The Lymphatic System - Marshall Middle
... A. Lymph: Lymph is essentially plasma with white blood cells that ‘seeps’ outside of the capillaries of the circulatory system. Lymph: • is a milky body fluid that contains a type of white blood cells called lymphocytes (that fight agents of infection, including bacteria and viruses), along with pro ...
... A. Lymph: Lymph is essentially plasma with white blood cells that ‘seeps’ outside of the capillaries of the circulatory system. Lymph: • is a milky body fluid that contains a type of white blood cells called lymphocytes (that fight agents of infection, including bacteria and viruses), along with pro ...
Chapter 22
... more oxygen is released in active tissues as they heat up. This occurs in the TISSUES, not in the lungs. ...
... more oxygen is released in active tissues as they heat up. This occurs in the TISSUES, not in the lungs. ...
Systems of the Human Body
... Skeletal System: The skeletal system includes bones and joints. (A joint is an area in which two or more bones make contact.) Bones provide the human body with structure and support. They also protect important organs. The skull is like a helmet that protects the brain. Ribs keep the heart and other ...
... Skeletal System: The skeletal system includes bones and joints. (A joint is an area in which two or more bones make contact.) Bones provide the human body with structure and support. They also protect important organs. The skull is like a helmet that protects the brain. Ribs keep the heart and other ...
Organism and nervous system
... They contain cells belonging to several tissues The co-location implies some level of dense inter-neighbour communications There is also a significant amount of communication with non-local cells Like organs the functional ‘systems’ of an organism are communication patterns of cells and tissue ...
... They contain cells belonging to several tissues The co-location implies some level of dense inter-neighbour communications There is also a significant amount of communication with non-local cells Like organs the functional ‘systems’ of an organism are communication patterns of cells and tissue ...
B1Mind Maps 2
... Bacteria mutate by chance Bacteria with mutation not killed by antibiotic These cells can survive to reproduce And pass the gene for resistance to their offspring – population of resistant bacteria increases What is a sterile culture. Culture of only one type of microorganism. Give 2 reasons it is i ...
... Bacteria mutate by chance Bacteria with mutation not killed by antibiotic These cells can survive to reproduce And pass the gene for resistance to their offspring – population of resistant bacteria increases What is a sterile culture. Culture of only one type of microorganism. Give 2 reasons it is i ...
7-2 Body Systems
... two kidneys are the major organs of the excretory system. Each kidney contains about a million nephrons, tiny structures that filter wastes such as urea from the blood. The wastes are eliminated in urine. Urine is stored in the bladder, a saclike organ, until it is released through a small tube call ...
... two kidneys are the major organs of the excretory system. Each kidney contains about a million nephrons, tiny structures that filter wastes such as urea from the blood. The wastes are eliminated in urine. Urine is stored in the bladder, a saclike organ, until it is released through a small tube call ...
CHAPTER 4 Lecture
... – Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation and each area represents about ...
... – Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation and each area represents about ...
How are humans like other life? 11/16/2015
... lungs. External respiration begins at the mouth and at the nose. Air filters through the small hairs of the nose and passes into the nasal cavity, located above the roof of the mouth. In the nasal cavity, mucous membranes warm and moisten the air, which helps prevent damage to the delicate tissues t ...
... lungs. External respiration begins at the mouth and at the nose. Air filters through the small hairs of the nose and passes into the nasal cavity, located above the roof of the mouth. In the nasal cavity, mucous membranes warm and moisten the air, which helps prevent damage to the delicate tissues t ...
EMBRYOLOGY GENERAL EMBRYOLOGY SECOND WEEK
... period.The length is expressed in cms,then correlated with age of the fetus.The growth in length is a striking feature in the 3rd5th month with an a verage of about 5 cm per month,while the increase in weight is a striking feature during the last two month with an a verage increase as 500 grams per ...
... period.The length is expressed in cms,then correlated with age of the fetus.The growth in length is a striking feature in the 3rd5th month with an a verage of about 5 cm per month,while the increase in weight is a striking feature during the last two month with an a verage increase as 500 grams per ...
Animal Form and Function Notes
... As the filtrate moves down the loop of Henle, water is Reabsorbed, and the urine becomes more concentrated. However, as it moves up the loop of Henle, salts move out and the urine becomes less ...
... As the filtrate moves down the loop of Henle, water is Reabsorbed, and the urine becomes more concentrated. However, as it moves up the loop of Henle, salts move out and the urine becomes less ...
Evolution of Metabolism Puzzle Race
... Organisms evolved to be multi-celled instead of being single-celled, like an amoeba. This cooperation allowed the cells that make up these tiny multicellular animals to start specializing, and carry out different roles. The bigger the organism, the more specialized cells it needed. Some cells on the ...
... Organisms evolved to be multi-celled instead of being single-celled, like an amoeba. This cooperation allowed the cells that make up these tiny multicellular animals to start specializing, and carry out different roles. The bigger the organism, the more specialized cells it needed. Some cells on the ...
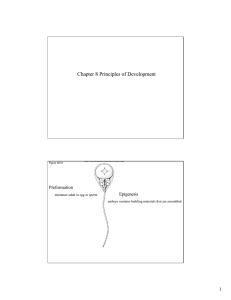
Chapter 8 Principles of Development
... cytoplasmic cleavage limited to a surface layer of yolk-free cytoplasm yolk-rich inner cytoplasm uncleaved meroblastic cleavage insects & many other arthropods ...
... cytoplasmic cleavage limited to a surface layer of yolk-free cytoplasm yolk-rich inner cytoplasm uncleaved meroblastic cleavage insects & many other arthropods ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... capillary, and the shared basement membrane between them Mechanisms that prevent alveoli from filling with fluid: 1) cells of alveolar wall are tightly joined together 2) the relatively high osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid draws water out of them 3) there is low pressure in the pulmonary ...
... capillary, and the shared basement membrane between them Mechanisms that prevent alveoli from filling with fluid: 1) cells of alveolar wall are tightly joined together 2) the relatively high osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid draws water out of them 3) there is low pressure in the pulmonary ...
Body Systems Matching Activity
... Teaching students about the different human body systems is one of my favorite things to do! But after I teach it, they always need some interactive ways to review. This activity should be done by students to review/summarize what they learned. There are MANY fun ways to teach the information! I pa ...
... Teaching students about the different human body systems is one of my favorite things to do! But after I teach it, they always need some interactive ways to review. This activity should be done by students to review/summarize what they learned. There are MANY fun ways to teach the information! I pa ...
Chapter 10: The Breath of Life-Respiration
... 4. Vital Capacity (VC): Refers to the total amount of air that can be moved into and out of the lungs ...
... 4. Vital Capacity (VC): Refers to the total amount of air that can be moved into and out of the lungs ...
Respiratory System[1] - missdannocksyear11biologyclass
... material called cartilage. They help to hold the tube open. ...
... material called cartilage. They help to hold the tube open. ...
Respiratory System
... segment has a tertiary (segmental) bronchus Segments are functionally divided into many lobules & each lobule receives a terminal bronchiole ...
... segment has a tertiary (segmental) bronchus Segments are functionally divided into many lobules & each lobule receives a terminal bronchiole ...
Document
... • The alveoli are the final branchings of the respiratory tree and act as the primary gas exchange units of the lung. The gas-blood barrier between the alveolar space and the pulmonary capillaries is extremely thin, allowing for rapid gas exchange. • There are two types of alveolar epithelial cells. ...
... • The alveoli are the final branchings of the respiratory tree and act as the primary gas exchange units of the lung. The gas-blood barrier between the alveolar space and the pulmonary capillaries is extremely thin, allowing for rapid gas exchange. • There are two types of alveolar epithelial cells. ...
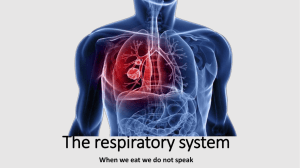
The respiratory system
... polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins) into smaller units (such as monosaccharides, fatty acids, nucleotides, and amino acids, respectively). ...
... polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins) into smaller units (such as monosaccharides, fatty acids, nucleotides, and amino acids, respectively). ...
Sponges, Cnidarian, Ctenophora, Worms Review - Cy
... 5. Define dioecious and monecious 6. Simple animals with no true organs must rely on which process in order to respirate (get oxygen to their cells)? 7. What characteristic sets cnidarians and ctenophores apart? Which features do each possess? 8. Define coelom. Which type of worms have a true coelom ...
... 5. Define dioecious and monecious 6. Simple animals with no true organs must rely on which process in order to respirate (get oxygen to their cells)? 7. What characteristic sets cnidarians and ctenophores apart? Which features do each possess? 8. Define coelom. Which type of worms have a true coelom ...
Dr. P`s Animal Notes
... • fission: splitting off of new individual from existing one, parent cell divides into two parts • budding: new individual grows from body of original, can detach (solitary lifestyle) or remain attached (colonial lifestyle) • fragmentation: breaking of the body into several pieces, each of which for ...
... • fission: splitting off of new individual from existing one, parent cell divides into two parts • budding: new individual grows from body of original, can detach (solitary lifestyle) or remain attached (colonial lifestyle) • fragmentation: breaking of the body into several pieces, each of which for ...
Cells
... finger, it heals, and weeks later you cannot even see where the cut used to be. Reproduction – your body can make sex cells. In humans, these cells are the sperm or egg cells. These cells contain genetic information. ...
... finger, it heals, and weeks later you cannot even see where the cut used to be. Reproduction – your body can make sex cells. In humans, these cells are the sperm or egg cells. These cells contain genetic information. ...
Chapter #16 Respiratory System
... Blood transport _______________ and __________________________ between the lungs and cells. Gases enter blood and they dissolve in the plasma or combine chemically with blood components. Almost all the oxygen that blood transports combines with the iron-containing protein hemoglobin in red blood ...
... Blood transport _______________ and __________________________ between the lungs and cells. Gases enter blood and they dissolve in the plasma or combine chemically with blood components. Almost all the oxygen that blood transports combines with the iron-containing protein hemoglobin in red blood ...















![Respiratory System[1] - missdannocksyear11biologyclass](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008654285_1-2b054e727f792a49d70ccbd4d097227d-300x300.png)