occurs when a single producer or corporation has co ...
... In a mixed economy, the market is still controlled by the mechanisms of a market economy (S+D+P, Competition), but also by the government or a central planning authority. In some cases, the government may allow or encourage a monopoly to exist—this occurs when a single producer or corporation has co ...
economic systems
... • What happens when demand exceeds supply? • What happens when supply exceeds demand? • How does supply and demand affect choices ...
... • What happens when demand exceeds supply? • What happens when supply exceeds demand? • How does supply and demand affect choices ...
Final Economics Assignment 1415 An auto assembly line would
... 6. A tax on an imported good is called a _____________. 7. Why do prices act as a signal to sellers in the market? 8. The Fed BUYS government bonds/securities on the open market. This _______________ the money supply and _____________ aggregate demand. 9. When the government makes a purchase of a ba ...
... 6. A tax on an imported good is called a _____________. 7. Why do prices act as a signal to sellers in the market? 8. The Fed BUYS government bonds/securities on the open market. This _______________ the money supply and _____________ aggregate demand. 9. When the government makes a purchase of a ba ...
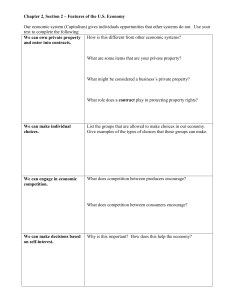
Chapter 2, Section 2 – Features of the U
... We can own private property How is this different from other economic systems? and enter into contracts. ...
... We can own private property How is this different from other economic systems? and enter into contracts. ...
Unit 3 Vocabulary Words with Answers
... 19. ______Profit__- Money that remains after all the costs of producing a product have been paid. 20. ___Market Economy____- An economy that allows business owners to compete in the market with little government interference. 21. _Consumers__- The people who use goods and services. 22. __Competition ...
... 19. ______Profit__- Money that remains after all the costs of producing a product have been paid. 20. ___Market Economy____- An economy that allows business owners to compete in the market with little government interference. 21. _Consumers__- The people who use goods and services. 22. __Competition ...
Chapter two econ
... market pricing , competition and consumer choice The central government answers the key economic questions of production and consumption It collects info and then tells each firm what and how much to produce They own the land, capital and control the labor (set wage prices and control where individu ...
... market pricing , competition and consumer choice The central government answers the key economic questions of production and consumption It collects info and then tells each firm what and how much to produce They own the land, capital and control the labor (set wage prices and control where individu ...
Ch - edl.io
... of European industries after WWI left the U.S., for a short time, the only healthy industrial power in the world. 3.The auto industry became among the most important industries in the nation & w/ the growth of suburbs helped fuel a boom in the construction industry. 4.Radio, commercial aviation, and ...
... of European industries after WWI left the U.S., for a short time, the only healthy industrial power in the world. 3.The auto industry became among the most important industries in the nation & w/ the growth of suburbs helped fuel a boom in the construction industry. 4.Radio, commercial aviation, and ...
3 Key Economic Questions
... However, each economic system will answer the 3 economic questions differently based on their beliefs of various economic goals. ...
... However, each economic system will answer the 3 economic questions differently based on their beliefs of various economic goals. ...
notes
... and resource owners from risks that exist in society. Each society must decide from which “uncertainties” individual can and should be protected, and whether individuals, employers, or the government should provide for this protection. ...
... and resource owners from risks that exist in society. Each society must decide from which “uncertainties” individual can and should be protected, and whether individuals, employers, or the government should provide for this protection. ...
3. Sweden and Canada economics - Social Studies 30-1
... • No profits simply make what you need • Workers are all paid equally. (From each according to their ability, to each according to their need – Karl Marx) ...
... • No profits simply make what you need • Workers are all paid equally. (From each according to their ability, to each according to their need – Karl Marx) ...
6. Sweden and Canada economics - socialstudies30
... • No profits simply make what you need • Workers are all paid equally. (From each according to their ability, to each according to their need – Karl Marx) ...
... • No profits simply make what you need • Workers are all paid equally. (From each according to their ability, to each according to their need – Karl Marx) ...
Economics Review - Cabarrus County Schools
... • Define specialization and explain how it makes the country interdependent. • When people, businesses, regions and or nations concentrate on goods and services that they can produce better than anyone else • It forces countries to rely on each other to obtain goods. • How do technological advances ...
... • Define specialization and explain how it makes the country interdependent. • When people, businesses, regions and or nations concentrate on goods and services that they can produce better than anyone else • It forces countries to rely on each other to obtain goods. • How do technological advances ...
Chapter 1
... Supply: Specific quantity of a product that the seller is able and willing to provide ...
... Supply: Specific quantity of a product that the seller is able and willing to provide ...