2.1 Living organisms 2.1.1 Useful products Scientists are looking for
... cancer. Other scientists culture cells that can be used for transplants and in techniques such as in-vitro fertilisation. Cutting edge, but controversial research on stem cells from human embryos may one day lead to the effective treatment of forms of diseases and injuries that are currently incurab ...
... cancer. Other scientists culture cells that can be used for transplants and in techniques such as in-vitro fertilisation. Cutting edge, but controversial research on stem cells from human embryos may one day lead to the effective treatment of forms of diseases and injuries that are currently incurab ...
Success Academy 1-6
... variation and environmental factors contribute to evolution by natural selection and diversity of organisms. Students will identify and/or explain ways in which fossil evidence is consistent with the scientific theory of evolution. Students will identify and/or explain how a species’ inability t ...
... variation and environmental factors contribute to evolution by natural selection and diversity of organisms. Students will identify and/or explain ways in which fossil evidence is consistent with the scientific theory of evolution. Students will identify and/or explain how a species’ inability t ...
The Biology Staff Handbook
... performing specific physiological functions. Organs are organised into organ systems, which work together to form organisms. Multicellular organisms Large multicellular organisms develop systems for exchanging materials. During the development of a multicellular organism, cells differentiate so ...
... performing specific physiological functions. Organs are organised into organ systems, which work together to form organisms. Multicellular organisms Large multicellular organisms develop systems for exchanging materials. During the development of a multicellular organism, cells differentiate so ...
Unit 2 summary notes
... performing specific physiological functions. Organs are organised into organ systems, which work together to form organisms. Multicellular organisms Large multicellular organisms develop systems for exchanging materials. During the development of a multicellular organism, cells differentiate so ...
... performing specific physiological functions. Organs are organised into organ systems, which work together to form organisms. Multicellular organisms Large multicellular organisms develop systems for exchanging materials. During the development of a multicellular organism, cells differentiate so ...
120:452 Lab in Cellular and Molecular Biology: Molecular
... Lecture and laboratory course on the principles and techniques of molecular biology. The laboratory portion of the course will immerse students in a semester-long laboratory project, in which the students will perform molecular methods (isolation of RNA and plasmid DNA, PCR, restriction digests, clo ...
... Lecture and laboratory course on the principles and techniques of molecular biology. The laboratory portion of the course will immerse students in a semester-long laboratory project, in which the students will perform molecular methods (isolation of RNA and plasmid DNA, PCR, restriction digests, clo ...
OAT Exam Overview
... quantitative reasoning, total science (comprising biology, general and organic chemistry, and physics), and an academic average (comprising all sections). On the OAT, the standard score ranges from 200 to 400, with 400 being the highest. The score report will tell you—and your potential Optometry sc ...
... quantitative reasoning, total science (comprising biology, general and organic chemistry, and physics), and an academic average (comprising all sections). On the OAT, the standard score ranges from 200 to 400, with 400 being the highest. The score report will tell you—and your potential Optometry sc ...
Chapter 18 - San Diego Mesa College
... "Vendian fauna" or "Ediacaran fauna“ happened during that time - scientist are not sure whether these fossilized creatures (see images below) were algae, lichens, giant protozoans, or even a separate (now extinct) kingdom of life (!) ...
... "Vendian fauna" or "Ediacaran fauna“ happened during that time - scientist are not sure whether these fossilized creatures (see images below) were algae, lichens, giant protozoans, or even a separate (now extinct) kingdom of life (!) ...
File
... Some of the strongest evidence of common ancestry is contained in our genetic code. Look at the table above which lists sequences of amino acids in the protein hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is used in all organisms to deliver oxygen to the tissues, but there are slight differences among the species. 9. Whi ...
... Some of the strongest evidence of common ancestry is contained in our genetic code. Look at the table above which lists sequences of amino acids in the protein hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is used in all organisms to deliver oxygen to the tissues, but there are slight differences among the species. 9. Whi ...
Unit One: Ecology - Ms. Schmidly`s Classes
... ❏ Create a model describing how matter cycles through the biosphere. (1.3A) ❏ Distinguish between an organism’s niche and habitat. (2.1A) ❏ Classify community members as a producer or type of consumer. (2.1B) ❏ Identify and contrast biological relationships (predatorprey and symbiotic). (2.1C) ...
... ❏ Create a model describing how matter cycles through the biosphere. (1.3A) ❏ Distinguish between an organism’s niche and habitat. (2.1A) ❏ Classify community members as a producer or type of consumer. (2.1B) ❏ Identify and contrast biological relationships (predatorprey and symbiotic). (2.1C) ...
Multicellular_System..
... But first, let’s look at how life is •Those organized organs make up the organ systems of the from the bottom body. up. ...
... But first, let’s look at how life is •Those organized organs make up the organ systems of the from the bottom body. up. ...
Comprehensive Review Packet - 2013-2014
... Electron transfer (oxidative phosphorylation)—Energy from the movement of electrons from one molecule to another, via electron carriers, is used to synthesize ATP. Most cellular ATP is synthesized by electron transfer in the mitochondria. Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an “uncoupler,” which means it inter ...
... Electron transfer (oxidative phosphorylation)—Energy from the movement of electrons from one molecule to another, via electron carriers, is used to synthesize ATP. Most cellular ATP is synthesized by electron transfer in the mitochondria. Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an “uncoupler,” which means it inter ...
AP Biology - Macomb Intermediate School District
... introduced into our waterways. Students do research on the species introduced into our lakes and present findings. In previous years, we have tested the water in a nearby river and reported our findings in conjunction with other schools to a website at our intermediate school district. This was also ...
... introduced into our waterways. Students do research on the species introduced into our lakes and present findings. In previous years, we have tested the water in a nearby river and reported our findings in conjunction with other schools to a website at our intermediate school district. This was also ...
Course Name: Anatomy and Physiology Level: H Points: 5
... Chapter 7: Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food An Overview of Photosynthesis The Light Reactions: Converting Solar Energy to Chemical Energy The Calvin Cycle: Converting CO2 to Sugars Photosynthesis Reviewed and Extended Photosynthesis, Solar Radiation, and Earth’s Atmosphere ...
... Chapter 7: Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food An Overview of Photosynthesis The Light Reactions: Converting Solar Energy to Chemical Energy The Calvin Cycle: Converting CO2 to Sugars Photosynthesis Reviewed and Extended Photosynthesis, Solar Radiation, and Earth’s Atmosphere ...
Cultural Niche Construction
... of atmospheric gases and modifying nutrient cycles; fungi decomposing organic matter; and bacteria fixing nutrients. Organisms also construct and destroy resources and habitat utilized by other species in their environments (‘ecosystem engineering’). These interactions connect diverse organisms and ...
... of atmospheric gases and modifying nutrient cycles; fungi decomposing organic matter; and bacteria fixing nutrients. Organisms also construct and destroy resources and habitat utilized by other species in their environments (‘ecosystem engineering’). These interactions connect diverse organisms and ...
Intermediate Filament Cytoskeleton, Vol 78. Methods in Cell Biology Brochure
... comprehensive resource of methodology essentials, describing a variety of essential tools and assays for studying intermediate filaments. The book provides user-friendly advice and protocols covering all aspects of intermediate filaments including protein isolation and structure, protein and gene re ...
... comprehensive resource of methodology essentials, describing a variety of essential tools and assays for studying intermediate filaments. The book provides user-friendly advice and protocols covering all aspects of intermediate filaments including protein isolation and structure, protein and gene re ...
Gateway Biology Review
... females. Why? Males have one X chromosome, so if one is defective, they do not have a backup copy as do ...
... females. Why? Males have one X chromosome, so if one is defective, they do not have a backup copy as do ...
English
... Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems to carry out life processes. ...
... Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems to carry out life processes. ...
AnatomyPhysiology-English
... Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems to carry out life processes. ...
... Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems to carry out life processes. ...
Gateway - OnMyCalendar
... females. Why? Males have one X chromosome, so if one is defective, they do not have a backup copy as do ...
... females. Why? Males have one X chromosome, so if one is defective, they do not have a backup copy as do ...
Scientific Method Web Resources
... Mel and Gerdy are two life science teachers with a true passion for curriculum design. We LOVE creating time-saving, fun and engaging activities for our classrooms & we’re excited to be sharing them with you. We look forward to hearing your feedback on this product. ...
... Mel and Gerdy are two life science teachers with a true passion for curriculum design. We LOVE creating time-saving, fun and engaging activities for our classrooms & we’re excited to be sharing them with you. We look forward to hearing your feedback on this product. ...
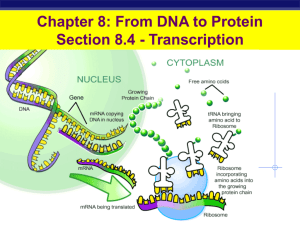
Transcription/translation
... Operator – area of DNA that turns gene “on” or “off”. It’s the switch ...
... Operator – area of DNA that turns gene “on” or “off”. It’s the switch ...
The Organism as the Subject and Object of Evolution
... traits that have a one-to-one correspondence to genes. Mendel succeeded where others had failed partly because he worked with horticultural varieties in which major differences in phenotype resulted from alternative alleles for single genes. Mendel's peas had a single gene difference between tall an ...
... traits that have a one-to-one correspondence to genes. Mendel succeeded where others had failed partly because he worked with horticultural varieties in which major differences in phenotype resulted from alternative alleles for single genes. Mendel's peas had a single gene difference between tall an ...
CHAP NUM="1" ID="CH
... fruit fly cell. Systems biologists develop such models from huge databases of information about molecules and their interactions in the cell. A major goal of this systems approach is to use the models to predict how one change, such as an increase in the activity of a particular protein, can ripple ...
... fruit fly cell. Systems biologists develop such models from huge databases of information about molecules and their interactions in the cell. A major goal of this systems approach is to use the models to predict how one change, such as an increase in the activity of a particular protein, can ripple ...
History of biology

The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to ayurveda, ancient Egyptian medicine and the works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world. This ancient work was further developed in the Middle Ages by Muslim physicians and scholars such as Avicenna. During the European Renaissance and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius and Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. The growing importance of natural theology, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (although it entrenched the argument from design).Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany and zoology became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics by Thomas Hunt Morgan and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the ""neo-Darwinian synthesis"". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson and Crick proposed the structure of DNA. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular and molecular biology. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics and proteomics were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.