Genetics Minor - Montana State University
... In order to earn a Genetics Minor, a student must take 13 units of required courses and 15 units of elective courses (see below) and must earn a grade of at least C- in every course. Students interested in this minor should consult the genetics advisor within each department to decide whether the Ge ...
... In order to earn a Genetics Minor, a student must take 13 units of required courses and 15 units of elective courses (see below) and must earn a grade of at least C- in every course. Students interested in this minor should consult the genetics advisor within each department to decide whether the Ge ...
E. coli - Marcotte Lab
... - ethanol, other bio-fuels 2 make new model systems 3 intervene in biological systems to figure out how they work, for example rearrange the genes in a bacterial operon 4 understand the limitations of evolution and perhaps augment biology with additional amino acids or protein coding 5 understand th ...
... - ethanol, other bio-fuels 2 make new model systems 3 intervene in biological systems to figure out how they work, for example rearrange the genes in a bacterial operon 4 understand the limitations of evolution and perhaps augment biology with additional amino acids or protein coding 5 understand th ...
2017 General externally set tasks Unit 3 content
... Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Unit description Organisms exhibit a diverse and interesting range of reproductive structures and behaviours to ensure reproductive success. This unit explores the genetic basis for variation and inheritance of characteristics by the next generation. Environ ...
... Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Unit description Organisms exhibit a diverse and interesting range of reproductive structures and behaviours to ensure reproductive success. This unit explores the genetic basis for variation and inheritance of characteristics by the next generation. Environ ...
Word Format
... Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Unit description Organisms exhibit a diverse and interesting range of reproductive structures and behaviours to ensure reproductive success. This unit explores the genetic basis for variation and inheritance of characteristics by the next generation. Environmen ...
... Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Unit description Organisms exhibit a diverse and interesting range of reproductive structures and behaviours to ensure reproductive success. This unit explores the genetic basis for variation and inheritance of characteristics by the next generation. Environmen ...
Bacteria (multiple kingdoms)
... Natural selection is an editing mechanism – It results from exposure of heritable variations to environmental factors that favor some individuals over others – Over time this results in evolution of new species adapted to particular environments – Evolution is biology’s core theme and explains uni ...
... Natural selection is an editing mechanism – It results from exposure of heritable variations to environmental factors that favor some individuals over others – Over time this results in evolution of new species adapted to particular environments – Evolution is biology’s core theme and explains uni ...
Evolutionary Principles - Bremen High School District 228
... members of a species will survive and reproduce under changed environmental conditions. Understand that reproductive or geographic isolation can lead to speciation. Understand that the millions of different species of plants, animals and microorganisms that live on Earth today are related to each ot ...
... members of a species will survive and reproduce under changed environmental conditions. Understand that reproductive or geographic isolation can lead to speciation. Understand that the millions of different species of plants, animals and microorganisms that live on Earth today are related to each ot ...
Science Grade 7
... _________________________ passageway throughout cell _________________________ stores water and waste _________________________ process by which water enters or leaves the cell _________________________ where photosynthesis takes place _________________________ jelly-like material inside the cell __ ...
... _________________________ passageway throughout cell _________________________ stores water and waste _________________________ process by which water enters or leaves the cell _________________________ where photosynthesis takes place _________________________ jelly-like material inside the cell __ ...
Biology Syllabus
... 2.1.2 Analyze the survival and reproductive success of organisms in terms of behavioral, structural, and reproductive adaptations. 2.1.3 Explain various ways organisms interact with each other (including predation, competition, parasitism, mutualism) and with their environments resulting in stabilit ...
... 2.1.2 Analyze the survival and reproductive success of organisms in terms of behavioral, structural, and reproductive adaptations. 2.1.3 Explain various ways organisms interact with each other (including predation, competition, parasitism, mutualism) and with their environments resulting in stabilit ...
Mini-Guide for incoming mobility students
... The central online course database is called „Core Teaching System“(CTS, in German: Kernsystem Lehre = KSL): www.ksl-vv.unibe.ch. This system can be accessed without a login to search for information on courses. After you have been registered at the University of Bern and once you have received your ...
... The central online course database is called „Core Teaching System“(CTS, in German: Kernsystem Lehre = KSL): www.ksl-vv.unibe.ch. This system can be accessed without a login to search for information on courses. After you have been registered at the University of Bern and once you have received your ...
“true” coelom
... blastula in an early _____________ embryo, the resulting organism will be missing body parts and will not survive. ...
... blastula in an early _____________ embryo, the resulting organism will be missing body parts and will not survive. ...
DNA and Proteins
... have been accumulating over recent years. Developments in molecular biology and gene mapping have made it necessary to develop a system where research can be shared easily. Click here to find out how scientists can use bioinformatics in their genetic research ...
... have been accumulating over recent years. Developments in molecular biology and gene mapping have made it necessary to develop a system where research can be shared easily. Click here to find out how scientists can use bioinformatics in their genetic research ...
Study of the evolution of animal parasite bacteria and plant symbionts
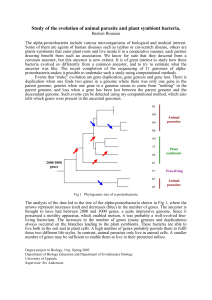
... Study of the evolution of animal parasite and plant symbiont bacteria. Bastien Boussau The alpha-proteobacteria include various microorganisms of biological and medical interest. Some of them are agents of human diseases such as typhus or cat-scratch disease, others are plants symbionts that enter p ...
... Study of the evolution of animal parasite and plant symbiont bacteria. Bastien Boussau The alpha-proteobacteria include various microorganisms of biological and medical interest. Some of them are agents of human diseases such as typhus or cat-scratch disease, others are plants symbionts that enter p ...
chapter01
... They are the units of inheritance. They control the structure and function of the cell. ...
... They are the units of inheritance. They control the structure and function of the cell. ...
molecular biology and genetics
... 1. Chromosomes show specific forms and sizes 2. Number of chromosomes is characteristic for each species 3. In most plants and animals chromosomes were present ...
... 1. Chromosomes show specific forms and sizes 2. Number of chromosomes is characteristic for each species 3. In most plants and animals chromosomes were present ...
Strand 3 - Biological Sciences
... C. 600 D. 800 23. Flowers known as four o’clocks may be red, white, or pink. The genes shows incomplete dominance. If a red gene and a white gene are inherited the flower is pink. If two red genes are inherited it will be red. If two white genes are inherited it will be white. What happens if you cr ...
... C. 600 D. 800 23. Flowers known as four o’clocks may be red, white, or pink. The genes shows incomplete dominance. If a red gene and a white gene are inherited the flower is pink. If two red genes are inherited it will be red. If two white genes are inherited it will be white. What happens if you cr ...
Background Metabolism shapes the cellular energy budget in
... Both projects are part of a multidisciplinary partnership with Dr Fuzhong Zhang’s synthetic biology lab at the U Washington in St Louis. We seek someone open-minded, creative and willing to explore and learn new ideas as part of a multidisciplinary team. For inquiries, please email d.oyarzun@imperia ...
... Both projects are part of a multidisciplinary partnership with Dr Fuzhong Zhang’s synthetic biology lab at the U Washington in St Louis. We seek someone open-minded, creative and willing to explore and learn new ideas as part of a multidisciplinary team. For inquiries, please email d.oyarzun@imperia ...
Strand 3 - Biological Sciences
... C. guanine D. thymine 19. If an individual is heterozygous for two genes the trait that will usually be demonstrated is A. the dominant trait B. the recessive trait C. the combination trait D. neither trait 20. A nucleotide is A. the base of a DNA molecule B. the building blocks for DNA and RNA C. a ...
... C. guanine D. thymine 19. If an individual is heterozygous for two genes the trait that will usually be demonstrated is A. the dominant trait B. the recessive trait C. the combination trait D. neither trait 20. A nucleotide is A. the base of a DNA molecule B. the building blocks for DNA and RNA C. a ...
Final Exam Review - Warren Hills Regional School District
... Aristotle~ first to classify organisms Fleming~ discovered penicillin Linnaeus~ modern classification system Hooke~ named the cell Lamarck~ acquired traits; evolution Mendel~ father of genetics Van Leeuwenhoek~ father of microscopy ...
... Aristotle~ first to classify organisms Fleming~ discovered penicillin Linnaeus~ modern classification system Hooke~ named the cell Lamarck~ acquired traits; evolution Mendel~ father of genetics Van Leeuwenhoek~ father of microscopy ...
Final Exam Review
... Aristotle~ first to classify organisms Fleming~ discovered penicillin Linnaeus~ modern classification system Hooke~ named the cell Lamarck~ acquired traits; evolution Mendel~ father of genetics Van Leeuwenhoek~ father of microscopy ...
... Aristotle~ first to classify organisms Fleming~ discovered penicillin Linnaeus~ modern classification system Hooke~ named the cell Lamarck~ acquired traits; evolution Mendel~ father of genetics Van Leeuwenhoek~ father of microscopy ...
What is an Organism??
... • Ecology studies this • Ecosystems are communities of living things and their environments • Humans really interact with the environment ...
... • Ecology studies this • Ecosystems are communities of living things and their environments • Humans really interact with the environment ...
ECU Burroughs Wellcome Lecturer to Discuss Genome Editing for Disease Treatment
... received several distinguished awards, including the prestigious National Institutes of Heath Director’s Pioneer Award. Currently, he serves as an elected member of the American Association of University Pathologists. Joung received his MD from Harvard Medical School and his PhD degree in genetics f ...
... received several distinguished awards, including the prestigious National Institutes of Heath Director’s Pioneer Award. Currently, he serves as an elected member of the American Association of University Pathologists. Joung received his MD from Harvard Medical School and his PhD degree in genetics f ...
b2revisioncards
... Peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria and warfarin resistant rats are all examples of natural selection not evolution Charles Darwin correctly said that most species have more young than ever survive, that there is variation, competition, and the fittest survive to pass on their genes La ...
... Peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria and warfarin resistant rats are all examples of natural selection not evolution Charles Darwin correctly said that most species have more young than ever survive, that there is variation, competition, and the fittest survive to pass on their genes La ...
mAb SAC1 INVESTIGATOR Name Zaven Kaprielian Address Albert
... Amino acid sequence analysis Functional effects Immunohistochemistry ...
... Amino acid sequence analysis Functional effects Immunohistochemistry ...
History of biology

The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to ayurveda, ancient Egyptian medicine and the works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world. This ancient work was further developed in the Middle Ages by Muslim physicians and scholars such as Avicenna. During the European Renaissance and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius and Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. The growing importance of natural theology, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (although it entrenched the argument from design).Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany and zoology became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics by Thomas Hunt Morgan and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the ""neo-Darwinian synthesis"". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson and Crick proposed the structure of DNA. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular and molecular biology. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics and proteomics were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.