Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Tissues, Organs and Nervous, Endocrine and Reproductive
... Major Organs of Female Reproductive System: Ovaries: contain follicles that become eggs Oviduct (fallopian tube): site of fertilization Uterus: site of embryo implantation Cervix and Vagina Hormones : Estrogen and Progesterone (ovary) FSH & LH (pituitary) ...
... Major Organs of Female Reproductive System: Ovaries: contain follicles that become eggs Oviduct (fallopian tube): site of fertilization Uterus: site of embryo implantation Cervix and Vagina Hormones : Estrogen and Progesterone (ovary) FSH & LH (pituitary) ...
Viruses & Bacteria
... DNA of host cell, remains harmless for a period of time (sometimes years), and then becomes harmful later. The viral genetic info. replicates along with the host cell’s DNA. Viral DNA that’s embedded in host’s DNA is called prophage. Unlike lytic, it does not lyse the host cell right away so it may ...
... DNA of host cell, remains harmless for a period of time (sometimes years), and then becomes harmful later. The viral genetic info. replicates along with the host cell’s DNA. Viral DNA that’s embedded in host’s DNA is called prophage. Unlike lytic, it does not lyse the host cell right away so it may ...
Week 1 - Speyside High School
... lead to evolution of new species Isolating barriers can be geographic, ecological or reproductive When a species becomes divided into two populations by an isolation barrier there is no interbreeding or exchange of genes between the groups The environment for both groups may differ Both muta ...
... lead to evolution of new species Isolating barriers can be geographic, ecological or reproductive When a species becomes divided into two populations by an isolation barrier there is no interbreeding or exchange of genes between the groups The environment for both groups may differ Both muta ...
Biology Common Syllabus
... repair, cellular respiration, and the need of living systems for continual input of energy. All single-celled and multicellular organisms have the same basic needs: water, air, a source of energy and materials for growth and repair, waste disposal, and conditions for growth and reproduction. In term ...
... repair, cellular respiration, and the need of living systems for continual input of energy. All single-celled and multicellular organisms have the same basic needs: water, air, a source of energy and materials for growth and repair, waste disposal, and conditions for growth and reproduction. In term ...
1) Which of the following correctly lists the levels of organization
... Cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water. As a result, _____. a. the temperature of living things tends to change relatively slowly b. a variety of nutrient molecules are readily available as dissolved solutes c. waste products produced by cell metabolism can be eas ...
... Cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water. As a result, _____. a. the temperature of living things tends to change relatively slowly b. a variety of nutrient molecules are readily available as dissolved solutes c. waste products produced by cell metabolism can be eas ...
BIO 15 SM 2016 FINAL EXAM 135 Q 160804.1rac
... Cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water. As a result, _____. a. the temperature of living things tends to change relatively slowly b. a variety of nutrient molecules are readily available as dissolved solutes c. waste products produced by cell metabolism can be eas ...
... Cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water. As a result, _____. a. the temperature of living things tends to change relatively slowly b. a variety of nutrient molecules are readily available as dissolved solutes c. waste products produced by cell metabolism can be eas ...
Press Release
... Heidelberg, 29 June 2007 - Hormones control growth, metabolism, reproduction and many other important biological processes. In humans, and all other vertebrates, the chemical signals are produced by specialised brain centres such as the hypothalamus and secreted into the blood stream that distribute ...
... Heidelberg, 29 June 2007 - Hormones control growth, metabolism, reproduction and many other important biological processes. In humans, and all other vertebrates, the chemical signals are produced by specialised brain centres such as the hypothalamus and secreted into the blood stream that distribute ...
BIOL 105 S 2014 QZM2 QA 140207.1
... A) fallopian tube. B) uterus. C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fe ...
... A) fallopian tube. B) uterus. C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fe ...
MODULE 1 FROM CELL TO ORGANISM
... The excretory system is another organ system that makes up an organism. It is made up of different organs that help the body eliminate metabolic wastes and maintain internal balance. These organs include a pair of kidneys. Figure 5 shows a model of a human kidney. What shape does it look like? The k ...
... The excretory system is another organ system that makes up an organism. It is made up of different organs that help the body eliminate metabolic wastes and maintain internal balance. These organs include a pair of kidneys. Figure 5 shows a model of a human kidney. What shape does it look like? The k ...
Biology Notes
... Peripheral proteins – are partially embedded in the inside or outside surface of the membrane ...
... Peripheral proteins – are partially embedded in the inside or outside surface of the membrane ...
Organisms have energy roles that they serve in their environments
... Protists with Flagella (for example the Euglena) These protists move pulling themselves with long whip like structure called flagella. These protists can have one or more flagella that help them move. The euglena is unique in that it has characteristics of both a plant and an animal, it contains chl ...
... Protists with Flagella (for example the Euglena) These protists move pulling themselves with long whip like structure called flagella. These protists can have one or more flagella that help them move. The euglena is unique in that it has characteristics of both a plant and an animal, it contains chl ...
Section 8.1
... Sex chromosomes – determine the sex of an organism; may also carry other information In humans sex chromosomes are X and Y Normal males have XY; normal females have XX Autosomes – all the other chromosomes (body chromosomes) In humans there are 44 autosomes (46 total) ...
... Sex chromosomes – determine the sex of an organism; may also carry other information In humans sex chromosomes are X and Y Normal males have XY; normal females have XX Autosomes – all the other chromosomes (body chromosomes) In humans there are 44 autosomes (46 total) ...
Anatomy and Physiology Summer Review HO2/EMT Answer Sheet
... 2. Cells vary in shape and size and perform many different functions. ...
... 2. Cells vary in shape and size and perform many different functions. ...
Eukaryotes
... How are animals put together? As multicellular organisms, animals are highly structured Cells are differentiated (specialized) Cells with similar functions are organized into tissues. Groups of tissues form organs, structures that carry out certain functions for a body. Organs work together ...
... How are animals put together? As multicellular organisms, animals are highly structured Cells are differentiated (specialized) Cells with similar functions are organized into tissues. Groups of tissues form organs, structures that carry out certain functions for a body. Organs work together ...
Grade 11 College Biology – Unit 3
... The skin is the largest organ in the human body. The skin is composed of three layers: (1) epidermis, (2) dermis and (3) subcutaneous layer. The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin. It consists of epithelial tissue in which the cells are tightly packed together providing a barrier between the i ...
... The skin is the largest organ in the human body. The skin is composed of three layers: (1) epidermis, (2) dermis and (3) subcutaneous layer. The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin. It consists of epithelial tissue in which the cells are tightly packed together providing a barrier between the i ...
Ch 10 Physiological Adaptations
... Mount Kenya, they have evolved into giants. One grows into a tree up to thirty feet tall. Each of its branches ends in a dense rosette of large robust leaves. As the branches grow, so each year the lower ring of leaves in the rosette turn yellow and die. But they are not shed. Instead, they remain a ...
... Mount Kenya, they have evolved into giants. One grows into a tree up to thirty feet tall. Each of its branches ends in a dense rosette of large robust leaves. As the branches grow, so each year the lower ring of leaves in the rosette turn yellow and die. But they are not shed. Instead, they remain a ...
Available - Ggu.ac.in
... Paleospecies or paleontological species: Species are now available in the form of fossils; it is also called as fossil species. Neontological species: Species are found living at present. Polytypic species: Species which are found in more than one subspecies. Sibling species: These are allopatric sp ...
... Paleospecies or paleontological species: Species are now available in the form of fossils; it is also called as fossil species. Neontological species: Species are found living at present. Polytypic species: Species which are found in more than one subspecies. Sibling species: These are allopatric sp ...
chapter 4 student notes
... 1. ____________: Group of similar cells that function together to carry out specialized activities and usually have a common embryonic origin 2. _____________: Science that deals with the study of tissues 3. _____________: Physician who specializes in laboratory studies of cells and tissues for chan ...
... 1. ____________: Group of similar cells that function together to carry out specialized activities and usually have a common embryonic origin 2. _____________: Science that deals with the study of tissues 3. _____________: Physician who specializes in laboratory studies of cells and tissues for chan ...
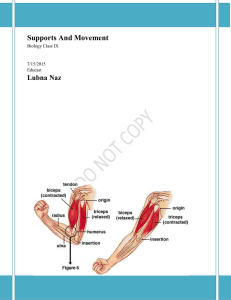
Supports And Movement
... effect they act against one another keep the whole tissue in a tense state stem becomes erect This occurs is all plants, especially important for herbaceous plants and young plant / seedling of woody plants which lack mechanical tissues If the plant received too little water, turgor pressure decreas ...
... effect they act against one another keep the whole tissue in a tense state stem becomes erect This occurs is all plants, especially important for herbaceous plants and young plant / seedling of woody plants which lack mechanical tissues If the plant received too little water, turgor pressure decreas ...
Document
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help the reactions that occur in our bodies by controlling the rate of reaction. An enzyme is basically a protein molecule made up of long chains of amino acids. These molecules are then “folded” to create a certain shape. Proteins are used in DNA replication, ...
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help the reactions that occur in our bodies by controlling the rate of reaction. An enzyme is basically a protein molecule made up of long chains of amino acids. These molecules are then “folded” to create a certain shape. Proteins are used in DNA replication, ...
Unit B2 - The Components of Life
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help the reactions that occur in our bodies by controlling the rate of reaction. An enzyme is basically a protein molecule made up of long chains of amino acids. These molecules are then “folded” to create a certain shape. Proteins are used in DNA replication, ...
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help the reactions that occur in our bodies by controlling the rate of reaction. An enzyme is basically a protein molecule made up of long chains of amino acids. These molecules are then “folded” to create a certain shape. Proteins are used in DNA replication, ...
Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader?
... cells in all organisms are identical. All living things are composed of cells. All cells are produced from other cells. All living things, except bacteria, are Return composed of cells. ...
... cells in all organisms are identical. All living things are composed of cells. All cells are produced from other cells. All living things, except bacteria, are Return composed of cells. ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are