Intro to Biology
... 2. 5 characteristics of a living thing: organized structure (made of cells), grow & develop, responds to environment, reproduces, need/use energy 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to ...
... 2. 5 characteristics of a living thing: organized structure (made of cells), grow & develop, responds to environment, reproduces, need/use energy 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to ...
Nervous System Vocab
... from the sense organs to the central nervous system. The motor division transmits impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles or glands. Stimulants increase heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. In addition, stimulants increase the release of neurotransmitters at some synapses ...
... from the sense organs to the central nervous system. The motor division transmits impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles or glands. Stimulants increase heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. In addition, stimulants increase the release of neurotransmitters at some synapses ...
7th Grade
... principle that describes the properties of an organism as the sum of the properties of its component cells. cell - The smallest structural unit of an organism that is capable of independent functioning, consisting of one or more nuclei, cytoplasm, and various organelles, all surrounded by a semiperm ...
... principle that describes the properties of an organism as the sum of the properties of its component cells. cell - The smallest structural unit of an organism that is capable of independent functioning, consisting of one or more nuclei, cytoplasm, and various organelles, all surrounded by a semiperm ...
Unit 1 PIG - Mrs Miller`s Blog
... pushes blood fluid out of the capillaries through tiny gaps • Lymph: some tissue fluid is drained into lymphatic vessels ...
... pushes blood fluid out of the capillaries through tiny gaps • Lymph: some tissue fluid is drained into lymphatic vessels ...
Print › Human Body Systems | Quizlet
... found in animal tissues, too much can lead to heart disease ...
... found in animal tissues, too much can lead to heart disease ...
Cell Specialization
... Red blood cells form from undifferentiated cells in the bone marrow throughout your life. Bone marrow is the soft, interior portion of certain bones found in the chest, upper arms, upper legs and hips. The cells located here are undifferentiated, but limited in the type of cell they can become. They ...
... Red blood cells form from undifferentiated cells in the bone marrow throughout your life. Bone marrow is the soft, interior portion of certain bones found in the chest, upper arms, upper legs and hips. The cells located here are undifferentiated, but limited in the type of cell they can become. They ...
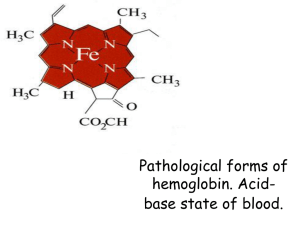
Pathological forms of hemoglobin. Acid
... iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of vertebrates,and the tissues of some invertebrates. In mammals, the protein makes up about 97% of the red blood cell's dry content, and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lu ...
... iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of vertebrates,and the tissues of some invertebrates. In mammals, the protein makes up about 97% of the red blood cell's dry content, and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lu ...
Micro Lab Unit 1 Flashcards
... 39) What muscles lift the ribs to expand the chest cavity when you breathe in? 40) What muscles depress the ribs and reduce the chest cavity in forced exhalation? 41) What is the muscle that plays a critical role in respiration by contracting to expand the chest cavity and relaxing to reduce it? 42) ...
... 39) What muscles lift the ribs to expand the chest cavity when you breathe in? 40) What muscles depress the ribs and reduce the chest cavity in forced exhalation? 41) What is the muscle that plays a critical role in respiration by contracting to expand the chest cavity and relaxing to reduce it? 42) ...
Unit 2 Homework
... You teacher will have given you a title that you will be debating and also whether you are for or against the idea. Prepare your arguments, either for or against, using information you have researched and been given in class. You should look for evidence like statistics or quotes from professionals ...
... You teacher will have given you a title that you will be debating and also whether you are for or against the idea. Prepare your arguments, either for or against, using information you have researched and been given in class. You should look for evidence like statistics or quotes from professionals ...
Unit 3 part 1 PPT
... • Help to regulate metabolism, homeostasis, growth, reproduction, and other processes. • Each hormone acts only on specific types of cells called target cells. How does a hormone recognize its target cell? • A hormone can stimulate (start or increase) or inhibit (stop or decrease) cell activity. • M ...
... • Help to regulate metabolism, homeostasis, growth, reproduction, and other processes. • Each hormone acts only on specific types of cells called target cells. How does a hormone recognize its target cell? • A hormone can stimulate (start or increase) or inhibit (stop or decrease) cell activity. • M ...
File - 8th Grade Science Ms. Neil
... 2. 5 characteristics of a living thing: organized structure (made of cells), grow & develop, responds to environment, reproduces, need/use energy 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to ...
... 2. 5 characteristics of a living thing: organized structure (made of cells), grow & develop, responds to environment, reproduces, need/use energy 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to ...
Anatomy of the Respiratory System in Children
... The lungs take in oxygen, which the body's cells need to live and carry out their normal functions. The lungs also get rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product of the cells. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped organs made up of spongy, pinkish-gray tissue. They take up most of the space in the chest, ...
... The lungs take in oxygen, which the body's cells need to live and carry out their normal functions. The lungs also get rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product of the cells. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped organs made up of spongy, pinkish-gray tissue. They take up most of the space in the chest, ...
The circulatory system
... Professions that involve the circulatory system The first profession is heart surgeon – when someone has a heart attack they might need surgery! So a heart surgeon is called in and might have to operate. This person would work at a hospital. The second profession is cardiac and vascular surgeon ...
... Professions that involve the circulatory system The first profession is heart surgeon – when someone has a heart attack they might need surgery! So a heart surgeon is called in and might have to operate. This person would work at a hospital. The second profession is cardiac and vascular surgeon ...
Marine Mammals without a Backbone
... Flatworms • Platyhelminthes – Have a central nervous system where information is stored processed – Have a SIMPLE brain- just an aggregation of nerve cells in the head – More complex tissues than that of cnidarians – Turbellarians- free living carnivores – Flukes/trematodes(largest group)- parasite ...
... Flatworms • Platyhelminthes – Have a central nervous system where information is stored processed – Have a SIMPLE brain- just an aggregation of nerve cells in the head – More complex tissues than that of cnidarians – Turbellarians- free living carnivores – Flukes/trematodes(largest group)- parasite ...
Cell Structure and Function - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
... microscope slide. Discard the rest of the onion piece. Trim the piece with a scalpel if necessary, and smooth any wrinkles. 3. Add 1 or 2 drops of Lugol’s iodine solution and a cover slip. 4. Examine the first slide with low power and then with high power. 5. Sketch a few cells as they appear under ...
... microscope slide. Discard the rest of the onion piece. Trim the piece with a scalpel if necessary, and smooth any wrinkles. 3. Add 1 or 2 drops of Lugol’s iodine solution and a cover slip. 4. Examine the first slide with low power and then with high power. 5. Sketch a few cells as they appear under ...
Warm Up Question: - Nick Williams` San Marin Science
... Multicellular • Then came the multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell. • Most life is multicellular, as are all animals (except for specialized organisms such as Myxozoa) and land plants. ...
... Multicellular • Then came the multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell. • Most life is multicellular, as are all animals (except for specialized organisms such as Myxozoa) and land plants. ...
Innate Immune Response
... protect against a wide variety of pathogenic organisms. • They are innate – meaning that they are always present and are not produced by prior contacts with a pathogen. ...
... protect against a wide variety of pathogenic organisms. • They are innate – meaning that they are always present and are not produced by prior contacts with a pathogen. ...
Growth and Development
... – Stage one: period from onset of uterine contractions until dilation of the cervix is complete – Stage two: period from the time of maximal cervical dilation until the baby exits through the vagina – Stage three: process of expulsion of the ...
... – Stage one: period from onset of uterine contractions until dilation of the cervix is complete – Stage two: period from the time of maximal cervical dilation until the baby exits through the vagina – Stage three: process of expulsion of the ...
The Human Respiratory System
... The smooth muscle in the walls of the bronchioles is very sensitive to the concentration of carbon dioxide. A rising level of CO2 causes the bronchioles to dilate. This lowers the resistance in the airways and thus increases the flow of air in and out. ...
... The smooth muscle in the walls of the bronchioles is very sensitive to the concentration of carbon dioxide. A rising level of CO2 causes the bronchioles to dilate. This lowers the resistance in the airways and thus increases the flow of air in and out. ...
Worms - DigitalWebb
... • Pharynx that may be collect or capture (if jawed) food • Food moved into esophagus, crop for storage, gizzard for grinding, digestive tract for absorption ...
... • Pharynx that may be collect or capture (if jawed) food • Food moved into esophagus, crop for storage, gizzard for grinding, digestive tract for absorption ...
Chapter 16
... – Chemokines: cytokines that are chemotactic for phagocytic and T cells; stimulate inflammatory response and an immune response ...
... – Chemokines: cytokines that are chemotactic for phagocytic and T cells; stimulate inflammatory response and an immune response ...