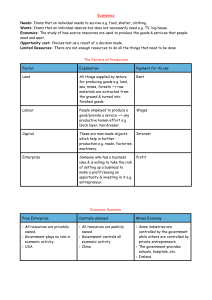
The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice
... and the Gains From Trade According to the theory of competitive advantage, specialization and free trade will benefit all trading parties, even those that may be absolutely more efficient producers. Is Colleen better off ? ...
... and the Gains From Trade According to the theory of competitive advantage, specialization and free trade will benefit all trading parties, even those that may be absolutely more efficient producers. Is Colleen better off ? ...
What Economics Is About YNP 2015
... Scarcity - The Economic Problem Faced by all Societies • Every society is endowed with scarce resources with which to produce the goods & services that provide its citizens with their standard of living. • 4 Basic Resources: Natural, Human, Capital, and Entrepreneurial • Economics is the study of h ...
... Scarcity - The Economic Problem Faced by all Societies • Every society is endowed with scarce resources with which to produce the goods & services that provide its citizens with their standard of living. • 4 Basic Resources: Natural, Human, Capital, and Entrepreneurial • Economics is the study of h ...
Production and Growth
... more current resources in the production of capital. • Firms create physical capital through investment. • Investment is often done on borrowed funds, and the role of the financial system is to move the funds from savers to borrowers. ...
... more current resources in the production of capital. • Firms create physical capital through investment. • Investment is often done on borrowed funds, and the role of the financial system is to move the funds from savers to borrowers. ...
What Is Capitalism?
... Keynesian economics challenged the notion that laissez-faire capitalist economies could operate well on their own without state intervention to promote aggregate demand and fight high unemployment and deflation of the sort seen during the 1930s. He postulated that government intervention (by cutting ...
... Keynesian economics challenged the notion that laissez-faire capitalist economies could operate well on their own without state intervention to promote aggregate demand and fight high unemployment and deflation of the sort seen during the 1930s. He postulated that government intervention (by cutting ...
Social Studies Vocabulary Resource
... Empire - an extensive group of states or countries under a single supreme authority, formerly especially an emperor or empress Entrepreneur - individual who takes the risk of producing a product for a profit Environment – the natural or human surrounding in which living things interact. Equality – e ...
... Empire - an extensive group of states or countries under a single supreme authority, formerly especially an emperor or empress Entrepreneur - individual who takes the risk of producing a product for a profit Environment – the natural or human surrounding in which living things interact. Equality – e ...
PDF
... Is the total package of investment policies and programs outlined above likely to be adopted? Probably not. For many people much of this policy medicine carries too stiff a price. (Here we find ourselves in agreement with the culture of contentment thesis recently advanced by J. K. Galbraith). Givin ...
... Is the total package of investment policies and programs outlined above likely to be adopted? Probably not. For many people much of this policy medicine carries too stiff a price. (Here we find ourselves in agreement with the culture of contentment thesis recently advanced by J. K. Galbraith). Givin ...
Yale U
... When I analyze a particular financial market, I find it useful to make a distinction between the financial side and the real side as if the two sides could be separated. The economic fundamental is the real side. The real side is different for different financial market. The real sides of the commod ...
... When I analyze a particular financial market, I find it useful to make a distinction between the financial side and the real side as if the two sides could be separated. The economic fundamental is the real side. The real side is different for different financial market. The real sides of the commod ...
chapter 4 - Spring Branch ISD
... bakes bread, and Harry makes cheese. Tom wants some bread to go with his wine and is willing to trade 1 gallon of wine for two loaves of bread. Dick wants some cheese to go with his bread and is willing to trade one loaf of bread for one-half pound of cheese. Harry doesn’t want bread, but wants some ...
... bakes bread, and Harry makes cheese. Tom wants some bread to go with his wine and is willing to trade 1 gallon of wine for two loaves of bread. Dick wants some cheese to go with his bread and is willing to trade one loaf of bread for one-half pound of cheese. Harry doesn’t want bread, but wants some ...
CPR - Federchimica
... Cefic Economic Outlook June 2014 Dr Moncef HADHRI (Chief Economist) Economic Affairs Manager [email protected] June 20, 2014 ...
... Cefic Economic Outlook June 2014 Dr Moncef HADHRI (Chief Economist) Economic Affairs Manager [email protected] June 20, 2014 ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 1. Define Macroeconomics. 2. Explain Keynes psychological law of consumption. 3. What is inflationary gap? 4. Define Marginal efficiency of capital. 5. Derive IS curve. 6. Differentiate GNP at market prices and GNP at factor cost. 7. Given the saving function S = -10 + 0.2y and autonomous investment ...
... 1. Define Macroeconomics. 2. Explain Keynes psychological law of consumption. 3. What is inflationary gap? 4. Define Marginal efficiency of capital. 5. Derive IS curve. 6. Differentiate GNP at market prices and GNP at factor cost. 7. Given the saving function S = -10 + 0.2y and autonomous investment ...
518297-LLP-2011-IT-ERASMUS-FEXI The impact of the translations
... ideas on the Romanian economy. Therefore, we try to make a comparison between the two editions of The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, written by John Maynard Keynes, translated in Romanian. More, we debate the present trend of monetary and fiscal policy as there is a big connection ...
... ideas on the Romanian economy. Therefore, we try to make a comparison between the two editions of The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, written by John Maynard Keynes, translated in Romanian. More, we debate the present trend of monetary and fiscal policy as there is a big connection ...
Belgrade Law Faculty Master-Course Human
... Fight for customers by offering them a Better deal in terms of price, quality, Range, reliability or associated services. Adam Smith: Wealth of nation just repartition of wealth with market freedom guaranteed by th “invisible hand” Competition: prices low, reduces costs and enhances quality ...
... Fight for customers by offering them a Better deal in terms of price, quality, Range, reliability or associated services. Adam Smith: Wealth of nation just repartition of wealth with market freedom guaranteed by th “invisible hand” Competition: prices low, reduces costs and enhances quality ...
Midterm 1
... b) raise the price of electricity, particularly when usage levels approach the maximum levels that can be produced. c) have government officials decide who really needs electricity and deny electricity to other people d) allow each household a fixed amount of electricity per day, and turn off the fl ...
... b) raise the price of electricity, particularly when usage levels approach the maximum levels that can be produced. c) have government officials decide who really needs electricity and deny electricity to other people d) allow each household a fixed amount of electricity per day, and turn off the fl ...
Title Goes Here - Binus Repository
... Sources: UNDP and WB, African Development Indicators, 1992 Note: Amounts are expressed in US dollar at 1980 prices. NA=not available ...
... Sources: UNDP and WB, African Development Indicators, 1992 Note: Amounts are expressed in US dollar at 1980 prices. NA=not available ...
The AD/AS model - Gore High School
... 4. Why might net social welfare be a better measure of economic growth than real GDP Net social welfare includes the value of goods and services being produced as well as non economic factors such as, levels of pollution, education and life expectancy. Real GDP only shows whether more is being produ ...
... 4. Why might net social welfare be a better measure of economic growth than real GDP Net social welfare includes the value of goods and services being produced as well as non economic factors such as, levels of pollution, education and life expectancy. Real GDP only shows whether more is being produ ...
“Things Fall Apart” by Gavekal Research
... Each of these post-crisis settlements was marked by transformations in economic thinking as well as politics. The sweeping away of agrarian semi -feudal economies described by the Communist Manifesto produced both free-trade liberalism and the “marginalist revolution” of William Jevons and Léon Walr ...
... Each of these post-crisis settlements was marked by transformations in economic thinking as well as politics. The sweeping away of agrarian semi -feudal economies described by the Communist Manifesto produced both free-trade liberalism and the “marginalist revolution” of William Jevons and Léon Walr ...
The Flexible Price Benchmark
... NEW KEYNESIAN MACROECONOMICS Why monopolistic competition? To model price pre setting one must allow for endogenous goods supply. This requires not assuming endowments of goods. The determinants of the cost of supplying goods are important because the supply costs are a prime determinant of the opti ...
... NEW KEYNESIAN MACROECONOMICS Why monopolistic competition? To model price pre setting one must allow for endogenous goods supply. This requires not assuming endowments of goods. The determinants of the cost of supplying goods are important because the supply costs are a prime determinant of the opti ...
The Non-Existent Hand Joseph Stiglitz Keynes: The Return of the
... demand: what happens when people want to buy less than the economy is able to produce. Even 75 years ago, he saw the issue from a global perspective. He was concerned, for instance, about the impact of the surplus countries – those that produced more than they consumed – on global demand. Today, we ...
... demand: what happens when people want to buy less than the economy is able to produce. Even 75 years ago, he saw the issue from a global perspective. He was concerned, for instance, about the impact of the surplus countries – those that produced more than they consumed – on global demand. Today, we ...
Press summary (PDF, 65 KB)
... the minimum wage in Germany will probably apply to a far larger share of employees than was the case in most of the other countries when a minimum wage was introduced. Many suppositions and assumptions must therefore be made to quantify the implications of a minimum wage for the labour market and ec ...
... the minimum wage in Germany will probably apply to a far larger share of employees than was the case in most of the other countries when a minimum wage was introduced. Many suppositions and assumptions must therefore be made to quantify the implications of a minimum wage for the labour market and ec ...
AGGREGATE DEMAND – the total amount demanded of
... As the U.S continues to experience the recession, further demand for goods fall. Many factory workers are now unemployed. The article states that we now have the highest unemployment rate of 16 and half years. The government’s stimulus package to jump start the economy is associated with the theory ...
... As the U.S continues to experience the recession, further demand for goods fall. Many factory workers are now unemployed. The article states that we now have the highest unemployment rate of 16 and half years. The government’s stimulus package to jump start the economy is associated with the theory ...