3.1 Classification
... Each organism has a_______________________________ name, describing its ___________________________ (the group of closely related ________________________ it belongs to) and _______________________________ (unique to each _________________________ in the group.) ...
... Each organism has a_______________________________ name, describing its ___________________________ (the group of closely related ________________________ it belongs to) and _______________________________ (unique to each _________________________ in the group.) ...
Chapter 3
... • Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. • An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all life processes in order for that cell to survive. • In contrast, multicellular organisms have specialized cells that depend on ...
... • Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. • An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all life processes in order for that cell to survive. • In contrast, multicellular organisms have specialized cells that depend on ...
Blood Cell Formation
... Attracted by bacterial products and are first line of defense in inflammatory response ...
... Attracted by bacterial products and are first line of defense in inflammatory response ...
Chapter 35 Directed Reading
... Every cell in the human body is both an independent unit and and interdependent part of a larger community- the entire ____________________. The organization of the human body enables our cells to work together. The levels of organization include: cells, tissues, organs, and systems. A __________ is ...
... Every cell in the human body is both an independent unit and and interdependent part of a larger community- the entire ____________________. The organization of the human body enables our cells to work together. The levels of organization include: cells, tissues, organs, and systems. A __________ is ...
Exercise 1.1 Leaves - Beck-Shop
... ions containing raw materials or energy for growth and tissue repair, absorbing and assimilating them ...
... ions containing raw materials or energy for growth and tissue repair, absorbing and assimilating them ...
Science 10 - SharpSchool
... this model is used to understand the types of transport in cells: 1. All matter is made of ____________________ however they can be of _________________________________________________ 2. The particles of matter are _______________________________ _________________________. They move the least in ...
... this model is used to understand the types of transport in cells: 1. All matter is made of ____________________ however they can be of _________________________________________________ 2. The particles of matter are _______________________________ _________________________. They move the least in ...
Cells Cells are the basic units of all living things Cells are composed
... Cells are the basic units of all living things Cells are composed of protoplasm Cell reproduction and metabolism takes place in the center nucleus Cytoplasm fluid surrounds the cell for growth, reproduction, repair Anabolism process of building larger molecules from smaller ones Catabolism breaks ...
... Cells are the basic units of all living things Cells are composed of protoplasm Cell reproduction and metabolism takes place in the center nucleus Cytoplasm fluid surrounds the cell for growth, reproduction, repair Anabolism process of building larger molecules from smaller ones Catabolism breaks ...
Molecular Models Concept Map
... Word Bank: Amino acids, animals, carbohydrates, DNA, disaccharide, fructose, glucose, glycogen, isoleucine, leucine, lipids, monosaccharide, nucleic acids, phospholipids, plants, polypeptides, polysaccharides, proteins, RNA, saturated, serine, starch, steroids, ...
... Word Bank: Amino acids, animals, carbohydrates, DNA, disaccharide, fructose, glucose, glycogen, isoleucine, leucine, lipids, monosaccharide, nucleic acids, phospholipids, plants, polypeptides, polysaccharides, proteins, RNA, saturated, serine, starch, steroids, ...
Pharmaceuticals
... The nervous system is divided into two main groups o The Central nervous system (CNS) comprises the brain and spinal cord and acts as the control centre for the nervous system. Information from the senses is interpreted here and command actions are issued to other parts of the body o The Peripheral ...
... The nervous system is divided into two main groups o The Central nervous system (CNS) comprises the brain and spinal cord and acts as the control centre for the nervous system. Information from the senses is interpreted here and command actions are issued to other parts of the body o The Peripheral ...
The Animal Kingdom and Sponges Laboratory
... and epidermal cells with each cell having a particular function. The amoebocytes may digest food and distribute the food to other cells, as they are capable of locomotion throughout the sponge’s body. The epidermal cells form the outer protective surface of the sponge and surround the porocytes, whi ...
... and epidermal cells with each cell having a particular function. The amoebocytes may digest food and distribute the food to other cells, as they are capable of locomotion throughout the sponge’s body. The epidermal cells form the outer protective surface of the sponge and surround the porocytes, whi ...
Grade 11 College Biology – Unit 3
... Means maintaining a healthy balance of all chemical reactions in an organism When environmental conditions change, body senses change AND responds to re-establish balance Normal Range and Diagnosis Diagnosis terms for abnormal levels (e.g., fast heart rate is tachycardia, slow heart rate is ...
... Means maintaining a healthy balance of all chemical reactions in an organism When environmental conditions change, body senses change AND responds to re-establish balance Normal Range and Diagnosis Diagnosis terms for abnormal levels (e.g., fast heart rate is tachycardia, slow heart rate is ...
Epigenetics - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Epigenetics Originally defined as “ the branch of biology which studies the causal interactions between genes and their products, which brings the phenotype into being” Waddington, 1942 “The study of any potentially stable, and ideally, heritable change in gene expression or cellular phenotype that ...
... Epigenetics Originally defined as “ the branch of biology which studies the causal interactions between genes and their products, which brings the phenotype into being” Waddington, 1942 “The study of any potentially stable, and ideally, heritable change in gene expression or cellular phenotype that ...
Human Body Systems - Liberty Union High School District
... The interneuron stimulated the _____________________, to move the foot Nerve Impulse: A progressive _________________________________________ and ___________________ activity along a _________________________ that ______________________ or __________ the action of a ______________________, _____ ...
... The interneuron stimulated the _____________________, to move the foot Nerve Impulse: A progressive _________________________________________ and ___________________ activity along a _________________________ that ______________________ or __________ the action of a ______________________, _____ ...
File
... • Then, the organism divides in half. It becomes two “daughter” cells. Each daughter cell is exactly alike. It also is exactly like the parent cell was—only each daughter cell is about one-half the size of the parent cell. Each new daughter cell carries on its own life functions. When each daughter ...
... • Then, the organism divides in half. It becomes two “daughter” cells. Each daughter cell is exactly alike. It also is exactly like the parent cell was—only each daughter cell is about one-half the size of the parent cell. Each new daughter cell carries on its own life functions. When each daughter ...
7 A - Reigate School
... whether it is concentrated or dilute. In factories and in the laboratory at school we need to carry out risk assessments. This allows us to consider the level of risk and take action to reduce the chance of harm. Common acids include vinegar and lemon juice. Fizzy drinks, pickles and spicy sauces al ...
... whether it is concentrated or dilute. In factories and in the laboratory at school we need to carry out risk assessments. This allows us to consider the level of risk and take action to reduce the chance of harm. Common acids include vinegar and lemon juice. Fizzy drinks, pickles and spicy sauces al ...
Chapter 3 - Cobb Learning
... • Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. • An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all life processes in order for that cell to survive. • In contrast, multicellular organisms have specialized cells that depend on ...
... • Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. • An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all life processes in order for that cell to survive. • In contrast, multicellular organisms have specialized cells that depend on ...
chapter3_Cells - Moore Middle School
... • Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. • An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all life processes in order for that cell to survive. • In contrast, multicellular organisms have specialized cells that depend on ...
... • Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. • An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all life processes in order for that cell to survive. • In contrast, multicellular organisms have specialized cells that depend on ...
Chapter 3
... • Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. • An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all life processes in order for that cell to survive. • In contrast, multicellular organisms have specialized cells that depend on ...
... • Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. • An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all life processes in order for that cell to survive. • In contrast, multicellular organisms have specialized cells that depend on ...
Revision Sheet Quarter 1 2014-2015 Department:
... A.the shoulder; both are ball-and-socket joints B.the shoulder; both are hinge joints C.the knee; both are ball-and-socket joints D.the knee; both are hinge joints ...
... A.the shoulder; both are ball-and-socket joints B.the shoulder; both are hinge joints C.the knee; both are ball-and-socket joints D.the knee; both are hinge joints ...
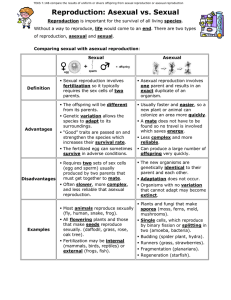
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
... The new organisms are genetically identical to their parent and each other. Adaptation does not occur. Organisms with no variation that cannot adapt may become ...
... The new organisms are genetically identical to their parent and each other. Adaptation does not occur. Organisms with no variation that cannot adapt may become ...
Unit 3- Body Basics - Heartland Community College
... both the forward and reverse reactions. 4) Each type of enzyme recognizes and binds to only certain substrates. ...
... both the forward and reverse reactions. 4) Each type of enzyme recognizes and binds to only certain substrates. ...
animalintro - Otterville R
... • Sponges are the ONLY animals that have just the cellular level • All other animals show these levels – cell, tissue, organ, and system • Cells may specialize (take own different shapes and functions) • Cells are held together by cell ...
... • Sponges are the ONLY animals that have just the cellular level • All other animals show these levels – cell, tissue, organ, and system • Cells may specialize (take own different shapes and functions) • Cells are held together by cell ...
asdfs - Home - South Johnston High School
... Plants- cell wall containing cellulose; animals-no cell wall Plants-a large central vacuole; animals- many, smaller vacuoles Plants- chloroplasts (autotrophs) and animal-don’t (heterotrophs) Animals-centrioles and plants- don’t Animals-cholesterol in their cell membranes ...
... Plants- cell wall containing cellulose; animals-no cell wall Plants-a large central vacuole; animals- many, smaller vacuoles Plants- chloroplasts (autotrophs) and animal-don’t (heterotrophs) Animals-centrioles and plants- don’t Animals-cholesterol in their cell membranes ...
No Slide Title
... 2. Sectioning (slicing) an organ or tissue reduces a 3-dimensional structure to a 2dimensional slice (see the next 3 slides) ...
... 2. Sectioning (slicing) an organ or tissue reduces a 3-dimensional structure to a 2dimensional slice (see the next 3 slides) ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are